* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EndoDontic Diagnosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
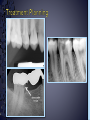
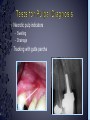
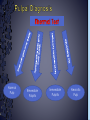
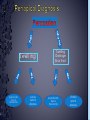
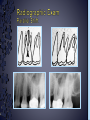
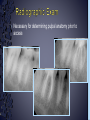
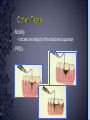
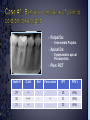
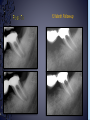
Medical History B. Retamozo DDS, MSD Department of Endodontics › Endodontic diagnostic testing should be performed on all patients in which endodontic treatment is anticipated › Diagnosis is done before administering anesthetic › Duplicate symptoms by performing clinical exam and vitality tests › Develop a pulpal and a periapical diagnosis › Assemble facts – Chief complaint – Medical history – Dental history – History of the present condition – Objective exam › Interpret the clues › Differential diagnosis › Final diagnosis › The history of the symptoms stated in the patient’s own words. › Can the patient point to where they think the pain is? – Can the patient reproduce symptoms by pressing on tooth? › Majority of patients are older with complex medical problems › Antibiotic premedication requirement › Are they on any pain medications? › Conditions that may present as tooth pain – Sinusitis – Clenching, bruxing – Angina › Bisphosphonates › How long? › How much has it been bothering patient? – Any medications? › Does any specific activity precipitate painful episode? – Chewing › Prevent sleep? › Recent dental work – – – – Cleaning Fillings Crowns Root Canal Therapy › Recent trauma › Soft tissue – Pain to palpation – Swelling – Sinus tract – Lymph node enlargement › Dentition – Caries – Discolorations – Fractures – Abrasions Acute Initial Tissue damage Fast Process Painful Response Chronic Long term tissue damage Slow process Lower Response › Use adjacent teeth › Localize within an arch › Use contra-lateral teeth › You are assessing the patient’s response to a stimulus › Vitality Tests – Rely on the stimulation of Aδ fibers – Pain is caused by vital pulp tissue › Thermal – Test multiple teeth – Inexpensive – Cold › -70°C elicits pain in acute pulpitis – Heated Gutta percha › Electric pulp test – Small electrical charge that gradually increases – Only tells you if pulp is vital › Good for calcified teeth › Can’t be used for crowned teeth – False positives › Nerve fibers in the periodontium › Partially necrotic teeth with multiple roots › Necrotic pulp indicators – Swelling – Drainage › Tracking with gutta percha Normal Pulp Reversible Pulpitis Irreversible Pulpitis Necrotic Pulp › Percussion › Biting pressure › Palpation › Response indicates the involvement of the PDL – Degree of response is directly proportional to the degree of inflammation – Chronic periapical inflammation is often negative Sw elli ng Symptomatic Apical Periodontitis Acute Apical Abscess Swelling Drainage Sinus Tract Asymptomatic Apical Periodontitis Chronic Apical Abscess › Radiolucencies › Caries – Restorability › Radiolucencies › Caries – Restorability › Periodontal disease › Necessary for determining pulpal anatomy prior to access › Mobility – Indicates the integrity of the attachment apparatus › PPD’s › Tooth Slooth › Transillumination › One piece of the puzzle won’t lead to a correct diagnosis › All the data must be considered as a whole to get a clear picture of the problem › Normal › Reversible Pulpitis › Irreversible Pulpitis › Necrotic › Previously initiated › Previously treated › Normal Pulp – Responds to cold, but no pain – Responds to EPT › Reversible Pulpitis – Exaggerated response to cold, but pain does not linger – Responds to EPT – Sensitive to Sweets › Irreversible Pulpitis – – – – Pain to cold that lingers May or may not have pain to heat Spontaneous intermittent pain Constant pain › Necrotic Pulp – – – – No cold response, it may relieve pain May or may not have heat response No response to EPT Spontaneous, intermittent or constant pain › Normal › Symptomatic Apical Periodontitis › Asymptomatic Apical Periodontitis › Acute Apical Abscess › Chronic Apical Abscess › Pulpal Dx: – Irreversible Pulpitis › Apical Dx: – Symptomatic apical Periodontitis › Plan: RCT Tooth # Cold Hot Percussion EPT PPD’s 29 + - - 23 WNL 30 +++ - + 21 WNL 31 + - - 32 WNL › Pulpal Dx: – Necrotic › Apical Dx: – Symptomatic apical Abscess › Plan: RCT Tooth # Cold Hot Percussion EPT PPD’s 18 - - +++ N/A WNL 19 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 20 + - - N/A WNL Large buccal swelling present#18 13 Month Follow-up