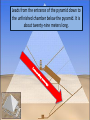
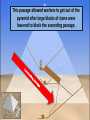
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Egyptian Empire
Survey
Document related concepts
Plagues of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Joseph's Granaries wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Egyptian pyramids wikipedia , lookup
Great Pyramid of Giza wikipedia , lookup
Art of ancient Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Egyptian pyramid construction techniques wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Egypt (Roman province) wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
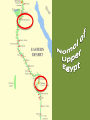
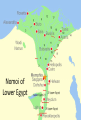
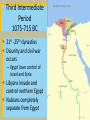
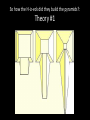
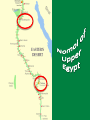
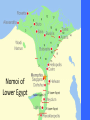
Learning Targets • Identify the three main kingdoms of Ancient Egypt. •Describe the major events that occurred in each kingdom. •Define pharaoh and intermediate period. Homework • Wordy Wed. Quiz Fri. •Egyptian webquest due Fri. Problem of the Day English word below is made of the first two letters of one country and the last two letters of a country that it borders. For example, PACA is a combination of Panama and Costa Rica. How many crossings can you make? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. PONY BOIL SWAY ECRU CHAR Problem of the Day 1.Poland/Germany 2.Bolivia/Brazil 3.Sweden/Norway 4.Ecuador/Peru 5.China/Myanmar The Egyptian Empire The Three Kingdoms • A dynasty is a series of rulers (pharaohs) from the same family or ethnic group • The Ancient Egyptian empire had 31 dynasties between 3100BC until 332BC • The dynasties were grouped into three major time periods: 1. The Old Kingdom 2. The Middle Kingdom 3. The New Kingdom • Menes or Narmer united Upper and Lower Egypt The Early Dynastic Period ( 2925 – 2575 BC) • • • • 1st , 2nd, and 3rd dynasties First dynasty Menes united Egypt Others believe it was Narmer Still others believe Narmer and Menes were the same person • Memphis chosen as first capital by King Narmer • King Narmer first king to unite Lower and Upper Egypt • Memphis disappeared; Heliopolis replaced it(close to Cairo) The Old Kingdom: 2686-2125 BC • The 3rd to the 8th Dynasties • Governmental capital located at Memphis • Advancements in technology, art, farming and architecture • “The Age of the Pyramid” – During the Old Kingdom, the Egyptians built the Great Pyramids, 20 major pyramids, and the Sphinx – The only era where Pharaohs were buried in pyramids. The First Intermediate Period 2055-1650 BC • 9th – 11th Dynasties • End of the Old Kingdom, pharaohs challenged by local governors called nomarchs – Egypt had 42 nomoi (nome =district or province) – Result: civil wars throughout the empire and the kingdom split into two dynastic kingdoms: Herakleopolian and Theban dynasties • Drought causes the Nile to stop flooding, which results in famine Nomoi of Lower Egypt The Middle Kingdom 2055 – 1650 BC • 11th – 13th Dynasties • One of the feuding dynasties from Thebes in the south was able to unify Egypt again into one kingdom: – Mentuhotep II, marked the beginning of a new era of unity and prosperity Mentuhotep II Mentuhotep II’s Burial Complex Mentuhotep II’s Burial Complex Mentuhotep II’s Burial Complex The Middle Kingdom 2055 – 1650 BC • Trade flourished, arts and literature flourished. • Egypt built strong armies to defend herself against her neighbors. • Religion- afterlife for common people too The Middle Kingdom 2055-1650 BC • Theban nobles reunited Egypt • Developed a new system of government – Less power given to king • During the middle kingdom, pharaohs were expected to be good kings and wise rulers. • Instead of building huge expensive pyramids, when pharaohs died, they were buried in hidden tombs The Second Intermediate Period 1630 – 1520BC • 14th – 17th Dynasties • Hyksos, nomads from Asia, invaded disunited Egypt, set fire to the cities, razed the temples, squandered the accumulated wealth, destroyed much of the accumulated art. – Rule over the north for 160 years. – Rule of the “Shepherd Kings” • Thebans rule the south. Hyksos Entering Egypt Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period New Kingdom 1540-1097 BC • 18th – 20th Dynasties • Ahmose united and restored Egypt under one central government • Ramses II (“the Great”) • Ruled 67 years and expanded empire into Middle East • Brief reign of Tutankhamun • Ramses III lost several wars in Syria against the “Sea People”, which started demise of empire • Increasingly beset by droughts, below-normal flooding of the Nile, famine, civil unrest and official corruption New Kingdom 1540-1097 BC • The new kingdom was Egypt's expansion period. • Egypt expanded her borders through military conquest and became a world power. • During the time period of the new