* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ID_781_Situational tasks
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Назва наукового напрямку (модуля):
Семестр: 8
Situational tasks (Phthisiology)
Опис:
4 course med
Перелік питань:
1.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
2.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
3.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
4.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
5.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
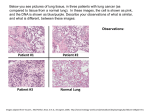
Set the proper diagnosis to the patient K. The upper right lung lobe reduced in volume with
decreasing it’s transparency, but retaining airiness. The expressed interstitial changes are increasing
toward to the root of the lung and to the large, irregular shapes, not intense focal shadows without
clear contours . Right root increased in volume, with a clear polycyclic nonstructural outer loop
The central lung cancer
right-sided pneumonia
infiltrative tuberculosis of upper lobe right lung
focal tuberculosis
disseminated tuberculosis
The patient O. has right-side spontaneous pneumothorax. The outer contour of the lung that
decreased projects on a region of the root of the lungs. What is the approximate degree of decreasing
lungs?
2%
30%
45%
90%
55%
In the patient R., with the bilateral fibro-cavernous tuberculosis revealed: proteinuria (1.32 g / l),
erythrocyte uriya (07-05-10 at n / s), leucocyturia (06-08-12 at n / s). Which are the leading causes of
these changes?
chronic pulmonary heart
amyloidosis of the internal organs
TB intoxication
Tuberculosis of kidney
accompanying pyelonephritis
The patient 22 years old are treated in a tuberculosis hospital with the infiltrative tuberculosis upper
left lobe of the lung. From the age of 11 suffers from diabetes (type2), complicated by diabetic
retinopathy. During the last 3 months he marks the reduction of daily insulin requirements from 40 to
35 units. On the background of anti-tuberculosis therapy, edema of the lower extremities appears in
the patient. Which of the following tests can determine the cause of edema with the highest
probability?
test
Zymnytskoho;
the definition of protein spectrum of blood;
urinalysis;
determine the level of blood creatinine
total blood
The patient is observed in the group of 5.1 strokes keeping with a diagnosis of "dense foci and
fibrosis of the upper right lobe of the lung," entered the hospital with such complaints as fever
(38C) and dry cough. The beginning of disease was subacute,the patient connects symptoms with
hypothermia. Radiological findings the homogeneous notintense eclipse without clear contours in the
projection of C2, 3 case. Objectively-the percussion tone of the upper divisions of the right lung are
blunting, wheezing isn’t listened clearly. What doctor’s tactic is the most appropriate to the patient?
treatment within 2 weeks with antimicrobial drugs of a wide spectrum followed by X-ray control
trial of over 1.5-2 months. TB drugs that do not affect the nonspecific microflora
a course of intensive anti-tuberculosis therapy within 1.5-2 months
Observation
chemoprophylaxis
6.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
7.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
8.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
9.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
10.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
The patient 20 year old has shortness of breath, pain in the right half of the chest, dry cough, fever
to 38C, sweating, weakness. He has been sick about a month and noted a gradual increase of
intoxication, and then pains and shortness of breath appeared. Previously, he considered himself
healthy. Physicaly in the lower right chest was noted shortening of pulmonary tone, diminished
bronhofoniya, voice trembling and breathing. For what disease this complaints and physical data are
tipical?
inflammation
of lower zone of left lung
atelectasis
exudative pleurisy
adhesive pleurisy
selective spontaneous pneumothorax
The patient 23 years old with no complaints . On physical examination pathology was undetected.
Hemogram within normal limits. Radiography and tomography: in the third segment of the right lung
in the basal zone not intense formation measuring 1.5 x 2.5 sm irregular configuration in a retort
shape is defined. A possible diagnosis:
lung cancer
benign tumor
tuberkuloma
retention cysts
infiltrative pulmonary tuberculosis
The patient 53 year old entered the examination on the fibrous changes in a C6 right lung, the
background is determined by the cavity from infiltrated walls. From history we know that about six
months ago after cranial trauma with loss of consciousness shivering emerged , body temperature
increased sharply, dry cough appeared. Body temperature is kept at 38-39,50 C level for a week.
Improvements came after one-time discharge of a large amount of foul-smelling sputum, but full
normalization condition hasn’t occurred. Coughing with purulent sputum and periodic subfebrile are
still hurting the patient. What is the correct diagnosis in this patient?
fibro-cavernous tuberculosis
chronic lung abscess
purulent cyst
chronic pneumonia
cirrhosis segment VI of right lung
The patient 54 years old complains on a dry cough with little phlegm mucus, periodic subfebrile.
Objectively - low power. Auscultation observed weakening of breathing over the left half of the
chest. Radiologically increased pulmonary picture on the left, some narrowing of the left lung field, a
slight shift to the left median shade. What resulted from the research can verify the diagnosis?
analysis of sputum of atypical cells
bronchoscopy
ECG
median tomography
complete blood count
The patient of '30 complains on a shortness of breath, pain in a right side, which increases during
breathing, increased body temperature.He illed acutely before admission to a hospital. There were
fever with chills, cough and then cough with the release of small quantities of rusty sputum . At
objective examination observed blunting percussion sound over the basal divisions of the right lung,
ibid auscultated bronchial breathing. What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
infiltrative tuberculosis
spontaneous pneumothorax
pleural effusion
lobar pneumonia
E.
lung cancer
11.
The patient N. of '34 complains with a slight shortness of breath on exertion, cough with the release
of small quantities of mucous sputum. Suffering from her childhood. The disease runs with periodic
exacerbations, during which symptoms of intoxication, increased cough, increased sputum quantity,
which acquires a purulent character. The general condition is moderate, diffuse cyanosis. Nail
phalanges have the form of drum sticks, nails - watch glasses. lung There is relaxed breathing above
the upper divisions of the right . Radiological deformation of the pulmonary picture is determined in
the upper right of lobe , the background is determined by multiple thin-walled cavity. What is the
most likely diagnosis in this patient?
fibro-cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis
cystic hypoplasia
bullous emphysema
bronchiectasis
progressive degeneration of the lungs
In the pleural aspirate of the patient C. revealed erythrocytes 5-6 in the field of view, neytrofils 80% limfotsyts - 20%,also mezothelian cells. Completely possible – it is:
TB
plevropneumonia
heart insufficiency
malignant process
sarkoidosis
In bioptate of lymphatic node was found a large number of neytrofils. - Completely possible it is:
TB
non specific inflammation
lymphogranulomatosis
sarcoidosis
fungal lesions
Which disease means the following picture: acute onset, fever - 39, weakness, chills, pain in the
chest, cough with little phlegm, wheezing, a high white blood cell count, erythrocyte sedimentation
rate:
pneumonia
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
12.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
13.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
14.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
15.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
16.
A.
abscess
infiltrative tuberculosis
Cancer
sarcoidosis
Patient C.,30 years old, worried about dyspnea, pain in the right side, which amplifies during
breathing, fever, blunting percussion sound over the basal segment, where is also bronchial breath.
Completely possible – it is:
pulmonary infarction
pneumonia
pleuritis
lung cancer
sarkoidosis
Patient of 39 years. Cough with phlegm, subfibrylitet, pain in the chest, food reduced. The
weakening of breathing over the left half of the chest. On the x-ray – strengthening of the
pulmonary picture, restriction of the left lung field, a shift to the left median shade. What method of
examination is the most significant?
sputum of atypical cells
B. *
C.
D.
E.
17.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
18.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
19.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
20.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
21.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
22.
A.
B.
C.
bronchoscopy
Tomography
respiratory function
ultrasound
The patient A.,with destructive tuberculosis, during the development of drug stability MBC to the
most effective chemotherapy, the optimal method of treatment is:
use chemotherapy drugs reserves + isoniazyd
Reserve use of preparations
Early treatment with intravenous introduction of isoniazidi
Early treatment in combination with the intensive treatment - drugs of II line
imposition an artificial pneumothoraxis
In the patient B.,during the chemotherapy appeared: sleep disorders, depression,polyneuritis. This is
due to admission:
ryfampitsine
pуrazinamide
etionamid
streptomycin
izoniazyd
A patient B. with tuberculosis, during the chemotherapy, appeared complaints of reduced vision, the
presence of the nets before the eyes. Ophthalmologist found in violation
of color feeling, idecrease of visual acuity. This is due to admission
izoniazyd
ethambutol
streptomitsyn
pirazynamid
ryfampitsyn
In the patient C. with first discovered infiltrative tuberculosis of upper lobe of right lung in phase of
decayin,was detected by microscopy MBC in sputum. Choose the most rationally combination of
chemotherapy for the first two months of treatment:
izoniazyd + streptomitsyn +ryfampitsyn
izoniazyd +ryfampitsyn + pirazynamid +streptomitsyn
izoniazyd + ryfampitsyn +pirazynamid
izoniazyd+ ryfampitsyn + pirazynamid+ streptomitsyn + ethambutol
izoniazyd+ ryfampitsyn + ethambutol + streptomitsyn
The patient F.,against chemotherapy disappeared appetite , which drug should be excluded from the
treatment plan:
streptomytsyn
protyonamid
rifampicin
izoniazid
kanamycin
The patient D. with tuberculosis of the third category of intensive phase is always necessary to assign
combination of:
izoniazyd +ryfampitsyn
izoniazyd + + ryfampitsyn+ streptomitsyn
izoniazyd + streptomitsyn +pirazynamid
D. *
E.
23.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
24.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
25.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
26.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
27.
A.
izoniazyd+ ryfampitsyn + ethambutol +pirazynamid
izoniazyd +ryfampitsyn + ethambutol
After the main course of chemotherapy about tuberculosis intoxication, from the 3
category children and teenagers are translated:
in 5.4
in 5.2
in 5.5
in 5.1
to 5.3
Patient B.,60 years old, arrived with complaints of weakness, growing dyspnea, subfibrylitet, pain in
the upper chest, slight cough, hemoptysis. The disease began gradually. Leuk. - 9 * 10 ^ 9, ESR 42 mm / hr. Tuberculin test is negative.There is not MBC in the sputum . On the X-ray in a case
of C3- large cavity irregularly rounded with thick, irregular wallthickness, internal contours are like
bay. The most possible diagnosis isabscessed pneumonia
cheesy pneumonia
Cancer, which decays
Acute abscess
Circular infiltrate in the collapse phase
Patient C.,49 years
old,notes grueling
dry cough, chest pain, hemoptysis,subfibrylity, catarrhal phenomena in the
lungs is not listened. ESR - 48 mm / hr., Blood parameters are not changed, in the sputum the
MBT was found only once. Radiological findings: in the case of C3,subpluevral, observed the
formation of circular d.of 3.5 cm with clear but unevencontours, homogeneous structure. Diagnosis:
Tuberkuloma
Circular infiltration
Peripheral cancer
eosinophilic infiltration
Asperhiloma
Patient B.,53 years old,general condition is severe, pronounsed dry cough, chest pain, dyspnea,
hemoptysis . In the lungs -dry scattered wheezing. ESR - 46 mm / hr., Leuk. - 9.8 x 10 ^ 9,Hb - 96 g
/ l, lymphocytes - 14%, Mantou test is negative. Radiological findings: the background of
lymphangoitis ,more in mid-medial and inferior parts of the lungs, determined by multiple round
shape and different size, with clear contours external pockets (a symptom of "small
change").Diagnosis:
disseminated
tuberculosis
Systemic lupus erythematosus
metastatic cancer
exogenous allergic alveolitis
Silicosis
Patient S., 45 years old. During X-ray examination about right-sided lower lobe pneumonia was
found single, low-intensity fire to 1 cm in diameter in the C2 of the left lung . After cure of
pneumonia due to focal tuberculosis of doubtful activity 3 months of chemotherapy was
conducted. Dynamics of the process is not seen. The diagnosis of tuberculosis has been
removed. After 2.5 years patient was examined again. The general condition is
satisfactory, no complaints.On the X-ray in the
left C2 observed rounded homogeneous shadow focus, medium intensity to 1.5 cm in diameter, small
size of banky contours and surrounding tissue intact. The most possible diagnosis isfocal pulmonary tuberculosis (fibroznovohnyschevyy)
B.
