* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice Set 1
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Fei–Ranis model of economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
2000s commodities boom wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
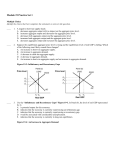
Module 18 Practice Set 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. The aggregate supply curve shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and: A. aggregate output supplied. B. the aggregate money supply. C. the aggregate unemployment rate. D. aggregate employment. E. average worker productivity. ____ 2. The short-run aggregate supply curve is positively sloped because: A. business people suffer from money illusion. B. wages are sticky or don't readily adjust to changes in economic conditions in the short run. C. workers care about nominal wages, not real wages. D. of diminishing returns to labor. E. productivity is positively related to wages. ____ 3. Which of the following will shift the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right? A. An economy-wide decrease in commodity prices. B. An increase in nominal wages. C. A decrease in productivity. D. A decrease in government purchases of goods and services. E. A decrease in personal income taxes. ____ 4. The short-run aggregate supply curve may shift to the right if: A. productivity increases. B. nominal wages increase. C. personal income taxes decrease. D. commodity prices rise. E. government spending increases. Figure 18-1: Aggregate Supply Movements ____ 5. Use the “Aggregate Supply Movements” Figure 18-1. Using the accompanying figure we can safely conclude that: A. an increase in the price level is responsible for pushing the SRAS curve to the right. B. a decrease in the price level is responsible for pushing the SRAS curve to the right. C. there has been an increase in the SRAS supply curve. D. there has been a decrease in the SRAS supply curve. E. an increase in the price level has caused an upward movement along the SRAS curve. ____ 6. A decrease in energy prices will: A. increase aggregate demand. B. decrease the quantity of aggregate output supplied in the short run. C. decrease aggregate demand. D. increase the quantity of aggregate output demanded. E. increase short-run aggregate supply. ____ 7. Which of the following will cause short-run aggregate supply to increase? A. A law that requires employers to provide health insurance for all employees. B. An increase in the aggregate price level. C. A large decrease in the price of oil. D. An increase in the minimum wage. E. A decrease in government transfer payments. ____ 8. Changes in short-run aggregate supply can be caused by changes in: A. wealth. B. commodity prices. C. government spending. D. the price level. E. short-term interest rates. ____ 9. The long-run aggregate supply curve is: A. upward sloping. B. downward sloping. C. horizontal. D. initially upward sloping, but approaches horizontal as GDP increases. E. vertical. ____ 10. According to the long-run aggregate supply curve, when _________, the quantity of aggregate output supplied _________. A. nominal wages rise; falls B. the aggregate price level rises; does not change C. the aggregate price level rises; falls D. the price of commodities falls; rises E. the unemployment rate rises; does not change ____ 11. A nation’s potential output is: A. the level of real GDP that exists when the economy is experiencing only cyclical unemployment. B. the level of real GDP that the economy would produce if there was no inflation. C. the level of real GDP that exists when the actual rate of unemployment is zero. D. the level of real GDP that the economy would produce if all prices, including nominal wages, were sticky. E. the level of real GDP that the economy would produce if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible. ____ 12. A nation’s potential output: A. is the level of output that the economy would produce if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible. B. varies with the price level. C. is dependent on the level of consumer confidence. D. is greater in periods of expansion than in recessions. E. is the level of output the economy would produce if there was no unemployment. ____ 13. The short-run aggregate supply curve is: A. an inverted U-shaped curve. B. vertical. C. horizontal. D. downward sloping. E. upward sloping. ____ 14. The level of output in the long run is known as: A. recognized output. B. structural output. C. potential output. D. balanced budget output. E. inflationary output. ____ 15. Producing a short-run level of aggregate output that exceeds the economy's potential output results in: A. a downward adjustment in nominal wages. B. an upward adjustment in profits per unit of output. C. a downward adjustment in production costs. D. an upward adjustment in nominal wages. E. a downward adjustment in the price level. Module 18 Practice Set 1 Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: SKL: 2. ANS: SKL: 3. ANS: SKL: 4. ANS: SKL: 5. ANS: SKL: 6. ANS: SKL: 7. ANS: SKL: 8. ANS: SKL: 9. ANS: SKL: 10. ANS: SKL: 11. ANS: SKL: 12. ANS: SKL: 13. ANS: SKL: 14. ANS: SKL: 15. ANS: SKL: A PTS: Definitional B PTS: Concept-Based A PTS: Concept-Based A PTS: Concept-Based C PTS: Concept-Based E PTS: Concept-Based C PTS: Critical Thinking B PTS: Fact-Based E PTS: Fact-Based B PTS: Concept-Based E PTS: Definitional A PTS: Definitional E PTS: Fact-Based C PTS: Definitional D PTS: Critical Thinking 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18 1 DIF: E REF: Module 18 1 DIF: E REF: Module 18 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18 1 DIF: E REF: Module 18 1 DIF: E REF: Module 18 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18