kingdom, pharaohs were all powerful (gods of earth) • Pharaohs were all buried in the same geographic area called the Valley of the Kings. The Valley of the Kings • Contains 63 known tombs – Some simple pits – Others with up to 120 chambers – King Tut’s Tomb Third Intermediate Period 1075-715 BC • 21st -25th dynasties • Disunity and civil war occurs – Egypt loses control of Israel and Syria • Libyans invade and control northern Egypt • Nubians completely separate from Egypt The Late Period 715-332 BC • 26th – 31st Dynasties • Egypt conquered briefly by Assyrians • Cultural revival under kings from Sais • Persian conquest of Egypt (525 BC) • Egypt independent again (404-343 BC) Sais The Greco- Roman Period 332BC-392AD • Macedonia, under Alexander the Great, occupies Egypt – Alexander's general, Ptolemy, becomes king and founds a dynasty – Cleopatra VII reigns as the last pharaoh (51-30 BC) • Egypt becomes a province of the Roman Empire (30 BC) Ptolemaic Egypt The Pharaoh • Meaning: “Great House” • Pharaoh emerged as a living god who ensured the annual flooding of the Nile that was necessary for crop production – Shared resources with the people in return for taxes and obedience. Pharaoh's Regalia • Scepters & Crook • The Uraeus • The Bull’s Tail Does this beard make me look fat? Pharaoh’s Regalia 1. Hedjet (symbol of upper Egypt) 2. Deshret (symbol of lower Egypt) 3. Pschent (symbolized the king’s rule of both Upper and Lower Egypt) Egyptian Webquest… • You will now work individually to do some research on ancient Egyptian culture and religion. • You have the duration of this period and tomorrow’s period to complete you research. • Also, the answers require you to READ and interpret…they are not directly spelled out for you!!! To access the assignment… • • • • Visit the S drive. Click on the HEP folder and 7th grade. Open the “Egyptian Webquest” document. SAVE the document to either your name drive or a flash drive. • You may then begin working! Mastabas were comprised of a deep underground burial area, and a chapel area within the structure itself where offerings could be made to the deceased. Sometimes it’s really hard to only breath through your mouth! The Great Sphinx at Giza The Great Sphinx at Giza • Largest monolith statue in the world – 66 feet high, 20 feet wide, 241 feet long • No one really knows what it was used for • His NOSE! No one knows for sure, but it is believed to have been shot off by a canon in Napoleon’s army… The Great Pyramid was part of a complex that included a special walkway, two temples, other pyramids, boat pits and the mastabas of nobles. This room under the great pyramid is a mystery. Some people believe that this room was left unfinished for religious reasons. Others believe that it was originally meant to be the burial chamber of Khufu, but that the architects changed their minds. Finally, some people believe that this room was built to fool tomb robbers and lead them away from the real burial chamber. Leads from the entrance of the pyramid down to the unfinished chamber below the pyramid. It is about twenty-nine meters long. Leads from the entrance of the pyramid down to the unfinished chamber below the pyramid. It is about twenty-nine meters long. This passage allowed workers to get out of the pyramid after large blocks of stone were lowered to block the ascending passage. This ascending passageway leads from the entrance of the pyramid up to the grand gallery. It is only about one meter wide and a little over one meter tall. The point where this passage meets the descending passage was plugged up with large stone blocks by the ancient Egyptians to discourage tomb robbers. This chamber is commonly known as the 'Queen's chamber'. However, it was never meant to be the burial chamber for a queen. Khufu's queens had their own separate pyramids built nearby. This chamber may have been built as a room to hold Khufu's funerary objects. Queen's chamber This passageway is called the grand gallery. It leads from the ascending passage to the king's chamber. The ceiling in this passageway is almost nine meters high. This was the burial chamber of the pharaoh Khufu. The room is now completely empty except for the granite sarcophagus in the corner. Khufu's mummy and all of his funerary goods for the next life were probably taken out of the pyramid by ancient tomb robbers after Khufu was buried there. These small shafts extend out from the rooms in the pyramid to the outer surface of the pyramid. Some experts believe that they were built to provide ventilation for the people working inside the pyramid while it was being built. Other experts believe that these shafts had a religious purpose because they are directed towards certain stars. This air shaft points towards the constellation of Orion. The ancient Egyptians associated Orion with their god Osiris. These small shafts extend out from the rooms in