* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Government Spending
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
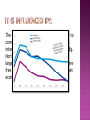
By Lauren, Toni and Lydia AD = C+I+G+(XM) Government spending includes: Social Security, NHS, Transport, Education, Defence, Debt Interest, Industry & Agriculture, Law & Order, Housing & Environment and others. The extent of market failure and the ability to correct it – In economies where government intervention is high (Command economies. Eg. North Korea), government spending forms a large proportion of AD than in countries where free market forces play a greater role (Market economies . Eg. America). The level of economic activity in the economy can influence government spending. For example: if there is a high level of unemployment, a government may rise its spending in a bid to increase aggregate demand and the output of the economy. In contrast, if there is a high inflation rate the government may reduce its spending. A desire to please voters – Pressure can be put on a government by people to spend money on services such as improving the NHS, education or the transport infrastructure. Before a general election, the government may increase their spending to win around the public and increase political support. War, terrorist attacks and rising crime, or their threat, can also increase government spending. Infrastructure – The basic physical and organisational structures and facilities (eg. Roads and buildings) needed for the operation of a society. Unemployment – A situation where people are out of work but willing and able to work. Inflation – A sustained rise in the price level over a period of time. 1. 2. 3. 4. How many ways of government spending can you remember? List them How does a government election effect government spending at that time? What are the main factors considered when the government decide what to spend money on? What do you think is the focus point of government spending in the past year? Thank you for watching! http://www.guardian.co.uk/news/datablog/2012/m ar/21/budget-2012-spending-tax-visualised#zoomedpicture