* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - geography and history 1eso social studies
Survey
Document related concepts
Hyperthermia wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Thermometer wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Köppen climate classification wikipedia , lookup
Precipitation wikipedia , lookup
Cold-air damming wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Climate change wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Weather lore wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
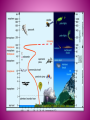
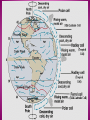
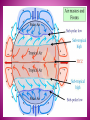
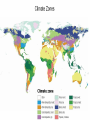
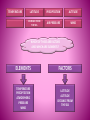
Respond to the following questions in your group • What do you know about the sky above your head? • What is weather and why does it change? • Why is it hot at the equator and cold at the poles? 4 MINUTES TO THINK AND WRITE THE ANSWERS ATMOSPHERE The atmosphere is a layer of gases that surrounds earth and protects it from solar radiation. Atmosphere makes life possible because: It contains vital gases for life. It regulates the Earth´s temperature. The ozone layer is a barrier against ultraviolet radiation. It protects the Earth from meteorites. TROPOSPHERE METEOROLOGICAL PHENOMENA SUCH AS CLAUDS AND PRECIPITATION STRATOSPHERE MESOSPHERE IT CONTAINS THE OZONE LAYER THAT ABSORBS ULTRAVIOLET RAYS FROM THE SUN. THIS PREVENT HARMFUL RADIATION FROM REACHING THE EARTH´S SURFACE TEMPERATURES ARE VERY LOW. THE TOP PART OF THIS LAYER IS THE COLDEST PART OF THE ATMOSPHERE TERMOSPHERE EXOSPHERE THE POLAR AURORAS OCCUR IN THIS LAYER. TEMPERATURES ARE VERY HIGH IT IS THE LAST LAYER BEFORE OUTER SPACE. ARTIFICIAL SATELLITES ORBIT IN THE EXOSPHERE. TEMPERATURES ARE EXTREMELY HIGH WEATHER Continuous movement of the air in the atmosphere causes the changes in the weather The weather is changeable Characteristics of air currents: THE CLIMATE TEMPERATURE PRECIPITATION RAIN HAIL SNOW ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE WIND Climate Zones THE ATHMOSPHERE DEFINITION The atmosphere is the layer of gases (mainly oxygen and nitrogen) that surrounds the Earth and protect it from solar radiation. It is about 1.000km wide and is divided into layers. WHY DOES THE ATMOSPHERE MAKE LIFE ON EARTH POSSIBLE? •IT CONTAINS GASES THAT ARE VITAL FOR LIVING CREATURES •THE OZONE LAYER FILTERS ULTRAVIOLET RAYS THAT ARE DAMAGING FOR LIVING THINGS. •IT REGULATES THE TEMPERATURE OF THE EARTH, PREVENTING IT FROM GETTING TOO HOT DURING THE DAY AND TOO COOL DURING THE NIGHT. •IT MINIMISES THE IMPACT OF METEORITES AND OTHER PARTICLES FROM OUTER SPACE THE WEATHER DEFINITION IT IS THE CONDITION OF THE ATMOSPHERE AT A GIVEN TIME AND PLACE. WHY DOES THE WEATHER VARY ? WEATHER VARIES BECAUSE THE MASSES OF AIR IN THE ATMOSPHERE ARE CONSTANTLY MOVING, FORMING A CIRCUIT KNOWN AS THE GENERAL ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION BUT, WHY ARE MASSES OF AIR CONSTANTLY MOVING? BECAUSE THEY HAVE DIFFERENT CHARACTERISTICS DEPENDING ON THE REGIONS WHERE THEY ARE FORMED. THEY CAN BE CHARACTERIZADED BY THEIR PRESSURE, TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY THERE ARE HIGH AND LOW PRESSURE SYSTEMS CURRENTS ARE COLD WHEN THE AIR COMES FROM THE POLES OR WARM IF IT COMES FROM TROPICAL AREAS CURRENTS CAN BE HUMID IF THEY HAVE COME FROM OR TRAVEL OVER THE SEA, OR DRY IF THEY COME FROM OR TRAVEL OVER CONTINENTS THE CLIMATE DEFINITION THE CLIMATE IS THE AVERAGE STATE OF THE ATMOSPHERE IN A REGION DURING A LONG PERIOD OF TIME (BETWEEN THIRTY AND FORTY YEARS) HOW CAN A CLIMATE BE DETERMINED? BY STUDYING THEIR ELEMENTS AND FACTORS ELEMENTS FACTORS THE ELEMENTS OF THE CLIMATE ARE MEASURABLE COMPONENTS OF THE ATMOSPHERE, THEIR SET OF ACTIONS DEFINE THE CLIMATE OF A PLACE. THE FACTORS OF A CLIMATE ARE THE AGENTS WHICH PERMANENTLY INFLUENCE AND MODIFY ITS ELEMENTS. TEMPERATURE LATITUDE PRECIPITATION ALTITUDE DISTANCE FROM THE SEA AIR PRESSURE WIND WHICH OF THESE ARE FACTORS AND WHICH ARE ELEMENTS? ELEMENTS FACTORS TEMPERATURE PRECIPITATION ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE WIND LATITUDE ALTITUDE DISTANCE FROM THE SEA ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE DEFINITION It is the degree of warmth in the It is the water that falls from It is the weight of the air air. the clouds onto the surface on the Earth. of the Earth. INSTRUMENT of It is measured with a It is measured with a It is measured with a MEASURE thermometer pluviometer barometer MEASURE It is expressed