* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Marketplace: Supply
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
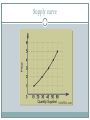
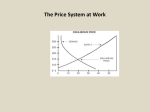
The Marketplace: Supply Review What is a Market? What things must a government provide for a market to work? Why? Law of Supply Supply is the seller’s plan for the amount of a product that would be offered for sale at different prices in a defined time period. Law of Supply – states that price and the quantity supplied are directly related. As prices rise the quantity supplied will also rise. Supply curve Law of Supply Why? Profit Incentive – producers would be able to make more profit from goods sold at higher prices Substitution – if producers can produce more than one type of good, they will naturally produce the good that makes them the most profit. What causes a shift? Anytime one of the other factors change, supply will shift. Supply Determinants Other than price, what things determine Supply? Costs of Production (Land, Labor, and Capital) Technology (increased efficiency) Number of firms (more companies in the market= greater competition) Taxes and Subsidies (Ford vs. Toyota) Expectations If all these remain constant, then supply is a function of price. Elastic Demand Price Elasticity of Demand Explains how the demand for a good will change with a change in price. What determines how elastic demand for a good will be? Availability of substitutes Importance of the product in a consumer’s budget Time period allowed for adjustment Elastic Supply Price Elasticity of Supply Explains how the supply will change with a change in price. What determines how elastic supply will be? Time Market-run (Time period so short that supply is fixed) Short-run (Plant capacity is fixed. Supply can vary from zero, to full capacity) Long-run (Additions to capacity possible. Nothing is fixed) Supply and Demand Supply and Demand Market/Equilibrium Price – price at which supply and demand meet. Market filters out all buyers unable to pay price P. Market filters out all suppliers whose costs exceed P. Surplus Price above will result in a surplus To eliminate the surplus (extra inventory) the seller must lower the price to the market price. How do sellers do this? Surplus Shortage Price below will result in a shortage To eliminate the shortage, the seller must raise the price to the market price. How do sellers do this? Shortage