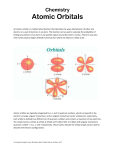
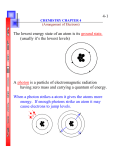
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry Chapter 5 Test Multiple Choice (1.5% each) Identify the
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Hartree–Fock method wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
James Franck wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry Chapter 5 Test Multiple Choice (1.5% each) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. When a scientist compares two objects or events, what is he or she looking for? a. causes and effects c. differences b. similarities 2. What is the electron configuration for nitrogen, atomic number 7? a. 1s2 2s2 2p3 c. 1s2 2s3 2p2 b. 1s2 2s3 2p1 3. Name this piece of lab equipment: a. Stirring Rod c. Beaker b. Thermometer d. Utility Clamp 4. Melting, cooling, and crystallization (freezing) are internal processes observed in the rock cycle. What type of change is each of these processes? a. a physical change b. both a chemical change and a physical change c. a chemical change 5. Which type of change is the rusting of iron into Iron(III) Oxide? a. Physical Change b. Chemical Change 6. Name this piece of lab equipment: a. Florence Flask c. Erlenmeyer Flask b. Evaporating Dish d. Beaker 7. The electron configuration for the carbon atom (C) is 1s2 2s2 2p2. The atomic number of carbon is a. 3. c. 11. b. 6. 8. The electron notation for aluminum (atomic number 13) is a. 1s2 2s2 2p3 3s2 3p3 3d1. c. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 2d1. 2 2 6 2 1 b. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p . A school implemented a peer-study group with one class of students to determine how it affected their science grade. The school had four grading periods. The average science grades of the students who participated in the study program were recorded for each grading period. The table below shows the results. Average Grade of Students in Study Program Grading Period Average Science Grade First 81 Second 85 Third 86 Fourth 89 ____ 9. Which graph correctly illustrates the results shown in the table? a. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ b. 10. Which statement best describes how the school might better analyze the impact of the study program? a. Examine the topics studied in the science class. b. Compare the results to the grades of students who did not participate in the study program. c. Compare the history grades of students who participated in the program to their science grades. 11. The lowest possible energy state the electrons in an atom can have. a. Ground State c. Quantum Mechanical Model b. Atomic Orbital 12. Calcium chloride is a pure substance used on roads to control dust and to melt ice and snow. Its formula unit shows that it contains one calcium ion for every two chloride ions. What type of matter is calcium chloride? a. molecular compound c. ionic compound b. covalent compound 13. With the quantum model of the atom, scientists have come to believe that determining an electron's exact location around the nucleus a. can be done easily. b. is impossible. c. can be done before 2005. 14. This shows the number of valence electrons in an atom using dots and the element’s symbol. a. Principal Quantum Number c. Electron Configuration b. Electron-Dot Structure 15. A region around an atom where it is possible to find an electron. a. Ground State c. Quantum Mechanical Model b. Atomic Orbital 16. An orbital that could never exist according to the quantum description of the atom is a. 3d. c. 6d. b. 3f. 17. The diagram shows an example of which of the following? a. homogeneous mixture c. heterogeneous mixture b. element 18. Which model of the atom explains the orbitals of electrons as waves? a. the Bohr model c. Rutherford's model b. the quantum model 19. How many electrons can occupy the s orbitals at each energy level? a. two, if they have the same spin c. two, if they have opposite spins b. one 20. A model of the atom where the electrons are treated like waves. a. Atomic Orbital c. Ground State b. Quantum Mechanical Model ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 21. The region outside the nucleus where an electron can most probably be found is the a. electron cloud. c. quantum. b. s sublevel. 22. The distance between two successive peaks on a wave is its a. frequency. c. quantum number. b. wavelength. 23. The major difference between a 1s orbital and a 2s orbital is that a. the 2s orbital is at a higher energy level. b. the 2s orbital can hold more electrons. c. the 2s orbital has a slightly different shape. 24. The set of orbitals that are dumbbell-shaped and directed along the x, y, and z axes are called a. f orbitals. c. d orbitals. b. p orbitals. 