in degrees (oC) It is expressed in millimetres It is expressed in millibars (mm) or l/m2 (mb). REPRESENT We use isotherms to represent We use isohyets to We use isobars to ATION the represent the temperature represent the temperature in a map. on a map. temperature on a map. Temperatures decrease as we There is less precipitation as LATITUDE move away from the equator. we move further away from the equator. The temperature falls 0.64oC for Precipitation is more Pressure decreases the ALTITUDE every 100 metre increase in frequent the higher the higher the altitude height (adiabatic gradient) altitude. FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE TEMPERATURE CLIMATE ELEMENTS PRECIPITATION DISTANCE FROM THE SEA The sea moderates the temperature because the water in seas and oceans changes temperature more slowly than the surface of the Earth does. Precipitation is usually more abundant in coastal areas. THE LETTER L SHOWS LOW PRESSURE AREAS,OR DEPRESSIONS. IN THESE AREAS THERE MAY BE RAIN AND STORMS WIND Wind is the air horizontal in movement. Its strength is measured with an anemometer. It is expressed in kilometers per hour. Its direction is represented by a weather vane. CLIMATE ZONES METEOROLOGY IT IS THE SCIENTIFIC STUDY OF THE WEATHER HAILSTONE SMALL BALLS OF ICE THAT FALL LIKE RAIN FROM THE SKY TEMPERATE ZONE LOCATED BETWEEN THE TWO TROPICS AND THE POLAR CIRCLES. TEMPERATE CLIMATE AND FOUR SEASONS. DEPRESSIONS AREAS WHERE THE PRESSURE IS LOWER THAN 1013 MB ANTICYCLONES AREAS WHERE THE PRESSURE IS HIGHER THAN 1013 MB CLIMATOLOGY IT IS THE SCIENTIFIC STUDY OF CLIMATE TORNADO IT IS A VIOLENT WIND STORM CONSISTING OF A TALL COLUMN OF AIR WHICH SPINS AROUND VERY FAST AND CAUSES A LOT OF DAMAGE HUMUS LAYER It is the part of soil which consists of dead plants that have begun to decay. SCRUBLAND It is an area of land covered with low trees and bushes, no taller than 4 meters. OZONE LAYER It is the part of the Earth's atmosphere that has the most ozone in it. It protects living things from the harmful radiation of sun. PARENT ROCK Rock under the soil . WEATHER VANE A device that indicates the direction of the wind. THE ATHMOSPHERE its layers EXOSPHERE IONOSPHERE where we find THE WEATHER determined by THE CLIMATE determined by affecting MESOPHERE PRESSURE ELEMENTS FACTORS CLIMATE ZONES LIVING THINGS STRATOSPHERE HUMIDITY LATITUDE TEMPERATURE WARM VEGETATION TROPOSPHERE TEMPERATURE ALTITUDE PRECIPITATION COLD FAUNA DISTANCE FROM THE SEA ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE TEMPERATE HUMAN BEINGS WIND SOIL TEMPERATURE CLIMATE ELEMENTS PRECIPITATION ATMOSPHE PRESSURE WIND DEFINITION It is the degree of warmth in the air. It is the water that falls from the clouds onto the surface of the Earth. It takes different forms: rain, snow and hail. It is the weight of the air on the Earth. Wind is the air horizontal in movement. The wind takes warm air into cold areas and cold air into warm areas. This is how the tempe rature of the Earth maintains an equilibrium. INSTRUMENT of MEASURE It is measured with a thermometer It is measured with a pluviometer It is measured with a barometer Its strength is measured with an anemometer. MEASURE It is expressed in degrees (oC) It is expressed in milimitres (mm) or litres per square metre (l/m2) It is expressed in millibars (mb). It is expressed in kilometers per When they hour. are higher than 1.013 mb are called anticyclones and when they are lower, depressions. REPRESENTATION We use isotherms to represent the temperature in a map. We use isohyets to represent the temperature in a map. We use isobars to represent the temperature in a map. Temperature decrease as we move away from the equator. There is less precipitation as we move Further away from the equator. The temperature falls 0.64oC for every 100 metre increase in height (adiabatic gradient) Precipitation is more frequent Pressure decreases the higher the the higher altitude the altitude. The sea moderates the temperature because the water in seas and oceans changes temperature more slowly than the surface of the Earth does. Precipitation is usually more abundant in coastal areas. OTHERS FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE LATITUDE ALTITUDE DISTANCE FROM THE SEA Air temperature: warm is lighter so it tends to rise, causing low pressures (depress sions). Cold air is heavier so it tends to descend and form anticyclones. Its direction is represented by a weather vane. Wind is caused by differences in pressure. The wind always blow from a high pressure area towards a low pressure one.