* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study each pair of right triangles. abc 1. Is each pair
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
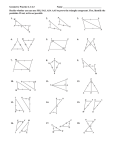
Extend 4-5 Geometry Lab: Congruence in Right Triangles Study each pair of right triangles. a. b. c. 1. Is each pair of triangles congruent? If so, which congruence theorem or postulate applies? SOLUTION: a. Two pairs of corresponding sides and one included angle are congruent. Therefore, by SAS postulate both triangles are congruent. b. Two pairs of corresponding angles and one non-included side are congruent. By AAS postulate the triangles are congruent. c. Two pairs of corresponding angles and one included side are congruent in the triangles. So, the triangles are congruent by using ASA postulate. 2. Rewrite the congruence rules from Exercise 1 using leg, (L), or hypotenuse, (H), to replace side. Omit the A for any right angle since we know that all right triangles contain a right angle and all right angles are congruent. SOLUTION: a. Two pairs of corresponding legs of the right triangles are congruent. By Leg-Leg (LL) congruence, the triangles are congruent. b. The hypotenuses and a pair of corresponding angles of the right triangles are congruent. So, the triangles are congruent by Hypotenuse-Angle (HA) congruence theorem. c. The pair of corresponding acute angles and the pair of corresponding legs are congruent. Therefore, the triangles are congruent by Leg-Angle (LA) congruence. 3. MAKE A CONJECTURE If you know that the corresponding legs of two right triangles are congruent, what other information do you need to declare the triangles congruent? Explain. SOLUTION: If the two legs are congruent then the included angle is the right angle. The two triangles would be congruent by the SAS postulate. Which corresponds to the Leg-Leg (LL) congruence. None; two pairs of legs congruent is sufficient for proving right triangles congruent using Leg-Leg (LL) congruence. eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 1 SOLUTION: If the two legs are congruent then the included angle is the right angle. The two triangles would be congruent by the SAS4-5 postulate. Which corresponds to theinLeg-Leg (LL) congruence. None; two pairs of legs congruent is sufficient Extend Geometry Lab: Congruence Right Triangles for proving right triangles congruent using Leg-Leg (LL) congruence. 4. Does the model yield a unique triangle? SOLUTION: All three sides of the triangle are specified. Yes, the triangle is unique. 5. Can you use the lengths of the hypotenuse and a leg to show right triangles are congruent? SOLUTION: Yes. Hypotenuse-Leg(HL) congruence can be applied here. 6. Make a conjecture about the case of SSA that exists for right triangles. SOLUTION: After performing the activity, knowing the length of the hypotenuse and a leg will yield the same triangle every time. SSA or HL-hypotenuse leg is a valid test of congruence for right triangles. Determine whether each pair of triangles is congruent. If yes, tell which postulate or theorem applies. 7. SOLUTION: eSolutions by Cogneroangles TwoManual pairs -ofPowered corresponding and a pair of corresponding legs are congruent. Therefore, the triangles are congruent by Leg-Angle (LA) congruence. Page 2 6. Make a conjecture about the case of SSA that exists for right triangles. SOLUTION: After4-5 performing theLab: activity, knowing the the hypotenuse and a leg will yield the same triangle every time. Extend Geometry Congruence in length Right of Triangles SSA or HL-hypotenuse leg is a valid test of congruence for right triangles. Determine whether each pair of triangles is congruent. If yes, tell which postulate or theorem applies. 7. SOLUTION: Two pairs of corresponding angles and a pair of corresponding legs are congruent. Therefore, the triangles are congruent by Leg-Angle (LA) congruence. 8. SOLUTION: The corresponding angles of the triangles are congruent but no sides are congruent. Therefore, no postulates can be applied here. The triangles are not congruent. 9. SOLUTION: The hypotenuses of the triangles are congruent and the corresponding legs are also congruent. By Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) congruence, the triangles are congruent. PROOF Write a proof for each of the following. 