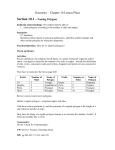
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download { {-1,-1,-1},{1,-1,1}, {1,1,-1},{-1,1,-1}, {-1,-1,1},{1,-1,1
Stereo photography techniques wikipedia , lookup
Anaglyph 3D wikipedia , lookup
Autostereogram wikipedia , lookup
Spatial anti-aliasing wikipedia , lookup
Stereo display wikipedia , lookup
Original Chip Set wikipedia , lookup
Graphics processing unit wikipedia , lookup
Indexed color wikipedia , lookup
Molecular graphics wikipedia , lookup
Mesa (computer graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Comparison of OpenGL and Direct3D wikipedia , lookup
BSAVE (bitmap format) wikipedia , lookup
List of 8-bit computer hardware palettes wikipedia , lookup
Color Graphics Adapter wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix 4010 wikipedia , lookup
Apple II graphics wikipedia , lookup
Waveform graphics wikipedia , lookup
Stereoscopy wikipedia , lookup
Perspective projection distortion wikipedia , lookup
Hold-And-Modify wikipedia , lookup
Computer Graphics (Spring 2003)
COMS 4160, Lecture 13: OpenGL 2
Ravi Ramamoorthi
http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160
Many slides courtesy Greg Humphreys
State
• OpenGL is a big state machine
• State encapsulates control for operations like:
– Lighting
– Shading
– Texture Mapping
• Boolean state settings can be turned on and off
with glEnable and glDisable
• Anything that can be set can be queried using
glGet
State Management
• glEnable, glDisable, glIsEnabled
• glGet
• Attributes
– glPointSize, glFrontFace, glCullFace,
• Other advanced topics (later)
– Vertex Arrays
– Display Lists
– Curved surfaces
Immediate vs. Retained Mode
• Two ways of specifying what is to be drawn
– Immediate Mode
• Primitives are sent to the display as soon as they are specified
• Graphics system has no memory of drawn graphics primitives
– Retained Mode
•
•
•
•
Primitives placed in display lists
Display lists can be kept on the graphics server
Can be redisplayed with different graphics state
Almost always a performance win (if you can get away with it)
Event Driven Interaction
• OpenGL does not dictate any particular model of
interaction
• Applications respond to events generated by
devices (i.e., mice) and window system events
(i.e., window resized)
• Events are usually placed in a queue awaiting
action
• Callbacks let you associate a function with a
particular type of event
– Mouse callback
Usual Interactions
• Initialization
– Open / place / resize window
• Expose/resize/hide window
• Mouse
–
–
–
–
Button click
Button release
Mouse motion
Mouse drag (motion + button)
• Keyboard
– What key was pressed (or released)?
– Where was the mouse?
– Were any modifier keys pressed? (control, alt, shift)
GLUT
• OpenGL Utility Toolkit
• Written by Mark Kilgard
• Provides basic window system interaction:
–
–
–
–
Open/close window
Mouse/keyboard callbacks
“Idle” callback for animation
Menus
Typical “main” Function
int main( int argc, char *argv[] )
{
glutInit( &argc, argv );
glutInitDisplayMode( GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB );
glutCreateWindow( “A window” );
glutDisplayFunc( display );
glutReshapeFunc( reshape );
glutMouseFunc( mouse );
glutIdleFunc( idle );
glutMainLoop();
}
Viewing (Chapter 3)
• Two parts
– Object positioning (GL_MODELVIEW)
– Projection (GL_PROJECTION)
•
•
•
•
Transformation stages (pp 98)
Perspective, Orthographic transformations
Camera always at origin, pointing –z direction
Transforms applied to objects
– Equivalent to moving camera by inverse…
– More details next…
Transformations
• Object in world coordinates (modelview)
– glTranslatef(x,y,z) ; glRotatef(θ,x,y,z) ; glScalef(x,y,z)
– Right-multiply current matrix (last is first applied)
• Matrix Stacks
– glPushMatrix, glPopMatrix, glLoad
– Useful for Hierarchically defined figures
• gluLookAt (fromv,atv,upv)
– Usually in projection matrix, sometimes in modelview
– Concatenate with perspective (orthographic) projection
Sample Code
glMatrixMode( GL_MODELVIEW );
glLoadIdentity();
glTranslatef( 1, 1, 1 );
glRotatef( 90, 1, 0, 0 );
DrawObject();
Positioning the Camera
• Use gluLookAt to specify:
– Eye location
– “Look-at point”
– “up” vector
