* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geography Overview 2016
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
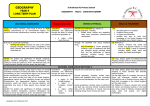
Geography Overview 2016-2017 Reception Term 1 and 2 Term 3 and 4 Term 5 and 6 MY INTERESTS AND ROUTINES/WHOOSH! BEARS AND BEASTS/OUT IN THE GARDEN TRADITIONAL TALES/THE ANIMAL KINGDOM Place knowledge – understanding of local journeys Skills: -use simple locational and directional observational skills of local environment (something is close/far) -observational skills on local journeys Human and physical geography Describe and talk about what they see. Show understanding of cause and effect. Skills: - observational skills to study the geography of the world around them and its grounds and features of surrounding environment. – form views and opinions about their environment Human and physical geography - Use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to key physical features. Looking at how environments vary, (similarities and differences) Show awareness of change Skills: - observational skills to study the geography of the world around them and its grounds and features of surrounding environment. – form views and opinions about their environment - Year 1 Use and develop enquiry skills BIG CHEF LITTLE CHEF CREAK, CRACK, CRASH THE SECRET GARDEN Place knowledge – Comparing England to India in food context Locational knowledgeName and locate the world’s seven continents. Name, locate and identify characteristics of the capital cities of the UK Human and physical geography – Use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to key human features including: farm, factory, village, town, city, house, office, port, harbour and shop Human and physical geography – Use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to key physical features including: beach, cliff, coast, forest, hill, mountain, sea, ocean, river, soil and valley (use to discuss where dinosaurs lived and settled). Skills: use world maps, atlases and globes to identify key physical features Place knowledge - understand geographical similarities and differences through studying the human and physical geography of specific areas Human and physical geography – Use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to key human features Skills: - use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features; devise Skills: Use world maps, atlas and globes to compare where India is to us in the UK and continents. a simple map; and use and construct basic symbols in a key - use simple compass directions (North, South, East and West) and locational and directional language [for example, near and far; left and right], to describe the location of features and routes on a map Year 2 A WALK IN THE WOODS TURRETS AND TIARAS DEEP DOWN UNDER Year 3 I LOVE WHERE I LIVE MYSTERIES AND MUMMIES OUR WONDERFUL WORLD Place knowledge- understanding geographical similarities and differences through studying human and physical geography of a small area of the UK and a small area in non-European country (where do we find wolves)? Skills: - Use world maps, atlas and globes to discuss location of areas in UK in comparison to a non European country and -Use simple compass directions (North, South, East, West) and locational and directional language to describe location of features and routes on a map Locational knowledge – name and locate countries/counties of the UK and identify human and physical characteristics Human and physical geography – describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including types of settlement and land use (stone age settlements) Place knowledge – understand geographical similarities and differences through studying the human and physical geography and how it changes over time. Human and physical geography- Use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to key human features (now and medieval times) Skills: Use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features; devise a simple map; use and construct basic symbols in a key (Rochester) Locational knowledge – Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (look at the flight path on the way to Egypt – which countries of Europe we would fly over)? Human and physical geography- Use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to key human features (topic based) Differences between physical and human features (sea/harbour and port). Locational knowledge – Name and locate the world’s seven continent and five oceans (link to whale migration) Skills: - use world maps, atlases and globes to identify the United Kingdom and its countries, as well as the countries, continents and oceans studied at this key stage Human and physical geography Describe and understand key aspects of physical geography (rivers, water cycle, and mountains) and human geography (types of settlement and land use). Skills: -Use maps of UK to locate countries and counties of the UK (maps of stone age settlements) Use sketch maps and plans to observe, record, measure and present the human and physical features in local area Use 8 points of a compass and use of Ordnance Survey maps to build knowledge of the UK Year 4 1000 YEARS OF BRITISH HISTORY Locational knowledge – name and locate the counties and cities , identifying key topographical features(including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers) and understanding how some of changed over time (e.g location of Hadrian’s Wall) Human and physical geography – describe and understand key aspects of physical geography (volcanoes) Skills: - Use maps of UK to locate counties and describe features studied Use maps and atlases to locate volcanoes around the world Identify the position and significance of the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere, looking at the location of Egypt. Human and physical geography: describe and understand key aspects of physical geography (River Nile). Skills: -Use world maps, atlases and globes to locate continents and countries. Describe and understand the distribution of natural resources (energy, water, food and minerals) Locational knowledge - Identify human and physical characteristics and their key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and landuse patterns; understanding how some of these aspects have changed over time. Skills: - use the eight points of a compass, four and six-figure grid references, symbols and key (including the use of Ordnance Survey maps) to build their knowledge of the United Kingdom and the wider world use fieldwork to observe, measure, record and present the human and physical features in the local area BUILDERS, BRONZES AND BELIEFS Locational knowledge – Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (look at the flight path on the way to Benin – which countries of Europe we would fly over), Place knowledge - understand geographical similarities and differences through studying the human and physical geography in the UK in comparison to another country Skills: -Use world maps, atlases and globes to locate continents and countries. THE RAINFOREST Locational knowledge - identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator and the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. Locate the world’s countries and focusing on Europe and North and South America (The Amazon) concentrating on their environmental regions and key physical and human characteristics. Human and physical geography – describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including: how people live in the rainforest, trade links (Fair Trade) and economic activity. Skills: - use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries, rainforests and describe features studied Year 5 REACH FOR THE STARS Locational knowledge – name and locate counties, cities and regions of the UK Naming and locating countries in Europe (including Russia) through The Space Race Identify the position and significance of the Prime/Greenwich Meridian (Trip to The Royal Observatory) Skills: - Use aerial photos to locate regions and counties of UK Use 8 points of a compass to locate and build knowledge of UK EXPLORATION AND ENDEAVOUR Locational knowledge - identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere and the Arctic. Place knowledge - understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the United Kingdom and a region within North or South America Skills: - use the four and six-figure grid references -use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied Year 6 BATTLE OF BRITAIN History focus CHANGING LANDSCAPES MAZES AND MYTHOLOGY Locational knowledge - locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (location of Greece) concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics. Place knowledge - understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the United Kingdom and a region in a European country (Greece). Human and physical geography: Describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including: types of settlement and land use in Greece (making comparisons to UK). Skills: use maps, atlases, and globes to locate countries and describe features studied. LIVING THINGS/CHANGING AND MOVING ON Locational knowledge: name and locate geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and landuse patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time. Human and physical geography: describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water, Skills: - use fieldwork to observe, measure, record and present the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies. Locational knowledge - name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics and key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers). Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe. Skills: use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied