* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psoriasis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
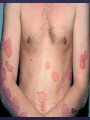
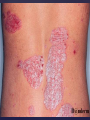
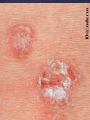
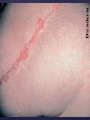
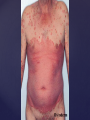
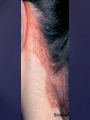
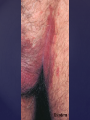
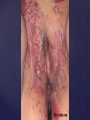
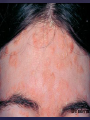
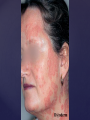
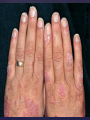
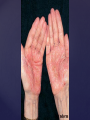
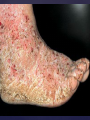
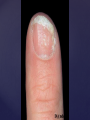
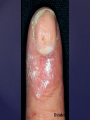
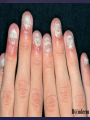
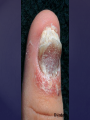
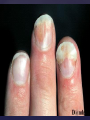
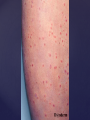
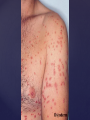
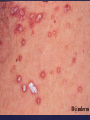
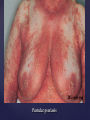
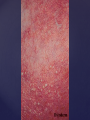
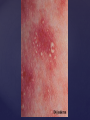
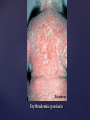
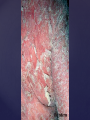
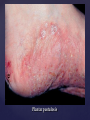
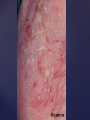
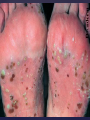
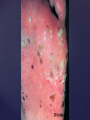
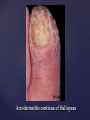
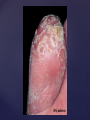
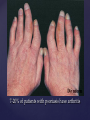
Psoriasis Psoriasis • • • • • Definition and causes Types GP management Pitfalls Hospital treatments Psoriasis • Definition A chronic, non-infectious, inflammatory skin disorder, with well defined, erythematous plaques & large adherent silvery scales • Prevalence 1.5-3% • Age onset 20-30y or 50-60y Psoriasis • Epidermal hyperproliferation • Vascular dilatation • Inflammatory infiltrate What causes psoriasis ? • T cell mediated autoimmune disease → increased keratinocyte proliferation • Environmental and genetic factors Psoriasis Genetics • 40% have FHx • 73% monozygotic twins concordant v 20% dizygotic twins • 1st degree relatives have 4-6 fold increased risk • Environmental triggers GP Management • Time (for proper examination and to communicate with the patient) • Explanation • Information and support sources (patient.co.uk, psoriasisassociation.org.uk) • Follow-up GP Management • • • Emollients Bath oils Site-specific topical treatments Topical treatments • • Vitamin D analogues Dovonex (calcipotriol) oint Dovobet (calcipotriol & betamethasone) oint or gel Silkis (calcitriol) oint Curatorderm (tacalcitol) oint & lotion Zorac (tazarotene) gel (retinoid) Dovonex cream and scalp application no longer available Topical treatments • Tar Carbo-dome Exorex Psoriderm Alphosyl HC Sebco Cocois Tar-based bath oils & shampoos Topical Treatments • • Steroids Often in conjunction with Vit D analogue as Dovobet or separate steroid Eumovate (only oint available) Trimovate Scalp preparations (eumovate to dermovate strength) BE CAREFUL (but not mean) Topical Treatments • • Dithranol Dithrocream Micanol Psorin Stains skin Has to be washed off Start and low strength and build up Topical treatments • Nails difficult potent topical steroids dovonex tazarotene systemic therapy Topical Treatments Scalp • Remove scale first • Sebco messy but effective • Tar or salicylic acid shampoo • Topical steroids if necessary for short periods Types of psoriasis • • • • • • • Plaque Guttate Rupioid Unstable Pustular Erythrodermic ?palmo-plantar pustulosis Guttate psoriasis Pustular psoriasis Erythrodermic psoriasis Plantar pustulosis Acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau Pitfalls • • • • • 'It's not working Doc' It did work, but then he stopped using it and the psoriasis returned It was too greasy/timeconsuming/smelly so he stopped using it He wasn't applying it properly It really didn't work Hospital Treatment • • • • • • • • Out-patient advice and support UVB PUVA Acitretin Methotrexate Ciclosporin Biologics Admission (tar, other topicals) UVB phototherapy • Suitability – age, PH skin cancer, medication, radiotherapy, photosensitive disease • X3 / week for ~6 weeks • Shield genitalia, uninvolved sites • SE burning (30%) • ↑ risk skin cancer (screen yearly if >150 treatments) PUVA • Suitability – as for UVB + CI in renal/hepatic disease, cataracts, pregnancy, children • X2 / week for ~6-8 weeks • Need eye protection for 24 h after psoralen • SE burning, nausea, itch ↑ risk skin cancer (screen yearly if >150 treatments) Systemic therapy acitretin methotrexate ciclosporin 7-20% of patients with psoriasis have arthritis Acitretin mec: affects keratinocyte differentiation CI: ? fertile women (as must avoid pregnancy for 2 years) SE: dry lips, teratogenicity, abnormal LFT, lipids, DISH Methotrexate mec: inhibits DNA synthesis by inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase → reduces proliferation of lymphocytes + keratinocytes CI: pregnancy, lactation, infection, liver/renal disease, peptic ulcers SE: anorexia, nausea, myelosuppression, hepatotoxicity, mouth ulcers, pulmonary toxicity, oligospermia, skin cancer Interactions: NSAIDs, septrin, trimethoprim, penicillin, phenytoin Given once a WEEK Ciclosporin Mec Inhibits T cell activation CI uncontrolled HBP, malignancy, infection SE HBP, nephrotoxicity, skin cancer, other malignancy, gum hypertrophy Not recommended for long term treatment New Biologicals Anti TNF drugs Infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab Targeted T - cell therapy alefacept (binds CD2 & blocks LFA3) efalizumab (binds to LFA-1 & blocks ICAM-1) Anti-IL 17 receptor antibodies Brodalumab Ixekizumab GP Issues • • • • Know what your patient is on (?record as outside script on EMIS) Know what monitoring you are responsible for Keep a look out for myelosuppression Don't be afraid of your local Derm department! SIGN 121 Patients with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis should have an annual review with their GP involving the following: documentation of severity using DLQI ƒscreening for depression assessment of vascular risk (in patients ƒ with severe disease) ƒassessment of articular symptoms ƒoptimisation of topical therapy ƒconsideration for referral to secondary care