the pyramid to the outer surface of the pyramid. Some experts believe that they were built to provide ventilation for the people working inside the pyramid while it was being built. Other experts believe that these shafts had a religious purpose because they are directed towards certain stars. This air shaft is directed towards the northern polar stars. So how the H-iz-eck did they build the pyramids?: Theory #1 So how the H-iz-eck did they build the pyramids?: Theory #2 So how the H-iz-eck did they build the pyramids?: Theory #3 The Giza Plateau The First Intermediate Period 2055-1650 BC • 9th – 11th Dynasties • End of the Old Kingdom, pharaohs challenged by local governors called nomarchs – Egypt had 42 nomoi (nome =district or province) – Result: civil wars throughout the empire and the kingdom split into two dynastic kingdoms: Herakleopolian and Theban dynasties • Drought causes the Nile to stop flooding, which results in famine Nomoi of Lower Egypt The Middle Kingdom 2055 – 1650 BC • 11th – 13th Dynasties • One of the feuding dynasties from Thebes in the south was able to unify Egypt again into one kingdom: – Mentuhotep II, marked the beginning of a new era of unity and prosperity Mentuhotep II Mentuhotep II’s Burial Complex Mentuhotep II’s Burial Complex Mentuhotep II’s Burial Complex The Middle Kingdom 2055 – 1650 BC • Trade flourished, arts and literature flourished. • Egypt built strong armies to defend herself against her neighbors. • During the middle kingdom, pharaohs were expected to be good kings and wise rulers. • Instead of building huge expensive pyramids, when pharaohs died, they were buried in hidden tombs. The Second Intermediate Period 1630 – 1520BC • 14th – 17th Dynasties • Hyksos, nomads from Asia, invaded disunited Egypt, set fire to the cities, razed the temples, squandered the accumulated wealth, destroyed much of the accumulated art. – Rule over the north for 160 years. – Rule of the “Shepherd Kings” • Thebans rule the south. Hyksos Entering Egypt Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period New Kingdom 1540-1097 BC • 18th – 20th Dynasties • Ahmose united and restored Egypt under one central government • Ramses II (“the Great”) • Ruled 67 years and expanded empire into Middle East • Brief reign of Tutankhamun • Ramses III lost several wars in Syria against the “Sea People”, which started demise of empire • Increasingly beset by droughts, below-normal flooding of the Nile, famine, civil unrest and official corruption New Kingdom 1540-1097 BC • The new kingdom was Egypt's expansion period. • Egypt expanded her borders through military conquest and became a world power. • During the time period of the new kingdom, pharaohs were all powerful (gods of earth) • Pharaohs were all buried in the same geographic area called the Valley of the Kings. The Valley of the Kings • Contains 63 known tombs – Some simple pits – Others with up to 120 chambers – King Tut’s Tomb Third Intermediate Period 1075-715 BC • 21st -25th dynasties • Disunity and civil war occurs – Egypt loses control of Israel and Syria • Libyans invade and control northern Egypt • Nubians completely separate from Egypt The Late Period 715-332 BC • 26th – 31st Dynasties • Egypt conquered briefly by Assyrians • Cultural revival under kings from Sais • Persian conquest of Egypt (525 BC) • Egypt independent again (404-343 BC) Sais The Greco- Roman Period 332BC-392AD • Macedonia, under Alexander the Great, occupies Egypt – Alexander's general, Ptolemy, becomes king and founds a dynasty – Cleopatra VII reigns as the last pharaoh (51-30 BC) • Egypt becomes a province of the Roman Empire (30 BC) Ptolemaic Egypt The Pharaoh • Meaning: “Great House” • Pharaoh emerged as a living god who ensured the annual flooding of the Nile that was necessary for crop production – Shared resources with the people in return for taxes and obedience. Pharaoh’s Regalia 1. Hedjet (symbol of upper Egypt) 2. Deshret (symbol of lower Egypt) 3. Pschent (symbolized the king’s rule of both Upper and Lower Egypt) Pharaoh's Regalia • Scepters & Crook • The Uraeus • The Bull’s Tail Does this beard make me look fat? • • • • Menes or Narmer – first Pharaoh Djoser – built the first stepped pyramid Sneferu – constructed 3 pyramids Khufu (Cheops in Greek) – built the Great Pyramid of Giza • Khafra– built the Sphinx at Giza and the second largest pyramid at Giza Egyptian Webquest… • You will now work individually to do some research on ancient Egyptian culture and religion. • You have the duration of this period and tomorrow’s period to complete you research. • Also, the answers require you to READ and interpret…they are not directly spelled out for you!!! To access the assignment… • • • • Visit my website. Click on the “World Civilization” tab. Open the “Egyptian Webquest” document. SAVE the document to either your name drive or a flash drive. • You may then begin working!