C. *
D.
E.
28.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
29.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
30.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
31.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
32.
A.
B.
Tuberkuloma of lung
Peripheral cancer
Benign tumor (hamartohondroma)
Metabolic retykuloz (lipidoz)
Which diseases in patients E. corresponds to the following X-ray picture? Mainly in corticalregions
of the upper segment of the right lung determined by multiple focal shadows different size
and intensity, irregular shape, without clear contours. Around
them locally pulmonary picture moderately excessive and distorted by the reticulated type
focal pulmonary tuberculosis
focal pneumonia
Peripheral cancer
Sarcoidosis of lung
Aspergillosis
A “range” of tuberculin reaction is established in a 18-years old patient, Mantaex test with 2 TU
PPD-L –a papule of 16mm in diameter. He complains of the general weakness, subfebrile
temperature, promoted perspiration. The blood analysis\: L -9,2? 10 /l, ESR-26 mm/hr. No
pathological changes in lungs is been revealed at roentgenological examination. What diagnosis is
most reliable?
Primary
tuberculous complex
Tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymphatic nodes
Nidus lung tuberculosis
Tuberculous intoxication
Infiltrative tuberculosis
A patient 23, has fallen ill acutely. He complains of the headache, dry cough, shortness of breath, the
body temperature rising up to 39,0?C. Objectively\: his general state is difficult, cyanosis of lips,
rales are not heard. The blood analysis\: L -12,6? 10 /l, ESR-16 mm/hr. Multiple small nidal shades
of weak intensity are observed throughout the whole lung length on the inspection roentgenogram.
Mantaex test with 2 TU PPD-L –a papule of 5mm in diameter. What clinical form of lung
tuberculosis is found in a patient?
Nidus
Infiltrative
Disseminated
Miliary tuberculosis
Caseous pneumonia
A patient aged 43. FDT (21.01.2004) of the upper particle of the right lung (infiltrative), Destr +,
MBT+ M- K+ Resist- HIST0, Cat1Cog1(2004), as to clinico-roentgenologicalal data was
established. What phase is answered by abbreviation after effective treatment?
infiltration
sowing
condensation
decay
suction
A patient is 50-ty.He is on treatment in antitubercular dispensary with a diagnosis\: CT (15.02.2000)
of upper particles of both lungs(fibrous-cavernous, phase of infiltration and sowing), Destr+,MBT+
M+ K+ Resist- ResistІІ0 HIST0, Cat4 cog1(2000). Roentgenologically decay cavities (in upper
particles of lungs), multiple fresh nidi in both lungs, fibrous deformation of lung picture has been
established in a patient. What phase of tubercular process is answered by the presence of multiple
fresh nidi?
Phase
of decay
Phase of condensation
C.
D. *
E.
33.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
34.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
35.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
36.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
37.
A.
B.
Phase of calcination
Phase of sowing
Phase of infiltration
A patient, 36th. She was hospitalized into an antitubercular dispensary in connection with infiltrative
changes with destruction in the upper particle of the right lung presence, which have been found on
roentgenogram. Complains on weakness, subfebrile temperature of body, cough with sputum
expectoration. No pathological changes from the respiratory organs have been revealed at physical
examination. MBT+ have been in sputum analysis (bacteriologically). The diagnosis of lung
tuberculosis has been established in a patient. What diagnosis formulation correct is?
FDT (15.11.2004) (nidus), Destr+, MBT- M- K- HIST0, Cat3 cog4(2003).
FDT (15.11.2004) of lungs (disseminated, the phase of infiltration), Destr-, MBT- K- HIST0, Cat3
cog4(2004).
FDT (15.11.2004) of the middle particle of the right lung (infiltrative) Destr+, MBT- K+ HIST0,
Cat3 cog4(2004).
CT (3.12.1999) of the upper particle of the right lung (cirrhotic) Destr-, MBT- K- HIST0, Cat3
cog4(2003)
FDT (15.11.2004) of the upper particle of the right lung (infiltrative) Destr+, MBT+ M- K+ Resist0
ResistІІ0 HIST0, Cat1 cog4(2004).
A patient, 44. She complains of a cough with sputum expectoration, weakness, raising of body
temperature. No changes from respiratory organs have been revealed at physical examination.
Roentgenologically decay cavity with perifocal inflammation of lung tissue and nidi of sowing in
both lungs has been found in S1,2 of the right lung. MBT are revealed in sputum. A diagnosis\:
FDT (15.01.2004) of the upper particle of the right lung (infiltrative), Destr +, MBT+ M+ K+ Resist0
ResistІІ0 HIST0,Cat1cog1 (2004) has been established in a patient. What method of revealing
tuberculosis mycobacterium is the answer to the abbreviation of M+?
bacteriological
biological
culturally
bacterioscopy
method of sowing
A rink-like shadow of 6 cm in diameter with thick walls in the upper part of the left lung, around
which there are fibrous traces and nidal shadows at roentgenological examination in a 53-years old
patient. MBT have been found in sputum. What form of lung tuberculosis is most reliable?
Cirrhotic
Infiltrative
Disseminated
Tuberculoma
Fibrous-cavernous
Each one tuberculosis patient can infect annually:
1-5 persons
10-15 persons
25-30 persons
35-40 persons
45-50 persons
What term it should be expect results of culturally examination with a view to reveal MBT at
using of hard eggs mediums?
2-5 days
10-14 days
C. *
D.
E.
38.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
39.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
40.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
41.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
42.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
2-2.5 months
4-6 hours
20-30 days
H was synthesized in the laboratory of:
S.Waksman
Fox
R.Koch
R.Roentgen
R.Philip
Multiple focal shades of weak and medium intensity in the upper and middle parts of lungs have
been found at roentgenological examination in a 19-years old patient. MBT have been found in
sputum. The blood analysis\: ESR-38 mm/hr. What diagnosis is most reliable?
Lung infiltrative tuberculosis
Nidus lung tuberculosis
Disseminated lung tuberculosis
Caseous pneumonia
Fibrous-cavernous lung tuberculosis
In the exposure of what changes in biopsy material is based histological confirmation of tubercular
character of inflammation?
Pirogov-Langerhans cells , caseous necrosis.
Cells of foreign bodies, fibroblasts.
A big amount of neutrophiles, colicvation necrosis.
Proliferation of lymphocytes.
Proliferation of poorly differentiated cells.
Patient 37-ty, complains of the shortness of breath at walking, pain is in the area of heart. He is ill
tuberculosis during 15 years. An intensive shade in the upper part of the left lung on inspection
roentgenogram. The left root dislocation upwards, a shade of mediastinum is dislocated to the left.
MBT have been found in sputum analysis. What clinical form of tuberculosis for a patient is marked?
Fibrous-cavernous
Infiltrative
Caseous pneumonia
Cirrhotic
Tuberculoma
Patient 33-th years. He complains of the body temperature rising up to 37,2?C, weakness, promoted
perspiration, cough with sputum expectoration. Roentgenologically infiltrative shade with decay
cavity in S1,2,3 of the right lung and nidi of sowing in S6 of healthy lung. Tuberculosis
mycobacterium was found in sputum. The clinical diagnosis of tuberculosis was established in a
patient. What diagnosis should be answered classification fully?
FDT (12.01.2005) of the upper part of the right lung (infiltrative) Destr+, MBT+ M+ K+ HIST0,
Cat1cog1(2005).
FDT (12.01.2005) of the upper part of the right lung (infiltrative) Destr+, MBT+ M+ K+ Resist0
ResistІІ0 HIST0, Cat1cog1(2005).
FDT (12.01.2005) (infiltrative), MBT+ M+ K+ HIST0, Cat1Cog1 (2005).
FDT (12.01.2005) of the upper part of the right lung (infiltrative) MBT+ M+ K+ Resist+ ResistІІ0
HIST0, Cat1cog1 (2005).
FDT (12.01.2005) of the upper part of the right lung (infiltrative) Destr+,Resist0 ResistІІ0 HIST0.
43.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
44.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
45.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
46.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
47.
A.
Patient 34th years. She is on treatment into an antitubercular dispensary. FDT (12.11.2004) of lungs
(disseminated, the phase of infiltration and decay) Destr+, MBT+ M+ K+ Resist- ResistІІ0, Cat1
cog4(2004) has been established in a patient at hospitalization.. Roentgenologically multiple nidi in
all pulmonary fields with decay cavities presence have been revealed in S1-2 of the left lung. MBT+
have been in sputum analysis. After the performed course of treatment during 4th months nidi in
both lungs have resolved partly, bacteria excretion and sizes of caverns have decreased. How to
estimate efficiency of treatment?
Cessation of bacterial excretion
Recovery
Prolongation treatment
Ineffective treatment
Completed treatment
Patient age 41 years. He is sick by fibrous cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis of the upper part of
the right lung during 8 years. Mycobacteriums tuberculosis+. He feels good during last 2 year.
Radiographic data\: the upper part of the right lung available thick cavern with fibrosis and perifocal
inflammation. The upper part is narrow due fibrosis. Both lungs have focuses of semination. Shadow
of mediastinum shifted right. What radiographic data are typical for fibrous cavernous pulmonary
tuberculosis of the lungs?
Caverns presence, well-defined fibrosis, focuses of semination.
Caverns presence, perifocal inflammation.
Perifocal inflammation, bronchogenic dissemination.
Organs on mediastinum are shifted in the side of lesion.
Intense dark patch, narrowed lung field.
Patient aged 26. He complains of a weakness, subfebrile temperature, insignificant cough with
sputum expectoration. FDT (16.12.2004) of lungs (disseminated, the phase of infiltration), Destr +,
MBT+ M- K+ Resist- ResistІІ0 HIST0, Cog4 (2004), as to clinico-roentgenologicalal and laboratory
data was established. What category does it follow to deliver a patient to?
Cat 5
Cat 4
Cat 1
Cat 2
Cat 3
Patient of 35 years. He was hospitalized into an antitubercular dispensary in connection with
changes which have been found in fluorography\: a shade about 1 cm in diameter of small intensity
with vague contours has been revealed in S1 of the right lung. On tomogrami destruction is
determined in the center of shade. MBT+ have been in sputum analysis (bacteriologically). A
diagnosis of nidus lung tuberculosis has been established in a patient. What phases of nidus lung
tuberculosis are representing changes which have been revealed on roentgenogram?
Infiltration and sowing
Infiltration and decay
Suction and scarring
Decay and sowing
Condensation and suction
Patient of 32, was on treatment in an antitubercular dispensary with a diagnosis\: FDT (16.06.2003)
S1-2 of the left lung(infiltrative), Destr +, MBT+ M+ K+ Resist- ResistІІ0 HIST0, VNII
Cat1cog2(2003). During 6 months a course of antimycobacterial therapy was performed in hospital.
Then next 2 months he was treated ambulatory. At the present time excretion of bacteria has ceased
in a patient, a cavern has scarred. How to define efficiency of treatment of this patient?
completed treatment
B. *
C.
D.
E.
48.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
49.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
50.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
51.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
52.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
53.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
54.
ineffective treatment
Interrupted treatment
Left
recovery
Patient of 31 years. At prophylactic examination nidal shade of small intensity with vague contours
has been found in lateral zone of the under clavicle area of the right lung. What segment of lung
should be noted in a clinical diagnosis?
ІІІ
X
ІV
VI
II
Single focal of small intensity with vague contours have been revealed in apexes segments of both
lungs at prophylactic fluorographic examination in a 19-years old patient. What form of tuberculosis
such changes are characteristic for?