• gluLookAt( 10, 10, 10, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 1 )
– Eye point is (10, 10, 10)
– Look at point is (1,2,3)
– Up vector is (0,0,1)
• This is usually done in the GL_PROJECTION
matrix, and combined with a perspective matrix
Viewing Volumes
• Orthographic projection
– glOrtho( left, right, bottom, top, front, back ) specifies
the boundaries of the parallel viewing volume
– Objects are clipped to the specified viewing cube
• Perspective Projection
– glFrustum, gluPerspective
– Clipping volume is a frustum
• Make sure the near and far clipping planes aren’t
too far apart
• Make sure the near plane isn’t too close to the eye
Complete Viewing Example
//Projection first
glMatrixMode( GL_PROJECTION );
glLoadIdentity();
gluPerspective( 60, 1, 1, 100 );
gluLookAt( 10, 10, 10, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 1 )
//Now object transformations
glMatrixMode( GL_MODELVIEW );
glLoadIdentity();
glTranslatef( 1, 1, 1 );
glRotatef( 90, 1, 0, 0 );
DrawObject();
Matrix Stacks
• OpenGL has multiple matrix “stacks”
• glPushMatrix pushes a copy of the top-ofstack matrix
• glPopMatrix throws away the top of the
stack
• Very useful for hierarchichally defined
figures
Color (Chapter 4)
• RGBA
– 8 (or whatever number) bits/color channel
– Alpha A important for transparency
– 32 bits, 16 million colors
• Color Index
– Index into color table, small number of colors (256)
• Shading model glShadeModel
– GL_FLAT, GL_SMOOTH (Goraud)
– Issues in smooth shading with color index?
Simple OpenGL Programs
Drawing Primitives
• Specify primitives using glBegin and glEnd:
glBegin( primitive_type );
…specify vertex attributes
…draw vertices
glEnd();
• primitive_type specifies points, lines, triangles,
quads, polygons, etc…
• GL_POINTS, GL_LINES, GL_TRIANGLES,
GL_QUADS, GL_POLYGON,…
Specifying Vertices
• glVertex{size}{type}{vector}
e.g. glVertex3fv
Coordinates are passed in an array
Coordinate types are float
3 coordinates passed (x,y,z)
glVertex2f( 1.0f, 1.0f );
glVertex3i( 20, 20, 20 );
float verts[4] = { 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 1.0 };
glVertex4fv( verts );
Example: A Wireframe Cube
GLfloat vertices[][3] = {
{-1,-1,-1},{1,-1,1},
{1,1,-1},{-1,1,-1},
{-1,-1,1},{1,-1,1},
{1,1,1},{-1,1,1}
};
void cube(void)
{
polygon( 1,0,3,2 ); polygon( 3,7,6,2 );
polygon( 7,3,0,4 ); polygon( 2,6,5,1 );
polygon( 4,5,6,7 ); polygon( 5,4,0,1 );
}
Example: A Wireframe Cube
void polygon( int a, int b, int
{
glColor3f( 1,1,1 );
glBegin( GL_LINE_LOOP );
glVertex3fv( vertices[a]
glVertex3fv( vertices[b]
glVertex3fv( vertices[c]
glVertex3fv( vertices[d]
glEnd();
}
c, int d )
);
);
);
);
Specifying Vertex Attributes
• Vertex attributes are state settings that are usually
applied between a glBegin/glEnd pair
• Vertex attributes are set using:
glColor, glNormal, glTexCoord, glEdgeFlag
• Vertex attribute routines take a form similar to
glVertex:
glName{size}{type}{vector}
e.g. glColor3us takes 3 unsigned short parameters
Pixel Primitives
• Provide a way to manipulate rectangles of pixels
• glDrawPixels, glReadPixels, glCopyPixels move
pixel rectangles to and from the framebuffer
• glBitmap takes a binary image and renders the
current color in framebuffer positions
corresponding to 1’s in the image. This might be
useful for drawing fonts
• glRasterPos defines where the pixels go in the
framebuffer
• The interaction between glRasterPos and glBitmap
is subtle and confusing
Hidden Surface Removal
• When we draw a fragment, record the z
(distance to the eye) in the depth buffer
• If the z stored in the depth buffer is greater
than the z for the fragment about to be
drawn, draw it
• Otherwise, the fragment is behind
something that has already been drawn, so
throw it away
Hidden Surface Removal
• When setting up your window, specify a depth
buffer:
glutInitDisplayMode( GLUT_DEPTH );
• When clearing, make sure to:
glClear( GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT );
• glEnable( GL_DEPTH_TEST );
• Set the depth test comparison operation:
glDepthFunc( GL_LESS ); (this is the default)
Simple Shading
Example: shading a sphere with lighting
glShadeModel(GL_FLAT)
glShadeModel(GL_SMOOTH)
OpenGL will interpolate the colors across the face of a polygon
if smooth shading is turned on.