* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Triangle Term Exterior Angle
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
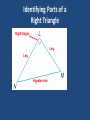
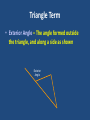
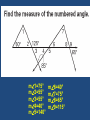
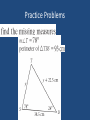
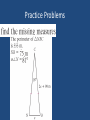
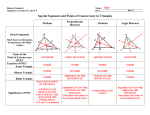
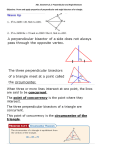
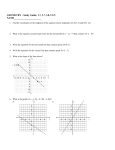
Chapter 5 and Triangle Properties review Identifying Parts of a Right Triangle Right Angle Leg Leg Hypotenuse Right Triangle Terms • Hypotenuse • Legs Properties of Triangles • Triangle Sum Theorem The sum of the measure of the interior angles of a triangle is 180° Triangle Term • Exterior Angle – The angle formed outside the triangle, and along a side as shown Exterior Angle Triangle Term • Exterior Angle – Exterior Angle Remote interior angles Exterior Angle Theorem • The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the measure of the two remote interior angles. Practice Problems m1=75° m2=55° m3=55° m4=40° m5=140° m6=40° m7=75° m8=65° m9=115° X=23 Exterior Angle = 100° mA=30° mB=60° mC=90° Right, Scalene Triangle ISOSCELES TRIANGLE PROPERTIES Isosceles Triangle Parts An Isosceles triangle has two congruent sides Isosceles Triangle Conjecture • If a triangle is isosceles, then its base angles are congruent Isosceles Triangle Conjecture • If a triangle has two congruent angles then it is an isosceles triangle Practice Problems Practice Problems Practice Problems Practice Problems Practice Problems Practice Problems Practice Problems Practice Problems Practice Problems Test Yourself on altitudes, medians, bisectors and points of concurrency Points of Concurrency Type Name Perpendicular Circumcenter Bisectors Angle Bisectors Incenter Medians Centroid Altitudes Orthocenter Points of Concurrency Properties Type Where Circumcenter Equal distance to vertices Incenter Equal distance to sides Centroid Balancing point 1/3 to side, 2/3 to vertex Nothing special Orthocenter Points of Concurrency Where they occur Type Where Circumcenter Incenter Inside Acute Outside Obtuse On hypotenuse of Right Inside Triangle Centroid Inside Triangle Orthocenter Inside Acute Outside Obtuse On Right Angle Name the line Connects the midpoint of a side with a vertex Median Name the line Bisects the angle of a triangle Angle Bisector Name the line Through a vertex, forming a right angle with the opposite side Altitude Name the line From the midpoint of a side, perpendicular to that side Perpendicular Bisector Name the line The height of the triangle Altitude Name the line Three of these meet to form the Circumcenter Perpendicular Bisectors Name the line Three of these meet to form the orthocenter Altitude Points of Concurrency Type Name Perpendicular Circumcenter Bisectors Angle Bisectors Incenter Medians Centroid Altitudes Orthocenter Review Concepts Intersecting points and how they look Vertices Sides Perpendicular Bisectors Angle Bisectors Medians May not intersect Bisects Perpendicular Bisect, Anywhere Starts here Bisects Altitudes Starts here Perpendicular to May be the side of a triangle itself Points of Concurrency Type Name Perpendicular Circumcenter Bisectors Angle Bisectors Incenter Medians Centroid Altitudes Orthocenter Points of Concurrency Where they occur Type Where is it located Circumcenter Incenter Inside Acute Outside Obtuse On hypotenuse of Right Inside Triangle Centroid Inside Triangle Orthocenter Inside Acute Outside Obtuse On Right Angle Points of Concurrency Superpowers Type Property Circumcenter Equal distance to vertices Incenter Equal distance to sides Centroid Balancing point 1/3 to side, 2/3 to vertex On Euler Line Orthocenter