* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Crime rates - UN Crime Congress
Survey
Document related concepts
History of criminal justice wikipedia , lookup
The New Jim Crow wikipedia , lookup
Feminist school of criminology wikipedia , lookup
California Proposition 36, 2012 wikipedia , lookup
Immigration and crime wikipedia , lookup
Crime concentration wikipedia , lookup
Critical criminology wikipedia , lookup
Sex differences in crime wikipedia , lookup
Broken windows theory wikipedia , lookup
Crime hotspots wikipedia , lookup
Social disorganization theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative methods in criminology wikipedia , lookup
Right realism wikipedia , lookup
Criminology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
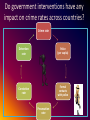
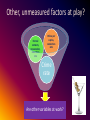
Crime Control Measures, Individual Liberties and Crime Rates: An Assessment of 40 Countries Jay S. Albanese, Ph.D. Virginia Commonwealth University [email protected] Do government interventions have any impact on crime rates across countries? Crime rate Detention rate Police (per capita) Conviction rate Formal contacts with police Prosecution rate The logic of government investment and intervention in crime control Government investment in crime control Government intervention in lives of citizens Impact on public safety? • Police per capita (law enforcement resources) • Conviction rate (trained, empowered prosecutors and judges) • Formal contacts with police (police activity in practice) • Prosecution rate (applying law in practice) • Detention rate (seriousness of convictions) • Crime rate (using both ICVS - to avoid citizen crime reporting issues - and homicide rates) Specific research questions: • 1. How does the extent of government involvement in attempting to control crime vary among countries (in terms of formal police contacts, prosecutions, convictions, and detention)? • 2. How does the extent of criminal justice resources vary among countries? • 3. Is there a relationship between criminal justice resources/capacity and the extent of formal police contacts, prosecutions, convictions, and detention? • 4. Do countries with a higher rate of formal police contacts, prosecutions, convictions, and detention experience less crime? • 5. Are there other variables that might be measured that could help to explain the relationship between government crime control efforts and crime rates? Measurement • The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) global statistical series on crime and criminal justice based on the responses of individual governments to provide these data. • Statistics on formal police contacts, prosecutions, convictions, and detention among multiple countries (UN Member States) are included in these data. • These data are limited in that they reflect only crimes known to the government, a limitation addressed by use of the International Crime Victimization Survey, which is carried out periodically in multiple nations, because crimes not reported to the police are included in this survey of citizens. • Data for 2010, excluding missing data, leaving 40 countries for analysis. Crime control measures 1) Police per capita 2) Conviction rates (gov't investments in criminal justice apparatus to control crime and criminals) Government intervention (use of available crime control measures): 1) Formal contacts 2) Prosecution rate 3) Detention rate Crime rates: 1) Crimes of theft, assault 2) Homicide rates (impact of crime control measures and their use) First results: Do crime control measures + government intervention impact crime and homicide rates? Crime control measures 1) Police per capita 2) Conviction rates Government intervention (use of crime control): 1) Formal contacts 2) Prosecution rate 3) Detention rate Impact on crime rates & homicide rates? 1. Impact on crime rates is significant. (R2 = .682, ANOVA sig. p<.003) with detention rate explaining nearly all the variance. (ICVS includes: car, bicycle theft, burglar, robbery, larceny, assault, sex offenses) 2. Impact on homicide rate is significant. (R2 = .714; ANOVA sig. p<.001 (ANOVA reports on how well the regression equation fits the data, i.e., predicts the dependent variable). A surprising result? Perhaps other variables can do a better job explaining crime and homicide rates across countries? Other, unmeasured factors at play? Formal contacts, prosecution, detention rate Police per capita, conviction rate Crime rate Are other variables at work? Social, political, economic factors? Social, Political, Economic Factors a. Civil liberties ranking b Democracy index c. Human development index d. Info communications tech index e. Political rights index f. Corruption Perceptions index g. Education index h. Index of Economic Freedom i. Press Freedom Index j. Prosperity Index Criminal Justice Factors 1) Police per capita 2) Conviction rates 3) Formal contacts 4) Prosecution rate 5) Detention rate Crime rates: 1) Theft & assault crimes 2) Homicide rates Added variables to explain differences in crime and homicide Indexes that combine multiple variables Variables included Civil liberties ranking Freedom of expression and belief, associational and organizational rights, rule of law, and personal autonomy and individual rights Democracy Index Electoral process, civil liberties, government operation, political participation, political culture Human development index Life expectancy, income per capita, education level Information & communication Connectivity, access, and policy related to Internet, technologies Index phones, and ISP markets. Political rights Index Electoral process, political pluralism and participation, and functioning of government Corruption Perceptions Index Surveys of extent of corruption in public sector, from perspective of businesspersons and country experts Education Index Av. years of schooling and expected yrs schooling Index of Economic Freedom Rule of law, limited government, regulatory efficiency, open markets Press Freedom Index Freedom of journalists, news organizations, and the internet, plus efforts made by governments to ensure respect for press freedom Prosperity Index Wealth, economic growth, education, health, personal well-being, and quality of life Impact of social, political, economic factors on crime and homicide rates? Variables that might help explain crime & homicide rates: a. Civil liberties ranking b Democracy index c. Human development index d. Information & comm. technologies index e. Political rights index f. Corruption Perceptions index g. Education index h. Index of Economic Freedom i. Press Freedom Index j. Prosperity Index Second result: adding additional factors 1. Impact on crime rates is NOT significant. (R2 = .103, ANOVA sig. p<.965) although detention rate remains the strongest factor in explaining the variance. (ICVS includes: car, bicycle theft, burglar, robbery, larceny, assault, sex offs) 2. Impact on homicide rate is significant (R2 = .654; ANOVA sig. p<000. reports on how well the regression equation fits the data, i.e., predicts dependent variable). Economic freedom & corruption perceptions were best predictors. Conclusions? • Government investment in crime control and intervention in the lives of citizens has measurable impacts on crime rates and homicide rates across 40 countries. • Social, political, and economic factors do not have a strong impact on crime rates, although they have a significant impact on homicide rates. The strongest factors were found to be economic freedom (rule of law, limited government, regulatory efficiency, open markets), and low corruption (the extent of corruption in the public sector). Remains to be determined: a. The precise ways in which government crime control & economic factors impact crime & homicide rates. b. Whether these findings will hold up over time with data in the coming years. c. Asian and African countries are under-represented in this group of 40 countries due to lack of data. Thank you for your attention! Jay S. Albanese, Ph.D. Virginia Commonwealth University [email protected] Crime LE – across jurisdictions Transnational Crime • Against Property • Against People • Against States Penalties – across jurisdictions Justice • Between and across nations Crime Adj – across jurisdictions Law Enforcement • Discretion within the rule of law Adjudication Penalties • Fair and impartial hearing of facts • Proportionality • Prevention International Crime • Violations of human rights LE – international conventions Adj –in international forum Penalties – how & where to punish?