* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP World History
Survey
Document related concepts
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
First Persian invasion of Greece wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Greek Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek philosophy wikipedia , lookup
First Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek warfare wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
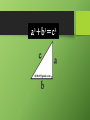
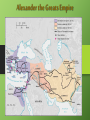
Friendly reminders • Read chapter 10 • I/O Circle Thursday • Is Alexander really worthy of the title “The Great”? Due Monday Greek Words • • • • • • • Gymnasium Theatre Opera Marathon Olympics Idiot democracy AP World History Ancient Greece “The Cradle of Democracy” Greece → Romans → Renaissance → Today The Geography of Greece • Very mountainousmeant little agricultural • Located in the Mediterranean It takes a Polis: Greek City States • Polis- Greek City States Sparta: A Hard Core Warrior society • Military State • Boys & men lived in military barracks until the age of 30 • “Come back with your shield - or on it" Spartan Society: Plain & Simple • Spartans were interested military & defensive matters not art, literature, or science • No jewelry, fancy clothes etc. • Spartans=simplicity, frugality, austerity Spartan: labor Systems • Helots- Agricultural slaves of the Spartans • Helots outnumbered Spartans 10-1 Spartan Gender Roles ( An exception to the rule) • • • • Generally patriarchal however women could : participate in athletic contests Receive tombstones for dying in labor Own businesses Serve as priestess Athenian Democracy • birth of democracy • Ways Athenian citizens participated: • voted, held public office, own property, speak in court • Excluded slaves, women, & foreign born The Acropolis Today Great Athenian Philosophers Socrates Socratic Method Honor is more important than wealth & fame, stressed personal integrity Sentenced to death in 399 bc Plato The Academy The world of the FORMS The Republic philosopher-king Aristotle -Plato’s student but distrusted idea of forms Athens: The Arts & Sciences $ DRAMA (tragedians): Aeschylus Sophocles Euripides $ THE SCIENCES: Pythagoras Democritus all matter made up of small atoms. Hippocrates “Father of Medicine” “Above all, do no harm” Gender Roles :Sappho • Lesbian poet • Island of Lesbos Other Greek Contributions • • • • Sports History -(Herodotus) Theatre Art & Architecture Greek politics • Delian Leaguealliance of Greek city-states, led by Athens, to defend against Persia Persian Wars: 499 BCE – 480 BCE Parthenon, Athens Jefferson Memorial, Washington D.C. The 2004 Olympics Peloponnesian Wars-Sparta V Athens Macedonia Under Philip II Alexander the Great Alexander the Greats Empire The Economy of the Hellenistic World $ $ Hellenistic Philosophers Cynics aka Skeptics Did not take positions on politics, moral issues, or social issues. live a humble, simple life. Epicurians Epicurus Suggested that individual needs could be met through reflection/quiet satisfaction Pleasure is greatest good; pleasure is inner peace that could protect them from pressure of Hellenistic World Hellenistic Philosophers $ Stoics (most popular philosophy) Had the duty to aid others & lead a virtuous live get involved in politics, not for personal gain, but to perform virtuous acts for the good of all. true happiness is found in great achievements. Hellenism: The Arts & Sciences $ Scientists / Mathematicians: Aristarchus heliocentric theory. Euclid geometry Archimedes pulley The Breakup of Alexander’s Empire