Infiltrative tuberculosis
Tuberculoma
Nidus lung tuberculosis
Caseous pneumonia
Disseminated lung tuberculosis
The vaccine BCG was produced by:
R.Koch
S.Waksman
A.Calmette and Guerin
F. Seibert
M.Linnykova
The all number of tuberculosis patients in the world is:
3-5 mln
10-15 mln
20-30 mln
40-45 mln
50-60 mln
The first antituberculosis dispansery world was founded by
R.Koch
R.Phylip
A.Calmette and Guerin
Abre
F.G.Yanovsky
Treatment of what state is most perspective and important from the epidemiological point of view?
At first diagnosed tuberculosis without destruction.
At first diagnosed tuberculosis with destruction.
Relapse.
Chronic tuberculosis.
Primary tuberculosis.
What changes in the number of leucocytes at the uncomplicated tuberculosis are the most typical?
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
55.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
56.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
57.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
58.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
59.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
60.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
61.
A.
B.
Expressed leucocytosis with a considerable bacillarnuclear shift, leukemia reaction
Changes are not characteristic
Moderate leucocytosis with an unsignificant bacillarnuclear shift
Leucopenia
Both leucopenia and leucocytosis is possible
What changes of ESR at the uncomplicated tuberculosis are most characteristic?
Accelerated up more than 60 mm on hour
Changes are absent
Reduction
Accelerated up to 30 mm on hour
Accelerated only in woman
What changes of the urine at a lung tuberculosis which courses with expressed phenomena of
intoxication are most characteristic?
Moderate proteinuria, moderate leucocyturia, total macrohaematuria
Moderate leucocyturia, single erythrocytes
Significant proteinuria without changes in the number of leucocytes, initial macrohaematuria
Pyuria, cylindruria, microhaematuria
Total macrohaematuria with a pain syndrome
What color is used for the revealing MBT?
According to Gram
According to Tsil-Nilsen
According to Romanovskij-Gimza
By fuxyne
By methylene-blue
What complication does specific belong to?
Haemophthisis
Chronic lung heart
Atelectasis
Larynx tuberculosis
Amyloidosis
What data clinical diagnosis formulation begin from?
The process phase
Clinical form
Bacterial excretion
Localization of process
Type of tuberculous process
What definition does atypical mycobacterium characterize most correct?
There are unpathogenic mycobacteria for a human being
They cause tuberculosis with atypical course
They cause an illness, similar to tuberculosis, for persons with lowered immunity
There are pathogenes of leprae
There are changed mycobacteria under act of chemotherapy
What definition of role of clinical blood examination in tuberculosis patients is most correct?
It allows to define an etiologic diagnosis
It has no importance
C. *
D.
E.
62.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
63.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
64.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
65.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
66.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
67.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
68.
A. *
It allows to evaluate expressiveness of inflammatory and intoxication changes in an organism
It form the basis of differential diagnostics
It form the basis of working capacity examination
What form of tuberculosis does primary belong to?
Nodus
Disseminated
Tuberculosis of the unstated localization.
Caseous pneumonia
Infiltrative
What form of tuberculosis is referring to primary?
Disseminated
Nidus
Infiltrative
Tuberculoma
Tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymphatic nodes
What formulation of clinical diagnosis of lung tuberculosis is not correct?
FDT (16.06.2003) of the upper parts of both lungs (disseminated, the phase of infiltration), Destr+,
MBT+ M+ K+ Resist0, HIST0, Cat1 cog2(2003).
CT (12.02.2000) of the upper part of the right lung (fibrous-cavernous), Destr+, MBT+ K+ M+
Resist+(8,K), HIST0, haemophthisis, CLH, HI ІІA degree, Cat4 cog1(2000).
TR (20.11.2003) of the lower part of the right lung (tuberculoma), Destr+, MBT- M- K-, HIST0, RI
1st degree, Cat2cog4(2003). Diabetes, І type, severe form.
FDT (20.09.2003) (nidus, the phase of infiltration), MBT- M- K0, HIST0, Cat3 cog3(2003)
State after the lobectomy of the upper part of the right lung (20.06.2003) on the occasion of
tuberculoma of the upper part of the right lung in the decay phase, MBT(+).
What information must not contain the classification of any illness according to the IKD-10?
Clinical form of disease.
Localisation of affection.
Prognosis.
Accompanimental diseases.
Complication.
What is the definition of primary tuberculosis?
At first diagnosed tuberculosis.
Initial signs of tuberculosis.
Nondestructive tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis which arose up just after infection.
Tuberculosis with an affection of only one organ or system.
What is the definition of secondary tuberculosis?
Relapse of tuberculosis.
Destructive tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis which arose up long after an infection.
Tuberculosis with the unfolded clinical picture.
Generalized tuberculosis.
What is the most probable distance at the infectioning by MBT by the aerogenic way?
To 1,5 m
B.
C.
D.
E.
69.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
70.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
71.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
72.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
73.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
74.
To 3,5 m
To 4,5 m
To 6 m
To 10 m
The “range” of tuberculin reaction was discovered in girl B. aged 9. Clinico-roentgenological and
laboratory examinations revealed no pathological changes. Your tactics regarding with the girl.{
To repeat Mantoux test with 2 TU in a year
To hospitalize to an antituberculous hospital
To perform chemoprophylaxis with isoniazidum and vitamin B6 within 3 months
The observation in an antituberculous dispensary for 1-2 years
To consider the girl healthy and not to take any prophylactic measures
The 11-year-old patient M. is diagnosed with tuberculin “turn”, Mantoux test with 2 TO – 16 mm
infiltrate. Complaints for general asthenia, increased sweating. Blood analysis\: leuk. – 9,2x109/l,
ESR – 26 mm/hour. Roentgenogram examination did not reveal pathologic alterations in the lungs.
What diagnosis is the most probable one?{
Primary tuberculous complex
Tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymphatic nodes
Nidus lung tuberculosis
Tuberculosis intoxication
Infiltrative lung tuberculosis
A 3-years old child reaction to Mantoux test with 2 TU – 7 mm infiltration, at the age of 4 – 3 mm.
Postvaccinal seam of 4 mm. Define the character of tuberculin reaction.{
Infectious allergy
A “range” of tuberculin testing
The child is ill with tuberculosis
Postvaccinal allergy
Doubtful Mantoux reaction
A 22-year-old patient fell ill acutely. Complaints for headache, dry cough, dyspnea, temperature rise
up to 39,0? C. Objectively\: general condition is grave, lips cyanosis, rales are not heard. Blood
analysis\: leuk. – 12x109/l, ESR – 16 mm/hour. Roengenogram\: the whole length of both lungs is
full with multiple, small focal shadows of low intensity. Mantoux test – 5mm infiltrate. What clinical
form of lungs tuberculosis does this patient have?{
Nidus
Infiltrative
Disseminated
Miliary tuberculosis
Caseous pneumonia
A 5 years old boy K., had a “range” of tuberculin reaction. What examinations should be done?{
General clinical examination, inspection roentgenogram of the thoracic cage organs, general blood
and urine test
Koch’s testing, general blood and urine test
Fluorography, general blood and urine test
Tomography, smear examination from pharynx for MBT
Fibrobronchoscopy, examination of contents from bronchi for MBT
A patient 34, complains of the cough with sputum, weakness, raising of body temperature to
37,52?C, during 3 weeks, appetite loss, indisposition. No changes have been revealed at objective
examination. What should be found out in a patient in the life anamnesis?{
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
75.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
76.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
77.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
78.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
79.
A.
B.
C.
Smoking
Following the routine of work and rest
Present the contact with tuberculosis patient
Sport occupation
Present the emotional labiality
A patient 36, appeal to the doctor with complains of the weakness, cough with sputum, raising of
body temperature to 37,2?C. Lung infiltrative tuberculosis was revealed in antitubercular dispensary
after finish examination. It is known from anamnesis, that a patient was ill with arthritis, infectious
hepatitis, tyreotoxicosis. Diabetes two years ago and glomerulonephrytis. What somatic disease is the
risk factor of tuberculosis occurring?{
Glomerulonephritis
Diabetes
Thyreotoxicosis
Infectious hepatitis
Gaimoritis
A patient 34, complains of the raising of body temperature to 37,5?C, appetite loss, indisposition,
weakness, cough with sputum excretion up to 50 ml per day of slime character. The state of patient
has worsened gradually, during a month. What disease in a patient can one suspect?{
Pneumonia
Lung tuberculosis
Lung abscess
Bronchial asthma
Chronic bronchitis
A patient 31, complains of the weakness, insignificant cough with sputum. An inhomogeneous
limited darkening sized more than 5cm. in the 81, 2 of the right lung has been revealed at
roentgenologic examination. Lung infiltrative tuberculosis of the upper part of the right lung has been
suspected. What most reliable auscultative data characterize will be observed above the lesion lungs
section of mentioned localization?{
Moist rales
Dry disseminated rales
Vesicular breathing
Amphoric respiration
Absence of breathing
A patient 43, is directed to antitubercular dispensary for finish examination and lung tuberculosis
diagnosis confirmation. A patient complains of the raising of body temperature to 37,5?C, weakness,
disposition to perspire, cough with sputum. What sputum characterized lung tuberculosis?{
Purulent with a stinking odor
Slime
Frothy
Slime sputum of canary color
Rusty
A patient 44, complains of the weakness, periodical raising of body temperature to 37,7?C, cough
with sputum expectoration more than 3 weeks. There are tuberculosis patients in a family. In what
thorax areas can one reveal auscultative changes at objective examination of the patient most
frequently?
In
the lower{part of lungs
In the lower third of lungs
In the area under scapular
D. *
E.
80.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
81.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
82.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
83.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
84.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
In the area under clavicle
In the axillary’s region
A patient 53, is ill with tuberculosis during 3 month, complains of the cough with sputum excretion,
raising of body temperature, weakness, shortness of breathe at physical tension. Amphoric respiration
is heard above the right lung, in the area under clavicle at auscultation. What changes in lungs do
such auscultative phenomenon at tuberculosis condition?{
Exudates
A big cavern
Lung atelectasis
A small cavern
Cirrhotic changes
A patient of 43 is on treatment in tuberculosis dispensary with a diagnosis\: FDT (15.01.2004) of
right lung’s upper part (focal) Destr-, Mbt - m- k- ,gist o, Cat 3 Cog1(2004). Roentgenological\:
in S1,2 of right lung darkening was determined 1 centimeter in the diameter of weak intensity. What
blood test is typical for patients with a tuberculosis? {
RBC.- 4,6х1012, НЬ - 134 г/л, WBC - 28х109, E-17%, п- 3%, с -60%, Li-15%, Mo-5%, ESR - ЗО
mm/hr.
RBC.- 3,6х10, НЬ - 128 г/л, WBC - 15х109, п- 7%, с -53%, Li - 30%. Mo - 10%, ESR - 70 mm/hr.
RBC.- 4,6х1012, НЬ - 136 г/л, WBC - 2,5х109, п- 1%, с -60%, Li - 29%, Mo - 10%, ESR - 40
mm/hr.
RBC.- 4,2х1012, НЬ - 130 г/л, WBC - 9,5х109, п- 5%, с -67%, Li - 20%, Mo - 5%, ESR - 20
mm/hr.
RBC.- 3,2х1012, НЬ - 120 г/л, WBC - 4,5х109, е- 20, п- 1% , с -49% , Li - 25%, Mo -5%, Blood
sedimentation test-2 mm/hr
A patient 5-year-old boy with primary tubercular complex, above the lower department of thorax in
right side auscultate pleural friction rub. What do pathological changes we think about?{
Spontaneous pneumothorax.
Dry pleurisy.
Ecsudatical pleurisy.
Pleuropneumonia.
Pleural empyema.