10. Theorem 4.6 SOLUTION: You need to walk through the proof step by step. Look over what you are given and what you need to prove. Here, you are given that both triangles are right and that the legs are congruent. So, you are given two congruent sides and one congruent angle. Now use what you have learned about triangle congruency to prove that if the legs of one right triangle are congruent to the corresponding legs of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Given: and are right triangles. ∠E and ∠S are right angles. Prove: Proof: We are given that and congruent, E S. Therefore, by SAS, eSolutions Manual4.7 - Powered by Cognero 11. Theorem SOLUTION: E and S are right angles. Since all right angles are Page 3 Prove: Proof: We are given that and E and S are right angles. Since all right angles are Extend 4-5 Geometry Lab: Congruence in Right Triangles congruent, E S. Therefore, by SAS, 11. Theorem 4.7 SOLUTION: You need to walk through the proof step by step. Look over what you are given and what you need to prove. Here, you are given that both triangles are right, their hypotenuses are congruent, and an angle is congruent. So, you are given two congruent angles and one congruent side. Now use what you have learned about triangle congruency to prove that if the hypotenuse and acute angle of one right triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and corresponding acute angle of another right triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. Given: and are right triangles. A and X are right angles. Prove: Proof: We are given that and are right triangles with right angles Y. Since all right angles are congruent, A X. Therefore, A and X, by AAS. and B 12. Theorem 4.8 (Hint: There are two possible cases.) SOLUTION: You need to walk through the proof step by step. Look over what you are given and what you need to prove. Here, you are given that both triangles are right, one of the legs is congruent, and one of the angles is congruent. So, you are given two congruent angles and one congruent side. Now use what you have learned about triangle congruency to prove that if one leg and an acute angle of one right triangle are congruent to the corresponding leg and acute angle of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Case 1: Given: F and are right triangles. C Prove: Proof: It is given that and are right triangles, By the definition of right triangles, A and D are right angles. Thus, A D since all right angles are congruent. by ASA. Case 2: Given: and are right triangles. Prove: eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Proof: It is given that Page 4 and are right triangles, . Prove: Proof: are givenLab: that Congruence and in Right are right triangles with right angles Extend 4-5We Geometry Triangles Y. Since all right angles are congruent, A X. Therefore, A and X, by AAS. and B 12. Theorem 4.8 (Hint: There are two possible cases.) SOLUTION: You need to walk through the proof step by step. Look over what you are given and what you need to prove. Here, you are given that both triangles are right, one of the legs is congruent, and one of the angles is congruent. So, you are given two congruent angles and one congruent side. Now use what you have learned about triangle congruency to prove that if one leg and an acute angle of one right triangle are congruent to the corresponding leg and acute angle of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Case 1: Given: F and are right triangles. C Prove: Proof: It is given that and are right triangles, By the definition of right triangles, A and D are right angles. Thus, A D since all right angles are congruent. by ASA. Case 2: Given: and are right triangles. Prove: Proof: It is given that and By the definition of right triangle, congruent. by AAS. are right triangles, A and E are right angles. Thus, A . E since all right angles are 13. Theorem 4.9 SOLUTION: You need to walk through the proof step by step. Look over what you are given and what you need to prove. Here, you are given that both triangles are right, their hypotenuses are congruent, and one of their legs is congruent. So, you are given two congruent sides and one congruent angle. Now use what you have learned about triangle congruency to prove that if the hypotenuse and a leg of one right triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and corresponding leg of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Given: are right triangles. Prove: eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 5 Proof: It is given that and are right triangles, By the definition of right triangle, A and E are right angles. Thus, congruent. Extend 4-5 Geometry Lab: Congruence in Right Triangles by AAS. A . E since all right angles are 13. Theorem 4.9 SOLUTION: You need to walk through the proof step by step. Look over what you are given and what you need to prove. Here, you are given that both triangles are right, their hypotenuses are congruent, and one of their legs is congruent. So, you are given two congruent sides and one congruent angle. Now use what you have learned about triangle congruency to prove that if the hypotenuse and a leg of one right triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and corresponding leg of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Given: are right triangles. Prove: Proof: 1. are right triangles, 2. AB = DE, BC = EF (Def. of ) 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 (Given) 2 2 3. (AB) + (CA) = (BC) , (DE) + (FD) = (EF) (Pythagorean Theorem.) 