* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The American Civil War, 1861-1865
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Cavalry in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
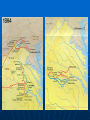
The American Civil War, 1861-1865 Comparison of Union and CSA Union CSA Total population 22,000,000 (71%) 9,000,000 (29%) Free population 22,000,000 5,500,000 1860 Border state slaves 432,586 NA 1860 Southern slaves NA 3,500,000 Soldiers 2,200,000 (67%) 1,064,000 (33%) Railroad miles 21,788 (71%) 8,838 (29%) Manufactured items 90% 10% Firearm production 97% 3% Bales of cotton in 1860 Negligible 4,500,000 Bales of cotton in 1864 Negligible 300,000 Pre-war U.S. exports 30% 70% Union Strengths Manufacturing and population advantages Centralized government institutions and traditions Loyal opposition (Democrats) Existing Army and Navy Investment capital and stable food supply Significant internal development (communication, transport) Union Weaknesses Long supply lines Occupation of hostile populations Early indecisiveness of commanders Confederate Strengths Defense of home soil Military leadership Confederate Disadvantages Lack of manufactured goods Blockaded coast and price inflation Lack of food and investment capital No diplomatic recognition No developed governmental traditions (political infighting) Fear of slave rebellions Small free population Lack of sizeable Navy Union War Strategies Anaconda Plan Take Mississippi River to split the Confederacy Blockade southern coast Take Richmond Multiple front war Burning campaigns (late war) Confederate Strategies Defensive perimeter, shift reserves to different fronts Wear down Northern fighting spirit Strike North to relieve pressure on Richmond Encourage peace movement in North Gain diplomatic recognition of France and/or England (cotton diplomacy) Modern War The rifled bullet, repeating rifle (Winchester) Tactics do not keep pace with technology 1861 Union defeat at Bull Run (July 1861) McClellan takes command, drills troops through the fall 1862 Union capture of New Orleans in April (Farragut) The Peninsular Campaign (April-July) Pope defeated at Second Bull Run (August) Robert E. Lee takes command, invades North Battle of Antietam (24,000 casualties) forces Lee’s retreat Burnside and Fredericksburg defeat (Nov-Dec) Union forces advance in the West (control Tennessee and Cumberland Rivers, Memphis) The Emancipation Proclamation and its Effects Delivered after Antietam (September 22, 1862) Frees slaves in rebelling states in 1863 War becomes one of abolitionism as well as Union preservation Appeals to international liberals to prevent foreign intervention Creates more opposition to war in the north (draft riots) Increases enlistment of Black soldiers (10% of Union army by 1865) 1863 Joseph Hooker defeated at Chancellorsville (May 1-5) Lee strikes north, Armies meet at Gettysburg (July 1-3) Pickett’s Charge repulsed(1,123 killed, 4,019 wounded, 3,750 captured of 12K soldiers) Total Gettysburg casualties • 23,001 Union killed, missing, or wounded • 20,448 Confederate killed, missing, or wounded Vicksburg falls in July after prolonged siege (Mississippi River effectively controlled by Union forces under U.S. Grant) 1864 U.S. Grant moved east to command Union forces William Tecumseh Sherman commands in Tennessee Methodical war of attrition Sheridan’s burning campaigns Battles of the Wilderness (May 5-7) and Cold Harbor (June 1-3) Bypassing Richmond and the siege of Petersburg (June 15 to March 25, 1865) The War in the Deep South Atlanta falls to Sherman (September 2) Sherman’s March to the Sea (Atlanta to Savannah) The Election of 1864 Fall of Atlanta aids Lincoln at the polls Lincoln creates Union Party (Republicans and War Democrats) Andrew Johnson as Union Party Vice President McClellan runs as peace Democrat (Copperheads) Soldiers vote in the fields War Opposition in the North Immigrants fear Black emancipation Civil War draft riots (July 1863) States rights ideology Profiteering the hiring of substitutes Copperhead leader Clement Vallandigham exiled (February 1864) 1865 Petersburg and Richmond fall (MarchApril) Lee surrenders at Appomattox (April 9) Lincoln assassinated (April 14) Johnston surrenders Confederate Army in North Carolina (April 18) War Costs Southern social and economic devastation One in five mobilized are killed (620,000 men) Civil War Effects Slavery abolished in 1865 (13th Amendment) Union indivisible, not a collection of sovereign states Racial questions in the South remain unresolved through the 1960s Enhances industrialization in the North Main Issues of the Post Civil War Era How to re-admit states into the Union? Should ex-confederates be punished or treated leniently? How to create a new southern society incorporating freedmen into its culture? The Civil War and the American South War devastation (Sherman’s March, siege warfare) Lack of towns and industry Illiteracy Lack of capital Crop monocultures War pensions Redeemers and enduring racism Reconstruction (1865-1877) Lincoln plan (leniency toward southerners) Congressional plans (occupation and reordering society) The Civil War Amendments Abolition of slavery Due process of law Voting rights for freedmen The Election of 1876 Rutherford Hayes and Samuel Tilden Withdrawal of Union troops from the South Symbolic end of Reconstruction