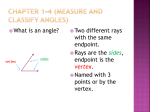* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
1.4 Measure and Classify Angles Goal Your Notes p Name, measure, and classify angles. VOCABULARY Angle Sides of an angle Vertex of an angle Measure of an angle Acute angle Right angle Obtuse angle Straight angle Congruent angles Angle bisector Example 1 You should not name any of these angles B because all three angles have B as their . 12 Name angles Name the three angles in the diagram. Lesson 1.4 • Geometry Notetaking Guide , or , or , or A C B D Copyright © Holt McDougal. All rights reserved. 1.4 Measure and Classify Angles Goal Your Notes p Name, measure, and classify angles. VOCABULARY Angle An angle consists of two different rays with the same endpoint. Sides of an angle In an angle, the rays are called the sides of the angle. Vertex of an angle In an angle, the endpoint is the vertex of the angle. ####$ and ###$ Measure of an angle In ∠ AOB, OA OB can be matched one to one with real numbers from 0 to 180. The measure of ∠ AOB is equal to the absolute value of the difference between the real OA and ###$ OB. numbers for ####$ Acute angle An angle that measures between 08 and 908 Right angle An angle that measures 908 Obtuse angle An angle that measures between 908 and 1808 Straight angle An angle that measures 1808 Congruent angles Angles with the same measure Angle bisector A ray that divides an angle into two angles that are congruent Example 1 You should not name any of these angles B because all three angles have B as their vertex . 12 Name angles Name the three angles in the diagram. ∠ ABC , or ∠CBA ∠CBD , or ∠ DBC ∠ ABD , or ∠ DBA Lesson 1.4 • Geometry Notetaking Guide A C B D Copyright © Holt McDougal. All rights reserved. POSTULATE 3: PROTRACTOR POSTULATE 80 90 10 0 70 10 0 90 80 110 1 70 2 60 0 110 60 0 1 2 3 50 0 1 50 0 13 A 170 180 60 0 0 1 20 10 15 0 30 14 0 4 Consider ###$ OB and point A on one side of ###$ OB. The rays of the form ###$ OA can be matched one to one with the real . numbers from 0 to 0 10 180 170 1 20 3 60 15 0 4 01 0 40 Your Notes O B is equal to between the real numbers The measure of ###$. for ###$ OA and OB Measure and classify angles A protractor is a drawing tool that allows you to measure angles. You can also use a protractor to draw angles of given measures. a. ∠ WSR b. ∠ TSW c. ∠ RST d. ∠ VST 80 90 10 0 70 10 0 90 80 110 1 70 2 60 0 110 60 0 1 2 3 50 0 1 50 0 13 R T scale of the on the angle. ST is lined up with the 08 on the b. ###$ SW passes through protractor. ###$ scale. So, m∠ TSW 5 . It is d. m∠ VST 5 V S a. ###$ SR is lined up with the 08 on the SW passes through protractor. ###$ scale. So, m∠ WSR 5 . It is c. m∠ RST 5 W 170 180 60 0 0 1 20 10 15 0 30 14 0 4 Use the diagram to find the measure of the indicated angle. Then classify the angle. 0 10 180 170 1 20 3 60 15 0 4 01 0 40 Example 2 scale of the on the angle. . It is angle. . It is angle. Checkpoint Complete the following exercises. 1. Name all the angles in the diagram at the right. J F G H 2. What type of angles do the x-axis and y-axis form in a coordinate plane? Copyright © Holt McDougal. All rights reserved. Lesson 1.4 • Geometry Notetaking Guide 13 POSTULATE 3: PROTRACTOR POSTULATE 80 90 10 0 70 10 0 90 80 110 1 70 2 60 0 110 60 0 1 2 3 50 0 1 50 0 13 A 170 180 60 0 0 1 20 10 15 0 30 14 0 4 Consider ###$ OB and point A on one side of ###$ OB. The rays of the form ###$ OA can be matched one to one with the real numbers from 0 to 180 . 0 10 180 170 1 20 3 60 15 0 4 01 0 40 Your Notes O B The measure of ∠ AOB is equal to the absolute value of the difference between the real numbers ###$. for ###$ OA and OB Measure and classify angles A protractor is a drawing tool that allows you to measure angles. You can also use a protractor to draw angles of given measures. a. ∠ WSR b. ∠ TSW c. ∠ RST d. ∠ VST 80 90 10 0 70 10 0 90 80 110 1 70 2 60 0 110 60 0 1 2 3 50 0 1 50 0 13 W R V 170 180 60 0 0 1 20 10 15 0 30 14 0 4 Use the diagram to find the measure of the indicated angle. Then classify the angle. 0 10 180 170 1 20 3 60 15 0 4 01 0 40 Example 2 S T a. ###$ SR is lined up with the 08 on the outer scale of the SW passes through 658 on the outer protractor. ###$ scale. So, m∠ WSR 5 658 . It is an acute angle. ST is lined up with the 08 on the inner scale of the b. ###$ SW passes through 1158 on the inner protractor. ###$ scale. So, m∠ TSW 5 1158 . It is an obtuse angle. c. m∠ RST 5 1808 . It is a straight angle. d. m∠ VST 5 908 . It is a right angle. Checkpoint Complete the following exercises. 