* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transcription Translation Molecular Structure of Ion Channels
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
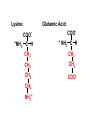
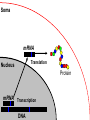
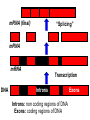
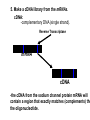
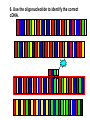
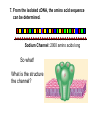
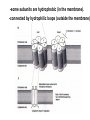
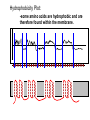
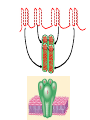
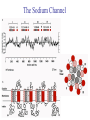
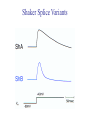
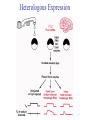
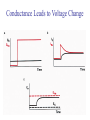
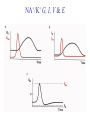
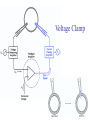
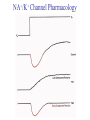
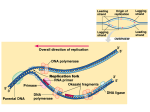
Transcription Translation Molecular Structure of Ion Channels Specialized proteins embedded within the bilayer: 1. Receptors 2. Cell Adhesion Molecules 3. Ion Channels -control the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. Proteins: chains of amino acids. Amino Acids: -there are only 20 different amino acids (AA). -each has a central carbon atom. NH3 (amino) C Side Chain -each has an amino group -each has an acid group COOH (acid) -they differ only in their side chains. Lysine: Glutamic Acid: COO- COO+NH 3 C H + NH3 C H CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 COO- CH2 NH3+ -type of protein is determined by the sequence of AAs. AA AA AA AA -fold because of differences in charge along the protein. Protein Synthesis Nucleic Acids: -control which proteins to make. -messenger RNA (mRNA). DNA: -found in the nucleus (chromosomes). -contains the instructions for protein synthesis. Soma mRNA Translation Nucleus Protein mRNA Transcription DNA mRNA (final) “Splicing” mRNA mRNA Transcription DNA Introns Introns: non coding regions of DNA Exons: coding regions of DNA Exons Studying Ion Channel Structure How to make a sodium ion channel: 1. Purify the protein from a rich source. Electric eel 2. Identify short sequences of amino acids within protein 3. Make a single strand of DNA that matches the sequence. (Oligonucleotide) -attach a fluorescent probe. 4. Take samples of mRNA from a source containing sodium channel mRNA. 5. Make a cDNA library from the mRNAs. cDNA: -complementary DNA (single strand). Reverse Transcriptase mRNA cDNA -the cDNA from the sodium channel protein mRNA will contain a region that exactly matches (complements) the the oligonucleotide. 6. Use the oligonucleotide to identify the correct cDNA. 7. From the isolated cDNA, the amino acid sequence can be determined. Sodium Channel: 2000 amino acids long So what! What is the structure of the channel? -some subunits are hydrophobic (in the membrane). -connected by hydrophilic loops (outside the membrane) Hydrophobicity Plot: -some amino acids are hydrophobic and are therefore found within the membrane. The Sodium Channel Mutant Flies The Shaker Mutation Alternative Splicing of Shaker Locus Shaker Splice Variants Heterologous Expression Site-Directed Mutagenesis Membrane Ion Currents Conductance Leads to Voltage Change NA+/K+ Conductance Ratio Summed Membrane Currents NA+/K+ G, I, V & E Voltage Clamp Depolarization and Currents Nonlinear Voltage-Dependent Currents Na+ Ions Produce Inward Current NA+/K+ Channel Pharmacology