* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download antigone webquest
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Greece wikipedia , lookup
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Greek mythology wikipedia , lookup
Greek Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Thebaid (Latin poem) wikipedia , lookup
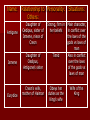
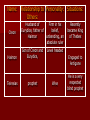
ANTIGONE WEBQUEST An Introduction to Greek Tragedy Welcome to the Antigone WebQuest! Before beginning your exploration into the world of Antigone, you must first become acquainted with Sophocles and The Greek Theater. The following pages will provide you with the information you need. Meet Sophocles (496-406 B.C.) Sophocles was born and raised in Athens He is regarded as one of the world’s greatest playwrights. He frequently won 1st place at the Dionysian festivals, which were competitions between playwrights. During his life, he wrote over 100 plays, but only 7 have survived. Among these 7 are: Oedipus the King, Oedipus at Colonus, and Antigone. The Greek Theater Theater was a celebration in ancient Greece that was held in honor of Dionysos (the god of wine). During these celebrations, Athenians gathered to watch competitions between playwrights. It was these competitions that Sophocles often won. The plays performed at these festivals usually exposed arrogance which emphasized reverence for the gods and included tragic events. Although violence and disrespect were central to the plot of most tragic plays, violence was never depicted on stage. Instead, these events occurred off stage. Tragedy Tragedy is a work of literature that results in a catastrophe for the main character. In Greek drama, the main character was always a significant person, a king or a hero, and the cause of the tragedy was a tragic flaw, or weakness in his or her character. Typical Structure of a Tragedy Ancient Greek playwrights used a consistent format for most of their productions. A Chorus is used to divide the scenes (similar to how a curtain does in present day performances) through a song that comments on the action of the previous scene. The Choragos is the leader of the chorus, and serves as another character in the play The typical structure of a tragedy is as follows: – Prologue – exposition which provide background to the conflict – Parados or parode – Opening song or ode Strophê – the chorus sings a stanza while moving from right to left while singing Antistrophê - the chorus sings a stanza while moving from left to right while singing Epode – included in some odes as a final stanza – Paean – a thanksgiving to Dionysos – Exodos – final exiting scene Now that you are familiar with Greek Tragedy, you are ready to begin your task… Your Task: You are a detective assigned to investigate the death of Antigone. Before you can understand her death, you must first become aware of the circumstances surrounding her life. You will obtain background information about Anigone’s family life, and the society in which she lived, by following the trail of clues linked to her death. Family Life – Antigone’s Dad Antigone, is part of a trilogy about the royal family of Thebes. The trilogy includes; Oedipus the King, Oedipus at Colonus and Antigone Follow the two links below to learn more about Antigone’s father, Oedipus: – Oedipus’ Early Life – Oedipus’ Exile A Tragedy between Brothers As if the tragedy surrounding her father’s life and exile was not horrific enough, Antigone must now face the death of her brothers. Click here to learn more about Eteocles and Polyneices Greek Society Religion Government Funeral Rites – only read the first paragraph Role of Women – click on the “Daily Life” tab and then click on “Women’s Life” Hubris – Find the definition The following information can be used to fill out your STUDY GUIDE… Title: Antigone Author: Sophocles Publication Date: 442 B.C Setting: The city of Thebes – Ancient Greece Genre: Drama Name: Relationship to Personality: Others: Situations: Antigone Daughter of Oedipus, sister of Ismene, niece of Creon Strong, firm in her beliefs Main character, in conflict over the laws of the gods vs laws of man Timid Ismene Daughter of Oedipus, Antigone’s sister Also in conflict over the laws of the gods vs laws of man Creon’s wife, mother of Haimon Obeys her duties as the King’s wife Wife of the King Eurydice Name: Creon Haimon Teiresias Relationship to Personality: Situations: Others: Husband of Firm in his Eurydice, father of belief, Haimon unbending, an absolute ruler Son of Creon and Eurydice, prophet Recently became King of Thebes Level headed Engaged to Antigone Wise He is a very respected blind prophet Congratulations! You have just completed the Antigone WebQuest. You are now ready to begin your reading of the play.