* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Orlistat (Alli, Xenical)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
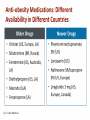
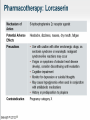
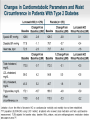
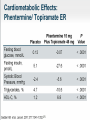
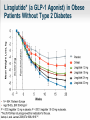
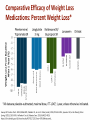
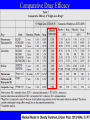
Obesity Management • Dr . Mouna Dakar Orlistat (Xenical, Alli) Type: lipase inhibitor Mechanism of action: inhibits the breakdown of triglycerides into absorbable free fatty acids by lipase enzymes in the stomach and pancreas, resulting in less fat being absorbed Year of approval: 1999 (Xenical – prescription 120 mg TID), 2007 (Alli – OTC 60 mg) FDA approved indication: as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie and low-fat diet for weight loss or to lower the risk of regaining weight after prior weight loss Efficacy: 2.9 kg mean weight loss (Xenical) beyond that achieved by placebo at one year (metaanalysis of 15 trials; Ann Intern Med 2005;142:532-46) Adverse effects: significant diarrhea, fecal incontinence, oily spotting, flatulence, bloating, dyspepsia (all can be reduced with avoidance of fat-rich foods), reduced absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, serious liver injury (rare) Contraindications: malabsorption, cholestasis, impaired liver function, pancreatic disease, pregnancy (added in 2012) Orlistat is a gastrointestinal lipase inhibitor that induces weight loss by inhibiting nutrient absorption. it may reduce the absorption of some fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) and beta-carotene. Administer a daily oral multivitamin supplement containing fat-soluble vitamins 2 hours before meals or 1 hour after meals. Lorcaserin (Belviq) Type: serotonin agonist Mechanism of action: activates 5-HT2C receptors in the hypothalamus, resulting in increased proopiomelanocortin (POMC) production, which promotes satiety Year of approval: 2012 FDA approved indication: treatment of obesity for adults with BMI ≥ 30 or ≥ 27 in the presence of other risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes or hyperlipidemia Efficacy: 3.6 kg mean weight loss beyond that achieved by placebo (5.8 kg vs. 2.2 kg) at one year (Phase 3 RCT; N Engl J Med 2010; 363:245-256) Adverse effects: headache, nasopharyngitis Contraindications: pregnancy, MAOIs, SSRIs (caution) Phentermine-topiramate (Qsymia) Year of approval: 2012 FDA approved indication: chronic weight management, as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and exercise, for BMI ≥ 30 or ≥ 27, in the presence of other risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes or hyperlipidemia Efficacy: 10.7 kg mean weight loss beyond that achieved by placebo (12.6 kg vs. 1.9 kg) at one year (Phase 3 RCT; Obesity (2012); 20 2, 330–342) Adverse effects: tachycardia, insomnia, paresthesias, dizziness, distorted taste sensation, constipation, dry mouth, anxiety, suicidality (rare), acute angle closure glaucoma (rare), metabolic acidosis (rare), increased serum creatinine (rare) Contraindications: pregnancy, glaucoma, hyperthyroidism, MAOIs, history of suicide attempt Phentermine (Adipex-P) http://phentermine-hcl.info/ Sibutramine (Meridia) http://www.sibutramineonline.org/ Orlistat (Alli, Xenical) http://www.nhplus.com/product_detail_e.cfm?I D=16111 Comparative Drug Efficacy Pharmacologic Agents for the Treatment of Obesity http://www.weightlossdietwatch.com/diet-pills-andsupplements/can-phentermine-diet-pills-really-help-you-tolose-weight/