2 2 2 2 4. (AB) + (CA) = (DE) + (FD) (Subs. Prop.) 2 5. (AB) + (CA) = (AB) + (FD) (Subs. Prop.) 2 2 6. (CA) = (FD) (Subt. Prop.) 7. CA = FD (A property of square roots) 8. (Definition of congruent segment) 9. (SSS) Use the figure at the right. 14. Given: Prove: SOLUTION: You need to walk through the proof step by step. Look over what you are given and what you need to prove. Here, you are given that both triangles are right, they have a congruent leg, and that their hypotenuses are congruent. So, you are given two congruent sides and one congruent angle. Now use what you have learned about triangle congruency to prove that if the legs of one right triangle are congruent to the corresponding legs of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Finally, use the fact that corresponding parts of congruent figures are themselves congruent, to prove the line segments congruent. Proof: eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 6 Statements (Reasons) 1. (Given) 2. ∠ABC is a right angle, ∠DCB is a right angle. ( lines from right angles) 5. (AB) + (CA) = (AB) + (FD) (Subs. Prop.) 2 2 6. (CA) = (FD) (Subt. Prop.) 7. CA = FD (A property of square roots) 8. 4-5 Geometry (Definition congruent segment) Extend Lab: of Congruence in Right Triangles 9. (SSS) Use the figure at the right. 14. Given: Prove: SOLUTION: You need to walk through the proof step by step. Look over what you are given and what you need to prove. Here, you are given that both triangles are right, they have a congruent leg, and that their hypotenuses are congruent. So, you are given two congruent sides and one congruent angle. Now use what you have learned about triangle congruency to prove that if the legs of one right triangle are congruent to the corresponding legs of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Finally, use the fact that corresponding parts of congruent figures are themselves congruent, to prove the line segments congruent. Proof: Statements (Reasons) 1. (Given) 2. ∠ABC is a right angle, ∠DCB is a right angle. ( lines from right angles) 3. is a right triangle, is a right triangle. (Definition of right triangles ) 4. (Given) 5. (Reflection Property of Congruence) 6. (HL congruence) 7. (CPCTC) 15. Given: E is the midpoint of Prove: and SOLUTION: You need to walk through the proof step by step. Look over what you are given and what you need to prove. Here, you are given that both lines are parallel, one right angle, and a midpoint. Use what you know about parallel lines and perpendicularity to prove that both triangles are right. Then use what you know about midpoints to prove segments congruent. Now use what you know about vertical angles to find another pair of angles congruent. So, you are given two congruent sides and one congruent angle. Now use what you have learned about triangle congruency to prove the triangles are congruent. Finally, use the fact that corresponding parts of congruent figures are themselves congruent, to prove the line segments congruent. Proof: Statements (Reasons) 1. (Given) 2. (In a plane, if a line is perpendicular to one of two parallel lines, then it is perpendicular to the other.) 3. ∠ABC is a right angle, ∠DCB is a right angle. ( lines form rt. s.) 4. is a right triangle, is a right triangle. (Def of rt ) 5. E is the midpoint of (Given) and 6. (Midpoint Thm.) eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 7 7. (Vertical angles are congruent.) 8. (SAS) 4. (Given) 5. (Reflection Property of Congruence) 6. (HL congruence) Extend 4-5 Geometry Lab: Congruence in Right Triangles 7. (CPCTC) 15. Given: E is the midpoint of Prove: and SOLUTION: You need to walk through the proof step by step. Look over what you are given and what you need to prove. Here, you are given that both lines are parallel, one right angle, and a midpoint. Use what you know about parallel lines and perpendicularity to prove that both triangles are right. Then use what you know about midpoints to prove segments congruent. Now use what you know about vertical angles to find another pair of angles congruent. So, you are given two congruent sides and one congruent angle. Now use what you have learned about triangle congruency to prove the triangles are congruent. Finally, use the fact that corresponding parts of congruent figures are themselves congruent, to prove the line segments congruent. Proof: Statements (Reasons) 1. (Given) 2. (In a plane, if a line is perpendicular to one of two parallel lines, then it is perpendicular to the other.) 3. ∠ABC is a right angle, ∠DCB is a right angle. ( lines form rt. s.) 4. is a right triangle, is a right triangle. (Def of rt ) 5. E is the midpoint of (Given) and 6. (Midpoint Thm.) 7. (Vertical angles are congruent.) 8. (SAS) 9. (CPCTC) 10. (Reflexive Property of Congruence) 11. (LL) 12. (CPCTC) eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 8