1. Name all the angles in the diagram at the right. J F G H ∠ FGH or ∠ HGF, ∠ FGJ or ∠ JGF, ∠ JGH or ∠ HGJ 2. What type of angles do the x-axis and y-axis form in a coordinate plane? right angles Copyright © Holt McDougal. All rights reserved. Lesson 1.4 • Geometry Notetaking Guide 13 Your Notes A point is in the interior of an angle if it is between points that lie on each side of the angle. interior POSTULATE 4: ANGLE ADDITION POSTULATE Words If P is in the interior of ∠ RST, then the measure of ∠ RST is equal to the sum of the measures of ∠ and ∠ . R m/RST S m/PST T Symbols If P is in the interior of ∠ RST, then m∠ RST 5 m∠ 1 m∠ Example 3 m/RSP P . Find angle measures Given that m∠ GFJ 5 1558, find m∠ GFH and m∠ HFJ. H (4x 2 1)8 (4x 1 4)8 Solution G J F Step 1 Write and solve an equation to find the value of x. m∠ GFJ 5 m∠ 5( 1 m∠ )8 1 ( Angle Addition Postulate )8 Substitute. 5 Combine like terms. 5 Subtract each side. 5x Divide each side by . from Step 2 Evaluate the given expressions when x 5 m∠ GFH 5 ( )8 5 ( )8 5 m∠ HFJ 5 ( )8 5 ( )8 5 So, m∠ GFH 5 and m∠ HFJ 5 . . . . Checkpoint Complete the following exercise. 3. Given that ∠ VRS is a right angle, find m∠ VRT and ∠ TRS. (x 2 4)8 V T (3x 1 2)8 R 14 Lesson 1.4 • Geometry Notetaking Guide S Copyright © Holt McDougal. All rights reserved. Your Notes A point is in the interior of an angle if it is between points that lie on each side of the angle. interior POSTULATE 4: ANGLE ADDITION POSTULATE Words If P is in the interior of ∠ RST, then the measure of ∠ RST is equal to the sum of the measures of ∠ RSP and ∠ PST . R m/RST m/RSP P S m/PST T Symbols If P is in the interior of ∠ RST, then m∠ RST 5 m∠ RSP 1 m∠ PST . Example 3 Find angle measures Given that m∠ GFJ 5 1558, find m∠ GFH and m∠ HFJ. H (4x 2 1)8 (4x 1 4)8 Solution G J F Step 1 Write and solve an equation to find the value of x. m∠ GFJ 5 m∠ GFH 1 m∠ HFJ 1558 5 ( 4x 1 4 )8 1 ( 4x 2 1 )8 Angle Addition Postulate Substitute. 155 5 8x 1 3 Combine like terms. 152 5 8x Subtract 3 from each side. 19 5 x Divide each side by 8 . Step 2 Evaluate the given expressions when x 5 19 . m∠ GFH 5 ( 4x 1 4 )8 5 ( 4 p 19 1 4 )8 5 808 . m∠ HFJ 5 ( 4x 2 1 )8 5 ( 4 p 19 2 1 )8 5 758 . So, m∠ GFH 5 808 and m∠ HFJ 5 758 . Checkpoint Complete the following exercise. 3. Given that ∠ VRS is a right angle, find m∠ VRT and ∠ TRS. (x 2 4)8 V T m∠VRT 5 198, m∠TRS 5 718 (3x 1 2)8 R 14 Lesson 1.4 • Geometry Notetaking Guide S Copyright © Holt McDougal. All rights reserved. Your Notes Example 4 Identify congruent angles L Identify all pairs of congruent angles in the diagram. If m∠ P 5 1208, what is m∠ N? M P Solution There are two pairs of congruent angles: ∠P > and ∠ L > Because ∠ P > So, m∠ N 5 Example 5 N , m∠ P 5 . . Double an angle measure In the diagram at the right, ###$ WY bisects ∠ XWZ, and m∠ XWY 5 298. Find m∠ XWZ. Z Y X W Solution By the Angle Addition Postulate, 1 m∠ XWZ 5 . Because ###$ WY bisects ∠ XWZ, you know > . So, m∠ XWZ 5 5 5 1 , and you can write 1 5 . Checkpoint Complete the following exercises. 4. Identify all pairs of congruent angles in the diagram. If m∠ B 5 1358, what is m∠ D? B C A D Homework 5. In the diagram below, ###$ KM bisects ∠ LKN and m∠ LKM 5 788. Find m∠ LKN. M N L K Copyright © Holt McDougal. All rights reserved. Lesson 1.4 • Geometry Notetaking Guide 15 Your Notes Example 4 Identify congruent angles L Identify all pairs of congruent angles in the diagram. If m∠ P 5 1208, what is m∠ N? M P Solution There are two pairs of congruent angles: N ∠ P > ∠ N and ∠ L > ∠ M Because ∠ P > ∠ N , m∠ P 5 m∠ N . So, m∠ N 5 1208 . Example 5 Double an angle measure In the diagram at the right, ###$ WY bisects ∠ XWZ, and m∠ XWY 5 298. Find m∠ XWZ. Z Y X W Solution By the Angle Addition Postulate, m∠ XWZ 5 m∠ XWY 1 m∠ YWZ . Because ###$ WY bisects ∠ XWZ, you know ∠ XWY > ∠ YWZ . So, m∠ XWY 5 m∠ YWZ , and you can write m∠ XWZ 5 m∠ XWY 1 m∠ YWZ 5 298 1 298 5 588 . Checkpoint Complete the following exercises. 4. Identify all pairs of congruent angles in the diagram. If m∠ B 5 1358, what is m∠ D? Homework B C A D ∠ B > ∠ D and ∠ A > ∠ C; 1358 5. In the diagram below, ###$ KM bisects ∠ LKN and m∠ LKM 5 788. Find m∠ LKN. 1568 Copyright © Holt McDougal. All rights reserved. M N L K Lesson 1.4 • Geometry Notetaking Guide 15