* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download most important cash crop in the South Slave state
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
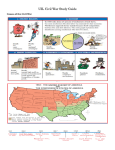
Social Notes – Unit 6 Cotton – most important cash crop in the South Slave state – a state where slavery was allowed Free state – a state where slavery was not allowed Underground Railroad – a secret network of trails and hiding places to help runaway slaves. Conductors helped the passengers, (slaves). Missouri Compromise – an agreement in 1820 that kept the balance of free and slave states (Missouri admitted as a slave state, Maine as a free state) Tariff – a special tax on goods coming into the U.S. (tariffs divided the North and South) * Dred Scott Decision – said that if enslaved people were taken to free states, they were still enslaved *South Carolina was the first state to secede from the Union. *The states that left the Union formed a new country called the Confederate States of America, or the Confederacy. The president was Jefferson Davis. *The first shots of the Civil War were fired at Fort Sumter, SC. *The first major battle of the Civil War was The Battle of Bull Run in July, 1861. *Technology transformed the way the Civil War was fought. Examples: rifles, iron-covered battle ships, torpedoes, and submarines. Strengths of the Union: - More railroads, people, factories, food Strengths of the Confederacy: - Strong military tradition, Southerners were skilled in riding and shooting, most battles were in the South, where people were defending their homes Draft – selection of men who must serve in the military Anaconda Plan – General Scott’s plan to defeat the South Total war – type of warfare in which each side strikes against the civilians and economic system of the other Emancipation Proclamation – document that freed all enslaved people in the South. Thousands of free African Americans joined the Union Army. Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address – a speech given to dedicate the Gettysburg cemetery - Lincoln reminded us that the world will not forget what others did for us, and that the war was not being fought in vain. The Union would be preserved. Clara Barton – served in the war by nursing the sick and wounded. She founded the American Red Cross. *General Grant had two major goals to bring the war to an end: - destroy General Lee’s army in Virginia - capture the Confederate capital (Richmond, Virginia) *Union General Sherman believed the North needed to wage “total war” against the South *General Lee surrendered to General Grant at Appomattox Court House in Virginia on April 9, 1865. *Less than a week after the surrender, Lincoln was assassinated and died on April 15, 1865. Assassination – murder of an important leader Malice – desire to harm Reconstruction – rebuilding of the South Black codes – laws that restricted African Americans’ rights Freedmen’s Bureau – provided food, shelter, jobs, and medical care to both African Americans and whites Sharecropping – renting land in return for a share of the crop Segregation – separation by race Jim Crow laws – rules that made segregation legal in the South Ku Klux Klan – KKK – people who terrorized African Americans by destroying property, harming them physically, and preventing them from voting