* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab # 3 Series Circuits
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
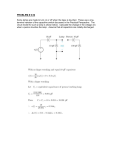
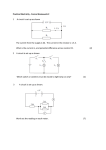
Name___________________ Lab # 3 Series Circuits In this lab you will explore how amp flow and voltage behave in a series circuit Obtain an Electro-Trainer and build a simple circuit that will perform “work” What load device did you use? Write out your definition of an electrical load. What device are you using to control the load? Which side of the load is the control device on? ____ positive ____ negative Does it matter if the control device is on the positive or negative side of the load? Draw a diagram of your electrical circuit. Positive is drawn at top or left of diagram. Ground is at the right or bottom Demonstrate your electrical circuit to get the Instructors O.K.________________ Rewire your board to function as shown on the next page. Page 1 of 4 With the switch turned ON measure and record the voltage at the following points Leave the negative voltmeter lead on a good ground for these tests! _____ A _____ B _____ C _____ D Which component uses the most volts? _____ E How many volts drop between points A and B when the switch is turned ON? (try connecting the two test leads directly to point A and point B with the meter on the mV scale) When current is flowing through a series circuit, when will voltage drop? (Voltage drop is the change in voltage as current flows through a circuit) Record the Amp flow at the following points (ask to be shown how to read amps) _____ A _____ B _____ C _____ D _____ E With the switch turned OFF, why is there no voltage drop across the lamp? With the switch turned OFF what stops the current flow? Turn the switch ON and unhook the ground. Measure changes in amps and volts. Leave the switch ON and hook the ground back up, disconnect connector C and measure changes in amps and volts. How can you use a voltmeter to locate an open (defective) ground or connection? Instructors O.K.________________ Page 2 of 4 Wire a 100 resistor in series with the lamp as shown On the above picture, complete volt drop and current flow for the lamp and resistor. Does it matter where you measure current flow in a series circuit? Why does the lamp burn dimmer when you add the 100Ω resistor? Why is there less volt drop across the lamp after you add the 100Ω resistor? What are the two electric loads in this circuit? What will determine how many volts drop across a load? As current flows through the lamp, how much power does it use? (P = E x I) (Power measured in Watts is equal to Volts used multiplied by Current Flow measured in Amps) As current flows through the 100Ω resistor, how much power does it use? (P = E x I) (Power measured in Watts is equal to Volts used multiplied by Current Flow measured in Amps) Page 3 of 4 Use Ohms Law to calculate the resistance for the lamp and the resistor. (E/I = R) (Voltage used up or Electromotive-force divided by the Intensity of current = Resistance) ______ Ω Lamp ______ Ω Resistor Measure the resistance of the lamp using an Ohm-meter. ______ Ω Lamp ______ Ω Resistor Why is the ohm meter’s resistance of the lamp different from your calculations? Which resistance value is real when the circuit is turned ON? A bad connection or wire will heat up as current flows through it. If there is a bad wire or connection that has too much resistance, which meter should you use to find it? A) Ohm meter B) Amp meter C) Volt Meter Explain what happens to current flow in a series circuit? What happens to voltage or electromotive force in a series circuit? What happens to current flow if there is an open circuit at any point in a series circuit? Instructor Signature ___________ Page 4 of 4