Patient 37, has been delivered on treatment into an antitubercular dispensary on the occasion of
firstly diagnosed infiltrative tuberculosis of the upper part of the right lung. The intoxication
syndrome is expressed. Which of cited complaints do intoxication syndrome at tuberculosis refer to?{
Haemophthisis, weakness, chest pain, cold, shortness of breathing
Cough, sputum excretion, hectic temperature, chest pain
Nausea, vomit, cough, pain in joints, indisposition
Subfebrile temperature, weakness, appetite and weight loss, disposition to perspire
Cough, sputum excretion, broken-sleep, headache, hoarseness of voice
Patient 31, has been delivered on treatment into an antitubercular dispensary on the occasion of
relapse of tuberculosis process. The presence of bronchi-lung-pleura syndrome has been determined
in a patient at examination. What are characterized symptoms for this syndrome?{
The raising of body temperature, weakness, appetite loss, weight loss, disposition to perspire
Cough, weakness, broken-sleep, headache, hoarseness of voice
Cough, sputum presence, chest pain, haemophthisis, shortness of breathe
Cough, weakness, hoarseness of voice, dry rales, shortening of percussion note
Shortness of breathe, broken-sleep, moist rales, increasing voice tremor, indisposition
85.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
86.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
87.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
88.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
89.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
90.
Patient 39, is on treatment into an antitubercular dispensary on the occasion of firstly diagnosed
infiltrative tuberculosis of the upper part of the left lung in decay phase (lobit).No changes have been
revealed at physical examination. How should patient breath right to improve informing of the
auscultative method?{
To breathe frequently
To breathe deeply
To cough strongly
To cough slightly and to do a deep breathe
To breathe by opened mouth
Patient R., 53. Roentgenologic examination showed in the upper segment of the left lung a ringlike
shadow with a diameter of 5cm with thick walls and fibrous heaviness and focusness. Sputum
contains MBT. What clinical picture is the most probable one?{
Lung cirrhotic tuberculosis
Infiltrative lung tuberculosis
Disseminated lung tuberculosis
Lung tuberculoma
Lung fibrous-cavernous tuberculosis
Patient L., 24. Roentgenologic examination showed multiple focal shadows in upper and medial
lungs segments of low and medium intensity. Sputum contains MBT. Blood analysis\: ESR – 38
mm/hour. What diagnosis is the most probable one?{
Infiltrative lung tuberculosis
Nidus lung tuberculosis
Disseminated lung tuberculosis
Caseous pneumonia
Lung fibrous-cavernous tuberculosis
Patient of 21 went to tuberculosis dispensary with complaints about a weakness, indisposition, cough
with sputum. On a survey rontgenography were discovered infiltrative changes on the upper part of
right lung with the presence of cavity of disintegration. Using bacterioscopic method MBT were
found in sputum.What amount of MBT should be found in 1 ml of sputum (at a revision 300
eyeshots)?{
500.
5000.
1000.
100.
100000.
Patient of 24 is on treatment in tuberculosis dispensary with a diagnosis\: FDT (2.02.2004)
of right lung’s upper part (infiltrative, phase of disintegration and semination), Destr- mbt+ m- k+
Resist+ (N,R) resist O, GIST O, Cat4 Cog1(2004). The patient was appointed proper treatment\: H,
R, S, Z. In two months during conducting roentgenological control positive dynamics was not seen.
As a result of determination of MBT sensitiveness to untytuberculosis preparations was got in 2
months after patient’s receipt .What is the principal reason of treatment’s ineffectiveness?{
Existence of MBT’s resistance to untymycobacterial medications.
Smoking.
Periodic using of alcohol.
Protracted reception of chemo medication.
In the absence of fifth preparation.
Patient of 28 years on a roentgenological inspection found out in the right lung under a collar-bone
dark patch in a diameter to 1sm, small intensity with unclear contours. What type of pathological
shade is certain in the woman?{
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
91.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
92.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
93.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
94.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
focal
Infiltrative .
focal-infiltrative .
Annular.
Linear.
Patient of 38 at a reception to tuberculosis dispensary complains about a weakness, promoted
sweating, cough with sputum of mucus character. Roentgenological\: in S1,2 of left lung darkening
of weak intensity with unclear contours was found. What kind of research should be done to confirm
diagnosis tuberculosis?{
General blood test.
Biochemical blood test.
Sputum’s test on MBT.
Immunological research of blood.
Sputum’s test on the second flora.
Patient of 31 is on treatment in tuberculosis dispensary with a diagnosis\: FDT (23.11.1997) of right
lung’s upper part (Fibrosis - cavernous, phase of infiltration and semination), Mbt+ ,m- ,K+ resist+
(R,E) resist O, GIST O, Cat4 Cog4(2004).What kind of research should be primarily done to a
patient?{
Histological
Luminescent microscopy.
Determine sensitiveness of MBT to chemo medication of the II row.
Immunological research.
Biological research.
Patient of 37 went to the stationary section of tuberculosis dispensary with complaints about cough
with sputum, weakness, temperature - 38,0°C, severe headache, nausea and vomit that does not bring
a facilitation. A disease has begun gradually. Patient went to the therapeutist and then X-ray
examination was made. As a result of examination small (1-2 mm in diameter) multiply nonintencive
shades with unclear contours along lungs were determined. Patient was diagnosed\: a FDT
(3.12.2003) of lungs (miliary in a phase of infiltration and disintegration), Destr+, Mbt+m-k+
rezist-rezistpo, GIST O Kat1kog4(2003). What kind of research will reliably confirm possibility
tubercular meningitis’ development?{
Bacterial analysis of sputum.
Immunologic research.
Encephalography.
Bacterioscopy of spinal liquid.
Biochemical analysis of composition of spinal liquid.
Patient of 41 grumbles about weakness, bad appetite and sleep, decline of body’s mass.
Roentgenlogical\: in S1 infiltrative darkening was found out in a right lung. General analysis of
blood\: Er.- 4,8х1012, Нb - 146 г/л, L - 8,5х109, E-3%, P-7%, s-66%, l-20%,m-4%, ESR - 22
mm/hr. What research should be done to a patient with the purpose to exposure MBT?{
Taking of washing liquid of bronchial tubes.
Tomography.
To take a Manta’s sample from 2 PPD-L.
To explore sputum.
To make immunological research.
95.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
96.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
97.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
98.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
99.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
Patient of 44 complains about weakness, bad appetite, decline of body’s mass, subfebrile temperature
(37,1°-37,4°C), pain in left side. During roentgenological examination in S 1-2 of a left lung limited
microfocal disseminations has been determinated, to the bottom from the IV rib exudation. At
bacterioscopic research of liquid MBT were not found.What research is optimum for confirmation of
etiology of found changes for this patient?{
Examination of sputum.
Making bronchoscopy.
Immunologic research.
Biopsy of pleura.
Cytological research of exudation.
Patient of 45 undergo a course of anmycobacterial medication treatment concerning FDT
(12.12.1998) of left lung’s upper part (fibrocavernous, phase of infiltration and
semination), Destr-+ Mbt+ M+ K+ reist 0, GISTO, Cat4 Cog4(2004). What research above
all should be done to a patient to set an optimum combination of chemo medication?{
Determine a type of MBT.
Determine presence of the second flora.
Determine sensitiveness of MBT to anmycobacterial medication.
To define massiveness of bacterioexcretion
To define virulence of MBT.
Patient of 46 underwent a course of medical treatment during 1 week. Patient was diagnosed\: ’
FDT (15.01.2004) (desemination, phase to infiltration and disintegration), Destr+,
MBT+M+KOrezisto GISTO Cat1 Cog1(2004). MBT has been discovered by bacteriological
method in 3 analyses. What is the most reliable reason that the record of K O was made in a
diagnosis?{ analysis was not conducted.
Kulturalniy
Negative result of sputum’s sowing was got.
Insufficient period for MBT’s growth
Absence of MBT in sputum.
Incorrect results of bacterioscopy.
Patient of 48 is on treatment in tuberculosis dispensary concerning FDT (13.12.2003) of upper part of
the right lung (infiltrative, phase of disintegration and semination ), Destr+ Mbt+ m+ k+
resist- , GIST O, Сat2 Сog4((2003). He does not use alcohol and narcotics and does not smoke. In
spite of adequate chemotherapy (N,R,S,E) patient still has a progressive tuberculosis. On the control
radiography the increasing of cavity disintegration and appearance of semination fires have been
determined on a left lung. What kind of research should be done to a patient to determine possible
reason of treatment’s ineffectiveness?{
General blood test.
Biochemical blood examination.
Koch’s test.
Immunological research.
Functions’ research of the external breathing.
Sick women 34 years old. She grumbles about a cough with sputum, pain in the right part of thorax,
weakness, increase body's temperature up to 37,8°C. On the survey sciagram of the right lung it is
found out an area of unhomogeneous structure without clear contours. It was established the
diagnosis\: tuberculosis What disease does have alike roentgenological signs?{
Bronchial asthma.
Pneumonia.
Cyst.
Bronchitis.
E.
100.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
101.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
102.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
103.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
104.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
105.
A.
B.
lungs oedema.
Sick men 36 years old. He is directed to the T.B. prophylactic center with a diagnos of tuberculosis.
It was made more inspection and as a result were revealed destructive changes in the overhead
particle of right lung. What roentgenological method of research was used for more inspection?{
Lateral sciagraphy.
Bronchography.
Radioxerography.
Tomography.
Fluorography.
Sick woman 24 years old is directed to phthisiatrician, concerning changes, that were discovered on
fluorogram (prophylactic inspection). We can see changes not very good, because they are hidden
behind the collar-bone. What roentgenological research we need to use, to find out these changes?{
entgenography.
Bronchography.
Rentgenoscopy.
Lateral sciagraphy.
Sciagraphy with the maximal taking of collar-bone.
Sick woman 40-ty years acted in to the T.B. prophylactic center complaining on a cough,
weakness, decline of mass , cough with sputum. A differential diagnostic is conducted between
infiltrative tuberculosis of upper particle of left lung and a cancer of lungs .What roentgenological
method of research is optimum to confirm the diagnosis?{
Radioxerography.
Bronchography.
Computerized tomography.
Pleurography.
Rentgenoscopy.
The patient of 47 years . He is on treatment in T.B. prophylactic center concerning the relapse of
tuberculosis of the left lung (infiltrative tuberculosis). In patient's phlegm appear MBT but on a
survey sciagram destructive changes are not determined. What roentgenological method of research
should we use to find the source which excretes bacterias?{
Tomography.
Bronchography.
Spot-film sciagraphy.
Rentgenoscopy.
Lateral sciagraphy
The Patient 38 years old. He is ill with cirrhotic tuberculosis of overhead particle of the right lung
during 10 years. The patient is prepared to the operation. It is needed to define mobile of lower edge
of lungs. What method of roentgenological research is used in this case?{
Tomography.
Bronchography.
Sciagraphy.
Rentgenoscopy.
NMR.
The patient is 39 years. At a prophylactic inspection in infraclavicular region of right lung (lateral
part of it) found out the area focal shade of small intensity. What segment of lung does the area
belongs
VIII. to?{
VI.
C.
D.
E. *
106.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
107.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
108.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
109.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
110.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
IV.
V
VII.
The patient of 25 years acted into the T.B. prophylactic center complaining about a weakness,
decline of appetite, cough with sputum. A survey sciagram was made, on which in the part of the left
lung an annular shade is determined. Such character of shade is inherent for\:{
Hearth.
Infiltration.
Fibrosis.
Disintegration of pulmonary tissue.
Exudat accumulation.
The patient of 38 years grumbles about the shortness of breath, weight in a right side increasing of
body's temperature up to 39°C. On a survey sciagram found out the homogeneous intensive dark
patch from the level of the IV rib to the diaphragm with an oblique high bound. Such
roentgenological changes are inherent for\: {
Pneumonia.
Cancer.
Eosinophylic infiltration.
Exudatic pleurisy.
Dry pleurisy.
