* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evidence from Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
DNA barcoding wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
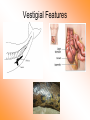
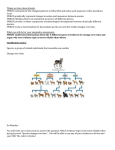
Chapter 5 Section 5.3 Evidence of Evolution from Biology Evidence from Anatomy • Homologous vs. Analogous Features: Homologous – features with similar structures but different functions, and are similar because they share evolutionary origin. Analogous – features that are similar in appearance and function, but do not appear to have the same evolutionary origin. Homologous Features Analogous Features Evidence from Embryology • Embryology is the study of embryos or the study of organisms before they are fully developed. • In the early weeks of development, human embryos possess a tail and gill slits, similar to those in chicken and fish embryos. • The embryonic tail serves no function in humans and later becomes the tailbone. • The gill slits become modified in both humans and birds to form various internal ear structures. • But these pre-development relationships show that there may have been a shared ancestor along the evolutionary line. Evolutionary Embryology Vestigial Features • Vestigial features – are structures found in an organism that have no useful function. • One explanation for vestigial organs is that they once served some function in an ancient ancestor, but due to changes in environmental conditions they were no longer needed. • Examples of vestigial features: - Appendix - Tonsils - Whale leg and hip bones - Snake leg and hip bones - Blind cave salamanders have empty eye sockets, suggesting they evolved from salamanders with fully functioning eyes. Vestigial Features Evidence from Biochemistry • Evidence for evolution has also been found by comparing biochemical characteristics of different species. • Proteins are molecules that are used to make structures in our bodies such as muscle cells and skin cells. • They are made of long chains of compounds called amino acids Amino Acids • In many species the sequence of amino acids is very similar. • Ex. Hemoglobin is an oxygen carrying protein found in the blood of all mammals, but each species has a slightly different amino acid sequence. • Suggesting that each species evolved to suit their own conditions. Such as animals that have adapted to low oxygen environments. • Scientists have also found evidence for evolution in DNA sequences. • DNA – deoxyribose nucleic acid is the hereditary material that determines which characteristics are passed on to the next generation. • Each DNA molecule contains many different genes that provide the instructions for traits such as eye colour or hair colour. • Gene – a segment of DNA that performs a specific function, such as coding for a particular trait (hair color, eye color, proteins). • DNA is composed of four chemicals called nucleotide bases that arranged in different sequences. • The four bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). • DNA sequences from different species that code for a particular trait vary in the number and order of the nucleotides. AGTCCCAAAGTGAAGGAGA AGTCC AAAGTGAAGGAGA • Geneticists have found homologous and vestigial genes in DNA sequences. • Ex. Humans possess a set of defective genes that would allow us to make our own Vitamin C. • We have lost the ability but still possess the genes. • Suggesting once again that we have evolved due to our environmental conditions. Evidence from Artificial Selection • Artificial selection – the process of humans selecting and breeding individuals that have desired characteristics. • The fact that we are able to change organisms artificially provides evidence that the same process is possible in nature. Artificial Selection Assignment • Lab Exercise 5.A • Pg. 147