25. In SI, the frequency of electromagnetic radiation is measured in a. quanta. c. hertz. b. nanometers. 26. Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding a bowl of vegetable soup? a. The broth contains all the compounds present in the soup. b. The broth contains a homogeneous mixture of salt and water. c. It is a heterogeneous mixture. 27. Which type of change is the freezing of a liquid to become a solid? a. Chemical Change b. Physical Change 28. Which of the following changes involved in manufacturing an automobile is a chemical change? a. mixing steel from iron, carbon, and other metals b. forming plastics from petroleum substances c. applying paint to the body of the automobile 29. What is plotted on the x-axis of a line graph? a. controls c. dependent variables b. independent variables 30. Which of the following is a physical change? a. aluminum oxidizing b. ice cream melting c. an acid and a base forming a salt and water 31. For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited state, a. radiation must be emitted. b. energy must be released. c. energy must be absorbed. 32. If electrons in an atom have the lowest possible energies, the atom is in the a. excited state. c. inert state. b. ground state. 33. The part of the atom where the electrons CANNOT be found is the a. nucleus. c. electron cloud. b. area surrounding the nucleus. 34. These are the outermost electrons of an atom (in s and p orbitals) that will be involved in bonding, and are shown in a dot diagram. a. Electron Configuration c. Valence Electrons b. Electron-Dot Structure 35. Which type of change is boiling a liquid to become a gas? a. Chemical Change b. Physical Change 36. Max Planck proposed that a hot object radiated energy in small, specific amounts called a. quanta. c. waves. b. hertz. 37. What is an inference? ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ a. A product c. A type of conclusion b. A hypothesis 38. The atomic sublevel with the next highest energy after 4p is a. 4f. c. 4d. b. 5s. 39. The number of orbitals for the d sublevel is a. 3. c. 5. b. 1. 40. In diagram A, what is the frequency of the wave? a. 1 wavelength c. 1 Hz b. 1 crest and 1 trough 41. Compare diagrams A and B. How does the wavelength of the wave in B compare to the wavelength of the wave in A? a. The wavelength of the wave in B is one-half the wavelength of the wave in A. b. The wavelength of the wave in B is four times the wavelength of the wave in A. c. The wavelength of the wave in B is twice the wavelength of the wave in A. 42. Which title would best describe the table? Properties Earth Venus Diameter (km) 12,756 12,104 Average Density (g/cm3) 5.5 5.3 Percentage of sunlight reflected 39 76 Daytime surface temperature (degrees) 300 750 Number of satellites 1 0 ____ 43. ____ 44. ____ 45. ____ 46. ____ 47. ____ 48. ____ 49. a. Characteristics of Venus and Earth c. Solar System Data b. Diameter of Venus and Earth The letter designations for the first four sublevels with the number of electrons that can be accommodated in each sublevel are a. s:1, p:3, d:5, and f:7. c. s:1, p:3, d:10, and f:14. b. s:2, p:6, d:10, and f:14. This shows how all the electrons are arranged in an atom. a. Electron-Dot Structure c. Principal Quantum Number b. Electron Configuration The element with electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 is a. Si (Z = 14). c. Mg (Z = 12). b. S (Z = 16). For the f sublevel, the number of orbitals is a. 5. c. 7. b. 9. The size and shape of an electron cloud are most closely related to the electron's a. mass. c. charge. b. energy. A spherical electron cloud surrounding an atomic nucleus would best represent a. a px orbital. c. a combination of px and py orbitals. b. an s orbital. Visible light, X rays, infrared radiation, and radio waves all have the same a. speed. c. wavelength. ____ b. energy. 50. A number that represents the size and energy of an orbital. a. Principal Quantum Number c. Electron Configuration b. Electron-Dot Structure Problem (3% each) Figure Z: 51. What element's orbital diagram is shown in the “figure Z” above? 52. Write the electron configuration of the “figure Z” above. 53. Write the electron configuration for beryllium, atomic number 4. 54. Use the periodic table. Which element has the following electron configuration: [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p5? 55. Use the periodic table. Which element has the following electron configuration: [Kr] 5s2 4d10 5p3? Figure X : 56. What element's orbital diagram is shown in the “figure X” above? 57. Write the electron configuration for argon, atomic number 18. 58. Write the electron configuration for nitrogen, atomic number 7.