* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is the cell membrane?
Survey
Document related concepts
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
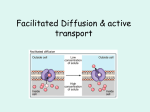
Type of Transport Simple Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport Transport Protein Used? Direction of movement Requires Energy input from cell? Classification of transport? Types of Substances CELL MEMBRANE AND CELL TRANSPORT NOTES Standard Cell Biology 1. a. Students know cells are enclosed within semipermeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=owEgq rq51zY What is the cell membrane? ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ The structure of the cell membrane The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer (lipid = fat; bi=2) plus proteins that straddle the bilayer. Attached to the proteins are carbohydrates. _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ Draw the cell membrane Cell Membrane Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S7CJ7 xZOjm0 You should be able to answer these questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Describe the structure of the cell membrane. How do molecules get into and out of the cell? What is selective permeability? What is diffusion and how does it work? What is facilitated diffusion and how does it work? 6. What is active transport and how does it work? 7. What is osmosis and how does it work? 8. What is the function of transport proteins? Transport through the Cell Membrane Cell membranes are selectively permeable (semipermeable). Permeable- Impermeable- Selectively Permeable (semi permeable)- Transport Through the Membrane Passive Transport: 1. ________________ 2. __________________ ________________ Active Transport Simple Diffusion Notes: Solution- Solvent- Solute- Concentration- Think of living cells like little bags of solutions surrounded by a semipermeable membrane! For the cell to survive, the concentration of solutes must stay within a safe range to maintain homeostasis. Concentration Gradient- when there is a difference in concentrations High concentration: ________________ Low concentration: ________________ In diffusion, __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ Facilitated Diffusion Notes: Carrier Proteins Channel Proteins Passive Transport: Facilitated Diffusion https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vKGN_ Zhz8AY Active Transport Notes: Active Transport Active Transport https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yz7EH JFDEJs Other Types of Active Transport Endocytosis – Phagocytosis – Pinocytosis – Exocytosis – Endocytosis and Exocytosis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qpw2p 1x9Cic Osmosis- the diffusion of water Notes: Concentration Strength Isotonic – Hypotonic – Hypertonic – Osmotic Pressure Notes: Red Blood Cells in a Hypertonic Solution https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OYoaL zobQmk Plants and Osmosis Applications of Osmosis Water overdose/intoxication High concentration of fertilizer kills plants Water enters the roots of plants Why drinking salt water can kill you Why putting salt on a slug or snail kills it How dialysis machines work The preservation of foods in salt brines (olives, fish vegetables) kills bacteria Refresh wilted salad greens by putting in water Cell Quiz 1. 2. What are two differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? An animal cell is a prokaryotic/eukaryotic cell. (circle the correct answer) 3. When preparing a wet mount, the cover slip should be put on at an angle to avoid ______. 4. The ______ contains the DNA and controls the cell. 5. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a ______ to a _______ concentration. 6. If a cell has 95% water and it is placed in a hypertonic solution, water will move out of/into the cell. (circle the correct answer) 7. _________ are where photosynthesis occurs in plant cells. 8. A bacteria is a prokaryotic/eukaryotic cell. (circle the correct answer) 9. On high power, more/less of the cell can be seen. circle the correct answer) 10. What two things happen to an image when viewed under a microscope? 11. Choose and explain one of the following: endocytosis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis, or exocytosis.