* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2 Vocabulary with definitions - Wynter Bounds
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
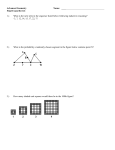
Unit 2 –Angles Vocabulary Study Guide 1. Point- The smallest unit in Geometry used to determine a specific location. 2. Line-An infinite series of connected points 3. Plane-A series of connected points that form an infinitely large flat surface. 4. Ray- Part of a line that has one endpoint and extends infinitely in the other direction. 5. Segment- Part of a line that has 2 endpoints 6. Angle- a figure formed by 2 rays that share a common endpoint 7. Vertex- The point of an angle where the 2 endpoints of each ray meet. 8. Right Angle- An angle whose measure is equal to 90⁰. 9. Obtuse Angle- An angle whose measure is larger than 90⁰, but smaller than 180⁰. 10.Acute Angle- An angle whose measure is less than 90⁰. 11.Straight Angle- An angle whose measure is equal to 180⁰. 12.Vertical Angles- Congruent angles that are formed when two lines cross, and are located opposite of each other. 13.Adjacent Angles- 2 angles that share a common side and common vertex. 14.Complementary Angles- Two angles whose sum is 90⁰. 15.Supplementary Angles- Two angles whose sum is 180⁰. 16.Linear Pair- Two adjacent angles whose sum is 180⁰. 17.Compass- An instrument that is used in constructions to draw circles and arcs with a given radius. 18.Protractor-An instrument that is used to measure angles. 19.Parallel Lines- Lines that have the same slope and will never intersect. 20.Perpendicular Lines- Lines that intersect and form right angles. 21.Transversal- A line that intersects two or more other lines. 22.Slope- The ratio of the vertical change to horizontal change of a line. 23.Construction- To create geometric figures using a compass and straight edge. 24.Angle Bisector- A line or ray that is drawn in such a way that it separates an angle into two congruent angles. 25.Segment Bisector- A line, ray, or segment that is drawn in such a way that it separates a segment into 2 equal parts at the midpoint. 26.Perpendicular Bisector- A line, ray, or segment that is drawn in such a way that it separates a segment into 2 equal parts and forms right angles at the midpoint. 27.Postulate- A geometric statement that is self-evident and does not require proof before using it as a rule for solving problems. 28.Theorem-A geometric statement that requires proof before it can be used as a rule for solving problems. 29.Proof- Using detailed mathematical reasoning to demonstrate that a proposition must be true. 30. Midpoint – The point located in the center of a segment that separates the segment into two congruent parts. 31. Collinear – Points that are on the same line.