The patient of 51 years old, during 9 months was treated because of the infiltrative tuberculosis of the
upper part of the right lung, decay phase, MBT (+). At X-ray examination\: the upper part of the right
lung became smaller in volume, under the clavicle there’s a decay cavity 3 cm in diameter, the
trachea is moved to the right, MBT (-). Define the form of tuberculosis.{
Cyrrhotic
Caseuos pneumonia
Fibrous-cavernous
Infiltrative
Nidus
A 15 years old child lives with her parents and grandfather. Grandfather suffers from tuberculosis of
the lungs (active form). The teenager is in constant contact with grandfather. The teenager should be
revaccinated. What dose of BCG SSI should be given to patient in this case?{
0,5 ml.
0,1 ml
0,25 ml
0,025 ml
0,05 ml.
A 24 year old patient is diagnosed with tuberculosive meningitis. In the lungs lymphatic knots are
observed. MBT is absent in cerebrospinal fluid. Which treatment should be prescribed to patient in
acute phase?{
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Ethambutol + Streptomycin
111.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
112.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
113.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
114.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
115.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
116.
A.
B.
A 26 year old patient suffers from diabetes of moderate degree. He became acutely ill. Temperature
increased up to 40'С, complains of cough with small amount of mucous sputum, weakness,
diaphoresis. On x-ray\\: observed darkening of the upper part of the right lung with small area of
brighter spots and presence of low intensity shadows at the bottom of both lungs. What treatment of
should be prescribed in acute phase?{
Isoniazid + Rifampicin+ Pyrazinamide+ Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin+ Ethambutol+ Pyrazinamide + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Streptomycin+ Ofloxacin + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin+ Ethambutol+ Pyrazinamide + Ofloxacin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Ethambutol
A 27 years old patient has been diagnosed for the first time with caseous pneumonia of the right lung.
MBT positive numerous times in sputum, sensitivity to all antituberculosis drugs is preserved. What
treatment should be prescribed to patient in acute phase?{
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Ethambutol + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol+ Ofloxacin
A 29 year old patient has been admitted with complaints of weakness, increased temperature up to 38
С, productive cough, decreased body weight. On x-ray\\: in the upper part of the right lung infiltrative
changes are noted with destructive changes. MBT present in sputum. What treatment should be
prescribed in acute phase?{
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Streptomycin + Pyrazinamide
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Kanamycin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Ethambutol + Ethionamide
A 3 months old child received BCG SSI vaccine. On the third day on the injection spot appeared
infiltration of 8mm in diameter, after a pustule appeared which bursted and formed a 5mm ulcer.
What should be the action of pediatrician?{
Apply Isoniazid powder to the wound.
Apply Streptomycin to the wound.
Patient should be under observation of pediatrician.
Laboratory analysis.
X-ray.
A 4 months old child has been vaccinated with BCG vaccine at birth. In left axilla increased
lymphatic node by 2cm,elastic, painless, no changes in skin. General state of the child is good,
temperature 36.5oC. General blood analysis is within norm. The child has{
Unspecific lymphadenitis;
Tuberculosis of the peripheral lymphatic node;
Generalized infective tuberculosis;
Normal reaction to vaccination;
Post-vaccination lymphadenitis (complication).
A 4 months old child has been vaccinated with BCG vaccine at birth. In left axilla increased
lymphatic node by 2cm,elastic, painless, no changes in skin. General state of the child is good,
temperature 36.5oC. General blood analysis is within norm. What treatment should be prescribed to
patient?{ wide spectrum antibiotics;
Prescribe
Treatment with Isoniazid for 3 months;
C. *
D.
E.
117.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
118.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
119.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
120.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
121.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
Treatment with Isoniazid and Rifampicin for 3-6 months, compress with Rifampicin and Dimexide in
distilled water;
Desensibilizing therapy;
No treatment is necessary only observation.
A 4 year old child has been vaccinated with BCG vaccine five days after birth. Mantoux test 2 TO
PPD has been negative for the past 3 years. Post vaccination scar 3 mm. What should be the action of
pediatrician?{
Continue with yearly Mantoux tests.
Repeat BCG SSI vaccination.
Yearly conduct chemoprophylaxis.
Repeat BCG SSI vaccination with a greater dose.
Conduct x-ray examination.
A 31 year old patient has been admitted to tuberculosis hospital with complaints of periodic increased
body temperature up to 37,0'С, weakness. After x-ray and laboratory analysis the patient was
diagnosed with tuberculosis(15.02.2005)of the upper right lung(acute infiltrative stage), Destr.-,
MBT- М-К- Resist-,Histo 0, Cat3 Cog 4 (2005). What should be the treatment plan for the patient?{
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Kanamycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Streptomycin + Pyrazinamide
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Streptomycin + Pyrazinamide + Ethionamidum
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Ofloxacini
A 38 years old patient has been suffering from fibro-cavernous lung tuberculosis for the past 6 years.
Treatment with ethiotropic drugs is ineffective. Surgical treatment is contraindicated. He complains
of high fever, weakness, productive cough, bloody sputum. MBT is present in sputum and resistant to
streptomycin. What treatment should be prescribed to patient?{
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Kanamycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethionamide
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol + Ofloxacin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Ethambutol + Kanamycin
A 5 month old child hasn’t been vaccinated at birth due to birth trauma. Presently the child is healthy.
What should be done?{
Vaccinate the infant at 6 months.
Vaccinate the infant at 12 months.
After test Montoux
Vaccination is contraindicated
Vaccinate the child when the weight is 15kg.
A 43 years old patient during childhood has been exposed to a tuberculosis patient. During a routine
x-ray in I segment of the right lung a 2cm moderate intensive darkening was noted with defined
margins. In pre pulmonary tissue single low intensity shadows were noted. Patient has no complaints.
Objectively no pathology. Blood analysis within norm, MBT absent. Given diagnosis\\: tuberculoma
of the I segment of right lung, MBT - . What treatment should be prescribed in acute phase?{
Dissolving drugs
Corticosteroids, immune-correctors
Chest ultrasound
Vitamin A
Tissue Electrophoresis
122.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
123.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
124.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
125.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
126.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
127.
A.
B.
A 45 year old patient has been diagnosed with fibro-cavernous lung tuberculosis. MBT present is
sputum, which is resistant to Isoniazid and Streptomycin. What treatment should be prescribed in
acute phase?{
Isoniazid + Rifampicin+ Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Ftivazide+ Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ofloxacin
Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol + Kanamycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin +Pyrazinamide +Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin +Ethambutol+ Ofloxacin
A 46 years old patient has been suffering from cirrhotic tuberculosis of the left lung. Periodically
bacterial discharge is observed. What treatment should be prescribed to patient in acute phase?{
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol + Streptomycin
A 51 year old patient is an inpatient. Clinical diagnosis\: tuberculosis(12.01.2005)of the upper part of
right lung (caseous pneumonia) Destr.+, MBT+ М+К+ Resist(Н)-,Histo 0, Cat 1 Cog 1 (2005) In
order to obtain results of sensitivity to MBT patient has been under treatment with \\: Isoniazid +
Rifampicin + Streptomycin + Pyrazinamide. What drug should be prescribed instead of Isoniazid?{
Rifabutin.
Ftivazide
Ofloxacin.
Dassa
Kanamycin
A 55 year old patient has been diagnosed for the first time with fibro-cavernous tuberculosis of the
lower lobe of the left lung. On x-ray decrease in size of lower left lobe, Mediastinum shifted to the
left. In VI segment on the background of cirrhosis thickening of the wall of the cavity is noted in the
lower lobe of the left lung small intensive shades are noted. MBT is present in sputum; sensitivity to
all antituberculosis drugs is preserved. What treatment should be prescribed to patient in acute
phase?{ + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ofloxacin
A 57 years old patient has been suffering from tuberculosis for the past 6 years. Two years ago he has
been diagnosed with chronic lung tuberculosis (2.09.1994) ( fibro-cavernous, infiltrative phase),
Destr.+, MBT+ М+К+ Resist(0)-,Histo 0, Cat 4 Cog 4 (2005). What treatment should be prescribed
in acute phase?{
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Streptomycin + Pyrazinamide
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Streptomycin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Kanamycin + Ethambutol
A 8 year old child is on living with a father who suffers from lung tuberculosis, MBT (+). Mantoux
test for the child is negative. What drug should be ordered for primary chemoprophylaxis for the
child?{
Ethambutol.
Pyrazinamide.
C.
D.
E. *
128.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
129.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
130.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
131.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
132.
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
133.
A.
B.
C. *
Rifampicin.
Ethionamide.
Isoniazide.
A 7 year old child lives with his mother who suffers from tuberculosis. Mantoux test negative. What
Chemoprophylactic therapy should be ordered for the child?{
Guarding.
Repetitive.
Secondary.
Primary.
Intensive.
A 7 year old child was vaccinated at birth with BCG vaccine. When she was 4 months on the
injection site a cold abscess appeared. A 2 months local treatment lead to disappearance of the
abscess. At present the Mantoux test with 2 ТU PPD is negative.What should be done in this case?
Revaccinate with BCG vaccine.
Revaccinate with BCG-M vaccine.
Prescribe chemoprophylaxis.
Do not revaccinate, it is contraindicated.
Perform X-ray.
A 8 years old child is presently healthy. Mantoux 2 To test is negative. It is known that after
receiving BCG vaccine at birth patient suffered from complication-lymphadenitis of the left axillary
lymph node. What should be done in this case?{
Revaccinate with BCG vaccine.
Do not revaccinate.
Conduct chemoprophylaxis following with BCG vaccine.
Do not revaccinate, once a year perform Mantoux 2 TO test.
Revaccinate wirh BCG , followed by chemoprophylaxis.
Family consisting of a husband and wife, husband has been diagnosed for the first time with
destructive lung tuberculosis, MBT+. The wife has been examined and is healthy. What treatment
should the wife undergo?{
Chemoprophylactic Isoniazid 0,3 g daily.
Chemoprophylactic Rifampicin 0,6 g daily.
BCG SSI vaccination.
Chemoprophylactic Ethambutol 1,2 g.
Treatment with three different antimycobacterial preparations.
The health 1,5 month old child was not able to receive BCG at birth due to fever. What should be
done ?{
Vaccinate with BCG M vaccine.
Conduct mantoux test with 2 ТО.
Conduct chemoprophylaxis.
Admit patient for surveillance.
Should be referred to a pediatrician.
A patient P. has been diagnosed with\\: Infiltrated tuberculosis(22.03.04)of upper part of the
lung(infiltrative), Destr+, MBT+ М +К + Resist-,Histo 0, Cat 1 Cog 1 (2004).\n What
antimycobacterial treatment should be prescribed in acute phase of the disease?{
Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Pasque Acre, Streptomycin
Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide, Streptomycin, Ofoxacin.
Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Streptomycin, Pyrazinamid.
D.
E.
134.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
135.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
136.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
137.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
138.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
139.
Isoniazid, Rifampicin.
Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Streptomycin.
A patient P. is diagnosed with tuberculosis (І4.02.2005) of the upper right lung (fibro-cavernous,
infiltrative phase), Destr.+, MBT+ М+К+ Resist(Н+К+Е+Z)-,Histo 0, Cat 2 Cog 4 (2005), In the
upper part of the right lung a large cavern is present(6,0x7,0 cm). Patient has been offered surgical
treatment. What surgical treatment should e performed in this case?{
Cavernotomy.
Pulmonectomy
Segmentectomy
Lobectomy
Cavernoplastics
A patient C. with tuberculosis(4.11.2004) of lungs(Disseminative, infiltrative and destructive
phase), Destr.+, MBT+ М+К+ Resist(0)-,Histo 0, Cat 1 Cog 4 (2005). Patient is being treated
according to I category drugs\\: Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Streptomycin + Pyrazinamide. Patient
abuses alcohol use. What non-specific patient should be prescribed to patient?{
Ambroksol
Carsil
Lidaza
Trental
Almagel
After x-ray examination of a 43 year old patient it was noted that on second segment of the right lung
small low intensity focal shadows moderate in size with unclear margins. Patient denies of any
complaints. No pathologies objectively. Blood analysis is within norms. He was diagnosed with acute
tuberculosis of the second segment of the right lung. Sputum test is negative. What treatment should
be prescribed in acute phase?{
Isoniazid + Rifampicin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide+ Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin +Ethambutol+ Pyrazinamide + Streptomycin
Ethambutol + Pyrazinamide
Infant has been vaccinated with BCG at the hospital. After 4 weeks on the area of injection a blue
coloured 4mm infiltrate appeared. These changes are typical for ?\:{
Complication of BCG vaccine.
