* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Male Reproductive System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
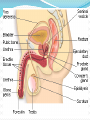
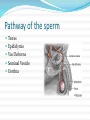
Additional Info 23 chromosomes in male and females. PMS- Post Menstrual Syndrome Ms. Richardson Puberty for Males Puberty for males is usually between 9 and 15. Boys gain weight. Shoulders get wider. Muscles start to get bigger and stronger. You may notice that you are getting an 'Adam's apple'. Penis growth Testes growth Facial hair Male Reproductive System Produces, stores and delivers sperm cells to the female reproductive system. Testes make sperm and testosterone. Testosterone is a major sex hormone in the male. During puberty testosterone causes facial and body hair to grow, the shoulders broaden and the voice to deepen. Testicles are located outside the body for temperature regulation. To produce sperm the testicles must stay around 3 degrees Fahrenheit below normal body temperature. If the testicles were inside the body the heat would bring the sperm to a holt. Scrotum is the tuff sack of skin and muscle tissue that hold the testicles. When the testicles become to cold a muscle contracts to draw them closer to the body and warm them with body heat. Male Reproductive System Penis- Removes urine from the body and delivers sperm. Made of soft tissue and blood vessels. During sexual activity the penis becomes erect or firm. Ejaculation occurs when sperm are released from the penis after sexual excitement. The tip of the penis is covered by skin called the fore skin. Foreskin is sometimes surgically removed after birth in a procedure called circumcision. Male Reproductive System The epididymis is a set of coiled tubes that the sperm travels down and were sperm matures and are stored. The mature sperm then moves to the vas deferens they mix with fluids made by 3 accessory reproductive organs. Vas deferens are the tube that transports sperm. Seminal vesicles, prostate gland and the cowper’s gland. 3 accessory reproductive organs. Seminal Vesicles- Produce semen. Prostate Gland- Secretes a thin milky fluid that protects the sperm from acid in the female reproductive system. Cowper’s Gland- Secret the pre ejaculated fluid that flushes out any urine from the urethra. Helps the sperm pass through the penis Pathway of the sperm Testes Epididymis Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicle Urethra What is a vasectomy? During a vasectomy, the vas deferens from each testicle is clamped, cut, or otherwise sealed. This prevents sperm from mixing with the semen that is ejaculated from the penis. An egg cannot be fertilized when there are no sperm in the semen. What is male sterility? There are several causes of male sterility, including: Abnormal sperm production Impaired delivery of sperm Testosterone deficiency Genetic defects Undescended testes Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nr5W9trSv8I