Normal local allergic reaction to vaccination.
Proper antiseptic measures were not followed during vaccination.
Severe reaction to the vaccine.
Subcutaneous injection of the vaccine .
Infant was vaccinated in the hospital. A 5mm post-activation scar has appeared. At the age of 1,
mantoux test resulted in 10mm induration during the first test and 6mm during the second test. How
would you evaluate these results ?{
Chronic tuberculosis intoxication
Tuberculosis infectivity
Turn of tuberculosis test
Early tuberculosis intoxication
Post vaccination allergy.
Infiltrative phase of primary tuberculosis complex of the middle lobe of the right lung was
discovered in a 10 year old child. MBT negative(pneumonic stage). What therapy should be
prescribed to the child in acute phase?{
A. *
B.
C.
D.
E.
140.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
141.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
142.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
143.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
144.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Kanamycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethionamide
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol + Ofloxacin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Ethambutol + Kanamycin
For the past few weeks a 34 year old patient complains of weakness, increased temperature up to
38,1'С, cough with small amount of sputum. Upon x-ray examination it was determined that in VI
segment in left lung a 4x4 cm darkening, with low intensity shadow with unclear borders. Infiltrative
lung tuberculosis of the left lung was diagnosed. Bacterioscopically MBT positive. What therapy
should be prescribed in acute phase ?{
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol + Streptomycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Kanamycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethionamide
In (4.11.2005) a patient has been diagnosed with lung tuberculosis (disseminative, phase of
infiltration and destruction), Destr.+, MBT+ М+К+ Resist-,Histo 0, Cat 1 Cog 4 (2004) Patient is
currently under treatment of 1st category\\: Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Streptomycin + Pyrazinamide.
Patient constantly abuses alcohol. What drug should be prescribed to patient for non specific
therapy?{
Ambroksol.
Thiotriazoline
Lidaza.
Trental
Almagel
In a 7 year old child, after 6 months after re-vaccination on the area of the BCG injection a 6 mm
keloid scar is noted. Patient feels well. What action should be taken ?{
antimycobacterial
Conduct chemoprophylaxis.
Perform Mantoux test.
Perform x-ray.
Observe the child at an outpatient base according to category 5.
On chest x-ray of a 26 year old patient it was noted that on II segment of the right lung low intensity
shadows with unclear margins. Patients has no complaints. Objectively no pathologies noted. Blood
analysis within physiological norm. MBT absent in sputum. Patient is diagnosed with tuberculosis.
What therapy should be prescribed in acute phase?
Isoniazid + Rifampicin+ Pyrazinamide
Isoniazid + Rifampicin+ Kanamycin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin+ Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Rifampicin+ Kanamycin + Ethambutol+ Streptomycin
Patient has been diagnosed with\: milliary tuberculosis (5.09.2005), ), Destr-, MBT- М -К Resist-,Histo 0, Cat 1 Cog 3 (2005) What scheme of treatment should be prescribed to patient in
acute phase?{
Isoniazid + Rifampicin - Streptomycin+ Ethionamide.
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Streptomycin + Pyrazinamide+ Ethambutol.
Rifampicin + Streptomycin + Ethambutol + Pyrazinamide.
Isoniazid + Streptomycin+ Ethambutol + Pyrazinamide.
E.
145.
A.
B.
C.
D. *
E.
146.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
147.
A.
B. *
C.
D.
E.
148.
A.
B.
C. *
D.
E.
149.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
150.
A.
Еthambutol + Rifampicin + Ethambutol + Ethionamide.
Patient has been diagnosed with\\: tuberculosis (8.01.2006) S2 (tuberculoma). Destr.+, MBT+ М+К+
Resist(0)-,Histo 0, Cat 1 Cog 1 (2006) After 2 months of treatment tuberculoma has increased in size
to 5,5cm in diameter. Bacterial sections are constant. A patient is getting ready for surgery. What
surgical intervention should be performed in this case?{
Pulmonectomy
Lobectomy
Bilobectomy
Segmentectomy
Resection of tuberculoma
Patient is undergoing a treatment for the diagnosis of\\: tuberculus meningitis. Diagnosis is confirmed
with presence of MBT in cerebrospinal fluid. The following treatment has been prescribed to
patient\\: Isoniazid +Ethambutal, Rifampicin - per os, Streptomycin - Intramuscularly, Pyrazinamideper os. What drug should be introduced intraspinally during cerebrospinal puncture?{
Rifampicin
Ethambutal
Streptomycin
Amikacin
Streptomycin with calcium chloride complex
What is the optimal scheme of treatment for antimycobacterial therapy in the beginning phase in
patient with tuberculosis (05.09.2004)of the upper right lung (tuberculoma. Destr.-, MBT- М-КResist(0),Histo 0, Cat 2 Cog 4 (2005){
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Streptomycin + Ofloxacin
Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol
Isoniazid + Streptomycin + Pyrazinamide
Rifampicin + Streptomycin + Ethambutol
Pyrazinamide + Kanamycin + Ethambutol
What is the optimal time of treatment for antimycobacterial therapy for patient with
tuberculosis(13.08.2003) of the upper part of left lung(acute, infiltrative phase), Destr.-, MBT- М-КResist(0)-,Histo 0, Cat 3 Cog 3 (2003) {
2 months.
4 months
6 months
8 months
10 months
A female patient of 45 is disturbed with cough, temperature rise up to 37,5°Got ill six weeks ago
after ”the flu”. In a 2 weeks treatment course for focal pneumonia, focal shadows in the upper
segment of the right lung remained without any changes. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Aspergilosis
Lung cancer
Eosiniphil infiltration
Lingering pneumonia
Nidus tuberculosis
Nidal shades of medium intensity with vague contours were revealed on the left apex of a 20-years
old youth during fluorographic examination. His general state is gooMantoux test with 2 TU – 19
mm infiltratYour preliminary diagnosis?
Primary tuberculous complex.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
151.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
152.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
153.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
154.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
155.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
Infiltrative tuberculosis.
Disseminated tuberculosis.
Lung tuberculoma.
Focal tuberculosis.
A group of shadows of small and medium intensity of 3-8 mm in diameter has been revealed in the
upper part of the right lung in a patient of 25 years old on a fluorogoram. The patient’s state is
satisfactory. Mantoux test with 2 TU – 16 mm infiltratWhat disease is the most probable one?
Sarcoidosis
Eosinophil infiltration
Nidus pneumonia
Peripheral lung cancer
Nidus lung tuberculosis
Small and average nidi of little intensity have been revealed on the apex of the right lung during
fluorographic examination of a man aged During the last month he notes the decrease of the appetite,
perspiration, inconsiderable cough. Prescribe of antimicobacterial therapy on the 1-st stage.
Isoniazidum + pyrazinamidum
Isoniazidum + rifampycinum + streptomycini + pyrazinamidum + ethambutolum.
Isoniazidum + rifampycinum.
Isoniazidum + rifampycinum + ethambutolum.
Isoniazidum + rifampycinum + pyrazinamidum
Patient V. suffers from tuberculosis for 17 years. Recent dyspnea aggravation, cough, new pain in the
right intercostal area, in heart area, drowsiness, edema in lower extremities. What is the most
probable complication?
Spontaneous pneumotorax
Lung atelectasis
Amiloidosis of internal organs
Tuberculosis of bronchi
Chronic lung heart
The patient M., 19 years old, got sick gradually: general weakness, the body temperature up to 37? C.
She had been in contact with a patient suffering from tuberculosis. The tuberculous meningitis was
suspected. Say, which one from the present symptoms is not typical for the tuberculous meningitis?
Dyplopia
Headache
Gradual development of the disease
Vomiting
Normal body temperature
A patient, 45years old, is diagnosed with tuberculous meningitis for the first time. The general
condition is grave, the meningeal symptoms are sharply pronounced, the consciousness is shadowed.
What is the total duration of the treatment of this patient?
1 month
3 months
5 months
7 months
12 months
156.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
157.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
158.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
159.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
160.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
The teacher O., 28 years old, was treated during 10 months because FDTB (05.05.2003) of the
upper part of the right lung (infiltration ), Destr+, MBT+M-C+, Resist-, HIST0, Cat1 Coh2(2003).
The state became much better (the absence of MBT, the closing of the cavity of decay). What is the
tactics for the employment?
To be let to the previous work
To continue the list of uncapacity to work up to 12 months and then to be let to work
To direct to the MSEC to indicate the II invalid group
To propose another job
To direct to the MSEC to indicate the III invalid group
A man of 48. The photoroengenologic examination showed multiple focuses of various dimensions
of low and medium intensity with illegible contours in the upper segments of both lungs. The patient
does not feel himself worse. Blood analysis: 8,2 x 109/l, ESR – 20 mm/hour. Which form of lungs
tuberculosis does the patient have?
Miliary
Disseminated
Nidus
Infiltrate
Disseminated (chronic)
Patient at the age of 35 years has complains concerning cough with sputum, weakness, shortness of
breath during minor activity. Three month ago was returned from correctional institutions. During
medical examination right part of the thorax is narroweLags during breath. Mycobacteriums
tuberculosis revealed bacterioscopy. Which clinic form of pulmonary tuberculosis was revealed in
the patient?
Tuberculoma.
Focal tuberculosis.
Tuberculous pleurisy.
Disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis.
Fibrous cavernous tuberculosis
Patient (woman) at the age 36 year first diagnosed fibrous cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis,
mycobacterium tuberculosis+, resist to ethambutol and streptomycin. Which combination of
antimicobacterial agents is the most optimal?
Isoniazid+rifampicin A+ thioacetazone+florimytcin.
Isoniazid+kanamycin+PAS(A)(para-aminosalicylic acid)+ethionamide.
Kanamycin+ethionamide+rifampicin+phthivazide.
Isoniazid+cycloserine+protionamide+kanamycin.
Rifampicin+isoniazid+kanamycin+pyrazinamide.
Patient age 42 years. He is sick by fibrous cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis of the upper part of
the right lung during 8 years. Mycobacteriums tuberculosis+. He feels good during last 2 year.
Radiographic data: the upper part of the right lung available thick cavern with fibrosis and perifocal
inflammation. The upper part is narrow due fibrosis. Both lungs have focuses of semination. Shadow
of mediastinum shifted right.What radiographic data are typical for fibrous cavernous pulmonary
tuberculosis of the lungs?
Caverns presence, perifocal inflammation.
Perifocal inflammation, bronchogenic dissemination.
Organs on mediastinum are shifted in the side of lesion.
Intense dark patch, narrowed lung field.
Caverns presence, well-defined fibrosis, focuses of semination.
161.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
162.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
163.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
164.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
165.
A.
Patient age 33 years admitted to hospital with complains about weakness, decreasing of the appetite,
hyper hydrosis, subfebrile temperature, cough with sputum. Tuberculosis of the left lung (infiltrative
form) was revealed 3 year ago. The patient systematically broke treatment course, excessive used
spirits, irregular took antimicobacterial medications. As a result patient has resistance of
mycobacteriums tuberculosis to isoniazid and rifampicin and has formed fibrous cavernous
tuberculosis of left lung.What reasons of forming fibrous cavernous tuberculosis in the patient?
Disturbance of medical treatment.
Alcohol abuse.
I rregular take medicine.
Resistance of mycobacteriums tuberculosis to isoniazid and rifampicin.
All above.
Patient age 42 years. He is sick by fibrous cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis during 8 years. Had
irregular treatment. He has complains about intense pain in the left part of thorax, breathlessness.
Objective: state of the patient is averagAbove left lung percussion data shows tympanitis,
auscultatory - breath not auscultates. What complications of fibrous cavernous pulmonary
tuberculosis arose in the patient?
Bullous emphysema.
Tuberculous atelectasis.
Chronical cor pulmonale.
Escudative pleurisy.
Pneumothorax spontaneous.
Patient`s (woman) age 52 years. She is sick by fibrous cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis during 15
years. She had irregular treatment. She admitted to hospital with complains about strong pain in the
left part of the thorax during breathing, shortness of breath. Objective: state of the patient is
averagLeft part of the lung lags during breathing, during percussion – tympanitis. Auscultatory breath very impaire What medical investigation need to do with patient at first for more accurate
diagnosis?
Medical
investigation of respiratory function.
Computer tomography.
Bronchoscopy.
Tomography.
Radiography of organs of thorax.
Patient (woman) age 54 years. She is sick by fibrous cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis during 15
years. She had irregular treatment. She admitted to hospital with complains about cough with
bright-red blood with bubbles (total amount of the flowed blood near 250 milliliters) , shortnes of
breath, weakness, giddiness, subfebrile temperature (low grade fever). During percussion above
upper part of right lung is tympanic shade of lung sounDuring auscultation - bronchial respiration
with different crepitations. Above other regions of lungs - diffused dry rales. Radiographic data: near
S2 right lung defines cavity of disintegration with diameter 5.0 x 4.0 centimeters, upper part is
reduced, right root pulled up. What complications of fibrous cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis
Pneumothorax
spontaneous.
arose in the patient?
Sputum with blood.
Pulmonary edema.
Chronical cor pulmonale.
Pulmonary hemorrhage.
Patient at the age of 49 years address to doctor with complains about weakness, decreasing of the
appetite, hyper hydrosis, subfebrile temperature, cough with spew. Tuberculosis of the left lung was
revealed 7 years ago. Patient had course of treatment in the hospital. Two year ago patient had
relapse of diseasRadiographic data:both lungs fibrous changeUpper part of left lung has cavity with
diameter 6 centimeters with area of perifocal inflammation.Upper part of right lung has some
cavities..Spew has mycobacteriums tuberculosis+. What clinic form of tuberculosis resides such kind
of radio data?
Caseous
pneumonia.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
166.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
167.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
168.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
169.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
170.
Infiltrative form.
Tuberculoma.
Cirrhosis form
Fibrous-cavernous form.
Patient at the age of 56 years has fibrous cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis during 13 years. He
admitted to hospital with complains about shortness of breath in quiet state, edema of legs. Objective:
available diffusive cyanosis, increased liver on 4 centimeters, edema of legs. Above both lungs, in
upper areas (against a background of hard breath) auscultates crepitation with middle bubbles. P8 –
100 per minute, arterial pressure 115/88 mm of mercury. Heart borders increased, present accent and
separation of II sound above pulmonary artery. What complication arose in the patient?
Pneumothorax spontaneous.
Pulmonary hemorrhage.
Spew with blood.
Pulmonary edema.
Chronical cor pulmonale.
Patient`s age is 40 years. Has tuberculosis during 7 years. Two years ago got diagnosed fibrous
cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis, mycobacterium tuberculosis+. Half year ago appeared progressive
shortness of breath during physical activity. Now shortness of breath appears during rising on the
second floor. Objective: respiration rate 24 per minute, pulse - 96 beats per minutHeart sounds
speeded up, rhythmical. Above pulmonary artery auscultates accent of second sound. Liver during
palpation not sickly, prominent from border of costal margin on 2 centimeters. What complication
arose in the patient?
Pneumothorax spontaneous.
Pulmonary hemorrhage.
Pulmonary edema.
Spew with blood.
Chronical cor pulmonale.
Patient age is 40 years. Has fibrous cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis during 8 years. Last time has
edema of legs. Urine examination shows: growing proteinuria, cylindruria, hyposthenuriWhat is the
most probable reasons for changing in urine examination?
Acute nephritis.
Renal tuberculosis.
Cystic disease.
Chronic renal insufficiency.
Amyloidosis.
The prophylactic photoroentgenographic examination of a 25-year-old patient showed in segments
1-2 of the left lung focal shadows of low intensity without distinct contours. Mantoux test with 2 TO
– 7 mm infiltratBlood analysis: leuk. – 9,9 x 109/l, ESR – 26 mm/hour. Which is the most probable
diagnosis?
Infiltrative lung tuberculosis
Nidus pneumonia
Lung cancer
Eosiniphil infiltration
Nidus lung tuberculosis
Patient, Underwent 4-months treatment in a hospital because of infiltrate tuberculosis of the upper
segment of the left lung in the phase of destruction.
He is achieved, but in the place of the
infiltrate a round 2 cm hole of medium intensity and with distinct exterior contours is formeWhat
treatment method is most advisable at this phase?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
171.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
172.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
173.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
174.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
175.
A.
B.
C.
To recommend sanatoric treatment
To use surgical intervention
To carry out 1,5-2th months course of hormonotherapy
To use means of popular medicine
To continue the treatment with antimycobacterial preparations
A man of 43, smoker, complains of cough with little sputum secretion, subfebrility, weight loss. With
the suspect for the abcess-forming pneumonia was hospitalized into a diagnostic department.
Roentgenogram: in the upper segment of the right lung – 4x4 cm round shadow with distinct exterior
contour. Blood analysis: leuk. – 9,0 x 109/l, ESR – 19 mm/hour. Sputum analysis: leuk. – 8-12 in the
vision fiel Mantoux test with 2 TO – 22 mm infiltrat.What is the most probable diagnosis?
Peripheral lung cancer
Abscess of lung
Non-malignant tumor
Aspergiloma
Lung tuberculoma
A man of 38 complains of pain in heart area, subfebrility, sweatness, weight loss. Pulse: 82
strokes/min., AP 110/75 mm m.Systolic murmur over the heart apex. Roentgenogram: focal shadows
up to 5mm in diameter on both lungs apexes. What disease is the most probable one?
Sarcoidosis
Eosinophil infiltration
Nidus lung tuberculosis
Peripheral lung cancer
Nidus pneumonia
Female patient Z., 3Got ill with diabetes mellitus six years ago. The roentgenologic examination
showed infiltrate shadow with enlightment in the center in the lower segment of the left lung. General
condition of the patient is satisfactory. Blood analysis: leuk. – 10,5 x 109/l, ESR – 25 mm/hour.
Mantoux test with 2 TO - positivWhat is the most probable diagnosis?
Lung cancer
Pneumonia
Abscess of a lung
Primary tuberculosis complex
Infiltrative tuberculosis
Patient K., Got ill acutely after a surgical operation for a stomach ulcer. Roentgenogram: massive
infiltration of pulmonary tissue with several hollows of destruction in the upper segment of the right
lung. Mantoux test with 2 TO – doubtful. Blood analysis: leuk. – 17,0 x 109/l, ESR – 52 mm/hour.
MBT are found in sputum. What is the most probable form of lungs tuberculosis?
Infiltrative
Nidus
Fibrous-cavernous
Cirrhotic
Caseous pneumonia
A cloud-like darkening of the upper part of the right lung with a lightening in the center, to the left
paracardially a group of small intensity nidi have been revealed during fluorographic examination of
a female patient, 30, suffering from a stomach ulcer. A preliminary diagnosis.
Lung tuberculoma.
Fibrous cavernous tuberculosis.
Caseous pneumonia.
D.
E. *
176.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
177.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
178.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
179.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
180.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
Disseminated tuberculosis.
Infiltrative tuberculosis.
Haemoptysis appeared in a day after hyperinsolation of a girl of No pathologic changes were found
in the lungs of fluorography six months ago. Damp middle-blistered rales are heard beneath the right
clavicle, Mantoux test with 2 TU – 23 mm infiltratWhat changes in lungs can one think about?
Spontaneous pneumothorax.
Lung tuberculosis.
Multiple nidi.
Cirrhosis of a lung.
Decay cavities.
Plan a specific treatment to a patient with FDTB (03.03.2001) of the upper part of the right lung
(caseous pneumonia), Destr+, MBT+M+C+, Resist-, HIST0, Cat1 Coh1(2001). The patient is 45,
weight – 46 kg. His general condition is difficult. There is no accompanying pathology. Prescribe
antimycobacterial preparations.
Isoniazidum + rifampycinum + streptomycini.
Isoniazidum + pyrazinamidum
Isoniazidum + rifampycinum.
Isoniazidum + rifampycinum + ethambutolum.
Isoniazidum + rifampycinum + streptomycini + pyrazinamidum .
Female patient, During the last five years has noted general weakness, cough, subfebrility;
menstruations absence for three months. General roentgenogram: in the 2nd segment of the left lung
– a round hole above 3cm in diameter of medium intensity. Mantoux test with 2 TO – 23 mm
infiltratWhat is the most probable diagnosis?
Aspergiloma
Peripheral lung cancer
Filled with a cyst
Chondroma
Lung tuberculoma
A patient R., aged During the last four months – dry cough, general weakness, perspiration,
subfebrile temperaturThere is a round formation of over 2 cm in diametre, of medium intensity in the
second segment of the upper part of the right lung on a fluorogram. At the age of 20, the patient
suffered from the infiltrative lung tuberculosis. The general blood analysis is within the norm.
Mantoux reaction with 2 ТU – 15 mm infiltratA preliminary diagnosis.
Primary tuberculous complex.
Infiltrative tuberculosis.
Disseminated tuberculosis.
Focal tuberculosis.
Lung tuberculom
A female patient Z., A shadow with vague contours sized 4 cm, MBT(-) has been found in the right
lung (1st segment) at a roentgenologic examination. After 3 months of antimycobacterial therapy a
round focus, 2 cm in diametre, of homogeneous structure with clear contours forme A diagnosis after
3-months treatment.
Primary tuberculous complex.
Infiltrative tuberculosis.
Disseminated tuberculosis.
Focal tuberculosis.
Lung tuberculoma.
181.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
182.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
183.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
184.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
185.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
A round shadow with wave-like outer contours was found in the 3-rd segment of the left lung of a
man of 60 during a fluorographic examination. There were single calcinates in the roots. ESR – 62
mm/hr. What illness can be suspected?
Infiltrative tuberculosis.
Disseminated tuberculosis.
Lung tuberculom
Focal tuberculosis.
Periferal cancer.
A female patient Z., 29, has been coughing for 2 years, with a small quantity of sputum, sometimes
subfebrilitet. She did not apply for a medical carA week ago a heterogeneous round darkening 2,5 x
3,0 cm with clear contours and a strip of excentric lightening was found in the sixth segment. A
preliminary diagnosis.
Fibrous-cavernous tuberculosis.
Infiltrative tuberculosis.
Disseminated tuberculosis.
Focal tuberculosis.
Lung tuberculom
In a patient S., 17, suffering from diabetes, a round shadow of 2,5 cm in diameter, of medium
intensivity with vague outer contours and a path to the root was found in the second segment of the
upper part of the right lung during fluorography. Mantoux test with 2 ТU – 24 mm infiltrate.A
preliminary
diagnosis.
Fibrous-cavernous
tuberculosis.
Infiltrative tuberculosis.
Disseminated tuberculosis.
Caseous pneumonia.
Lung tuberculom
A patient 35, complains of the weakness, insignificant cough with sputum. An inhomogeneous
limited darkening sized more than 5cm. in the 81, 2 of the right lung has been revealed at
roentgenologic examination. Lung infiltrative tuberculosis of the upper part of the right lung has been
suspecteWhat most reliable auscultative data characterize will be observed above the lesion lungs
section of mentioned localization?
Moist rales
Dry disseminated rales
Vesicular breathing
Amphoric respiration
Absence of breathing
Fluorographic examination has been conducted for a patient 25, on the occasion of the complains of
the raising of body temperature and cough, as a result of which darkening of small intensity of
4,0-5,0 cm in diameter with the destruction present has been revealed in the upper part of the right
lung. MBT has been revealed in sputum. What rales will be the most characteristic for such changes
in lungs?
Disseminated
rales
Diffused single rales
Moist and dry rales along lung lesion
Moist rales in lower parts of lungs
Local rales
186.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
187.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
188.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
189.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
190.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
191.
A.
B.
A patient 35, appeal to the doctor with complains of the weakness, cough with sputum, raising of
body temperature to 37,2?Lung infiltrative tuberculosis was revealed in antitubercular dispensary
after finish examination. It is known from anamnesis, that a patient was ill with arthritis, infectious
hepatitis, tyreotoxicosis. Diabetes two years ago and glomerulonephrytis. What somatic disease is the
risk factor of tuberculosis occurring?
Glomerulonephritis
Thyreotoxicosis
Infectious hepatitis
Gaimoritis
Diabetes
Patient 38, is on treatment into an antitubercular dispensary on the occasion of firstly diagnosed
infiltrative tuberculosis of the upper part of the left lung in decay phase (lobit).No changes have been
revealed at physical examination. How should patient breath right to improve informing of the
auscultative method?
To breathe frequently
To breathe deeply
To cough strongly
To breathe by opened mouth
To cough slightly and to do a deep breathe
A patient 40, is directed to antitubercular dispensary for finish examination and lung tuberculosis
diagnosis confirmation. A patient complains of the raising of body temperature to 37,5?C, weakness,
disposition to perspire, cough with sputum. What sputum characterized lung tuberculosis?
Purulent with a stinking odor
Frothy
Slime sputum of canary color
Rusty
Slime
Patient 30, has been delivered on treatment into an antitubercular dispensary on the occasion of
firstly diagnosed infiltrative tuberculosis of the upper part of the right lung. The intoxication
syndrome is expresseWhich of cited complaints do intoxication syndrome at tuberculosis refer to?
Haemophthisis, weakness, chest pain, cold, shortness of breathe
Cough, sputum excretion, hectic temperature, chest pain
Nausea, vomit, cough, pain in joints, indisposition
Cough, sputum excretion, broken-sleep, headache, hoarseness of voice
Subfebrile temperature, weakness, appetite and weight loss, disposition to perspire
Patient 32, has been delivered on treatment into an antitubercular dispensary on the occasion of
relapse of tuberculosis process. The presence of bronchi-lung-pleura syndrome has been determined
in a patient at examination. What are characterized symptoms for this syndrome?
The raising of body temperature, weakness, appetite loss, weight loss, disposition to perspire
Cough, weakness, broken-sleep, headache, hoarseness of voice
Cough, weakness, hoarseness of voice, dry rales, shortening of percussion note
Shortness of breathe, broken-sleep, moist rales, increasing voice tremor, indisposition
Cough, sputum presence, chest pain, haemophthisis, shortness of breathe
A patient 35, complains of the raising of body temperature to 37,5?C, appetite loss, indisposition,
weakness, cough with sputum excretion up to 50 ml per day of slime character. The state of patient
has worsened gradually, during a month. What disease in a patient can one suspect?
Pneumonia
Lung abscess
C.
D.
E. *
192.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
193.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
194.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
195.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
196.
A.
B.
Bronchial asthma
Chronic bronchitis
Lung tuberculosis
A patient 55, is ill with tuberculosis during 3 month, complains of the cough with sputum excretion,
raising of body temperature, weakness, shortness of breathe at physical tension. Amphoric respiration
is heard above the right lung, in the area under clavicle at auscultation. What changes in lungs do
such auscultative phenomenon at tuberculosis condition?
Exudates
Lung atelectasis
A small cavern
Cirrhotic changes
A big cavern
A patient 33, complains of the cough with sputum, weakness, raising of body temperature to
37,52?C, during 3 weeks, appetite loss, indisposition. No changes have been revealed at objective
examination. What should be found out in a patient in the life anamnesis?
Smoking
Following the routine of work and rest
Sport occupation
Present the emotional labiality
Present the contact with tuberculosis patient
Female patient Z., 29 years old, was brought by an urgent medical service car to a regional
tuberculous dispensary. She complains on cough, dyspnea, pain in the right half of the thorax.
Objectively – wooden sound at percussion, auscultatively – the absence of breathing above the right
half of the thorax. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Lung infarction
Lung atelectasis
Exudative pleurisy
Pleropneumonia
Spontaneous pneumothorax
A female patient K., 30, two years ago underwent treatment on the occasion of the FDTB (16.09.2002) of the
first segment of the right lung (nidal tuberculoisis), Destr-, MBT-M-C-, HIST0, Cat3 Coh3(2002). 10 days ago
a right-side purulent otitis was diagnosed. At the present time she complains of a terrible headache, vomiting,
general weakness. She has difficulty in making a contact. Roentgenologically there are two nidal shadows of
more than medium intensity in the first segment of the right lung. The liquor analysis: turbid, cytosis – 650
cells in 1 ml, neutrophiles – 85 %, lymphocytes – 15 %, sugar – 3,1 mmol/L, chlorides – 115 mmol/L. Your
diagnosis.
Serous meningitis
Tuberculous meningitis
Meningo-coccal meningitis
“Meningism”
Secondary purulent meningitis
Patient, 62. Complaints of accessive cough, dyspnea, drop of appetite, weight loss for 10 kg.
Contacted with his brother who is ill with tuberculosis of lungs. 6 months ago had a surgical
operation because of cancer of the prostatic gland. Blood analysis: anemia, ESR – 65 mm/hour.
Roentgenogram: multiple focal shadows (5-6 mm) with distinct contours in medial and especially in
lower lungs segments. Your preliminary diagnosis.
Disseminated lung tuberculosis
Nidus lung tuberculosis
C.
D.
E. *
197.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
198.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
199.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
200.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
201.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Tromboembolism of branches of lung arteria
Bilateral nidus pneumonia
Carcinomatosis
Patient, 35. Has been a drift miner for 10 years. Complains for dyspnea during physical load, cough
with little of sputum. Normal body temperature. Rales in the lungs are not heard. Blood analysis:
leuk. – 7,8 x 109/l, ESR – 8 mm/hour. Mantoux test with 2 TO – 10mm infiltrate. Roentgenogram:
small focal shadows of high intensity with distinct contours on both sides, especially in the
medial-lateral segments. What is the preliminary diagnosis?
Small-nidal pneumonia
Miliary tuberculosis
Disseminated lung tuberculosis
Carcinomatosis
Pneumoconiosis
Patient L., 35. The illness started acutely – with body temperature rise up to 39°C, cough with
sputum secretion. Received antibiotics during a week time – no effect. Not numerous moist fine
bubbling rales between the scapulae. Roengenogram: focuses of various dimensions with illegible
contours along the whole extent of both lungs. Blood analysis: leuk. – 13,2 x 109/l, ESR – 45
mm/hour. Which is the most probable diagnosis?
Bilateral nidal pneumonia
Infarction-pneumonia
Stagnation phenomena in lungs
Caseous pneumonia
Disseminated lung tuberculosis
The patient, 34 years old, 8 years ago was treated because of the infiltrative tuberculosis of
lung. Her state became much better. During the last 6 years the X-ray picture was stable.
To what group of dispensary observation does she belong?
5.3
5.2
5.1
5.5
5.4
In a seven-years-old girl in 5 months after the revaccination, in the place of vaccine injection of BCG
a swelling with cyanotic touch of skin appeared, at palpation – fluctuation. What is the postvaccinal
complication?
Lymphodenit
Cyst
Keloid seam
Ulcer
Cold abscesse
At the 5 years old boy, who suffers from the tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymphatic nodes suddenly
appeared coughing, pain behind the stern, shortness of breath, mild cyanosis of lip mucose. Body
temperature is 38,4? C. Upon the upper part of the right lung there is the dulling of the percussion
note, in the same place there is the weakened breathing. The most probable complication of the
tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymphatic nodes.
Exudative pleurisy
Spontaneous pneumothorax
Tuberculosis of bronchi
Pleural empyema
E. *
202.
A.
B.
C.
Atelectasis
A girl of 7 years old, 2 months ago suffered from “influenza”, after which coughing, general
weakness, decreased appetite, sweating appeared, the body temperature rose up to 37,5? C. At the
percussion and auscultation pathological changes are not found. On the X-ray: the enlarged
tracheobronchial and bronchopulmonal lymphatic nodes on the left side. Blood: leuc. 9,0 x 109/l,
ESR – 22 mm/hour. Mantoux test with 2 TU – infiltrate of 17 mm. What is the most probable
diagnosis?
Sarcoidosis
Lymphogranulomatosis
Lymphosarcoma
D.
E. *
203.
Central cancer
Tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymphatic nodes
A.
Lymphogranulomatosis
Unspecific adenopathy
Sarcoidosis
Tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymphatic nodes
Lympholeucosis
A boy of 6 complains for cough, poor appetite, sweating, temperature rise up to 37,5°C.
Roentgenogram – on the left: enlarged bronchopulmonary lymph nodes with illegible exterior
contours. Mantoux test with 2 TO – 15 mm infiltrate. Blood analysis: leuk. – 9,0 x 109/l, ESR – 30
mm/hour. The most probable diagnosis.
Unspecific pneumonia
Central cancer
Tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymphatic nodes
Lymphosarcoma
Sarcoidosis
Patient K., 53. Roentgenologic examination showed in the upper segment of the left lung a ringlike
shadow with a diameter of 5cm with thick walls and fibrous heaviness and focusness. Sputum
contains MBT. What clinical picture is the most probable one?
Lung cirrhotic tuberculosis
Infiltrative lung tuberculosis
Disseminated lung tuberculosis
Lung tuberculoma
Lung fibrous-cavernous tuberculosis
A 10-year-old patient M. is diagnosed with tuberculin “turn”, Mantoux test with 2 TO – 16 mm
infiltrate. Complaints for general asthenia, increased sweating. Blood analysis: leuk. – 9,2x109/l,
ESR – 26 mm/hour. Roentgenogram examination did not reveal pathologic alterations in the lungs.
What diagnosis is the most probable one?
Primary tuberculous complex
Tuberculosis of intrathoracic lymphatic nodes
Nidus lung tuberculosis
Infiltrative lung tuberculosis
Tuberculosis intoxication
B.
C. *
D.
E.
204.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
205.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
206.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
Prophylactic examination of a 17-year-old boy revealed bilateral enlargement of bronchopulmonary
lymph nodes. General condition – satisfactory, no complaints. No pathologic alterations were found
at physiacal examination. Mantoux test with 2 TO – negative. General blood analysis – without any
pathologic deviations. The most probable diagnosis.
207.
B.
C.
Patient of 45 is on treatment in tuberculosis dispensary concerning FDT (13.12.2003) of upper part of
the right lung (infiltrative, phase of disintegration and semination ), Destr+ Mbt+ m+ k+
resist- , GIST O, Сat2 Сog4((2003). He does not use alcohol and narcotics and does not smokIn spite
of adequate chemotherapy (N,R,S,E) patient still has a progressive tuberculosis. On the control
radiography the increasing of cavity disintegration and appearance of semination fires have been
determined on a left lung. What kind of research should be done to a patient to determine possible
reason of treatment’s ineffectiveness?
General blood test.
Biochemical blood examination.
Koch’s test.
Functions’ research of the external breathing.
Immunological research.
Patient of 36 is on treatment in tuberculosis dispensary with a diagnosis: FDT (23.11.1997) of right
lung’s upper part (Fibrosis - cavernous, phase of infiltration and semination), Mbt+ ,m- ,K+ resist+
(R,E) resist O, GIST O, Cat4 Cog4(2004).What kind of research should be primarily done to a
patient?
Histological
Luminescent microscopy.
Immunological research.
D.
E. *
Biological research.
Determine sensitiveness of MBT to chemo medication of the II row.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. *
208.
A.