* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Report
Mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of calculus wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Secondary School Mathematics Curriculum Improvement Study wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
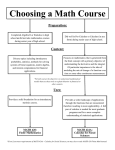
s Title Engineering Mathematics Code FY009 Level 3 Credit rating 20 Prerequisites FY001, AS Maths or equivalent. Type Double module, weekly delivery over one semester. Aims To provide the student with the appropriate mathematical background required for study in a branch of Engineering. Learning outcomes/objectives On successful completion of the module the students should be able to: 1. understand basic concepts within integral and differential calculus; 2. use integral and derivative tools; 3. choose appropriate calculus methods to solve problems relevant to engineering applications; 4. add, subtract, multiply and invert matrices. 5. add, subtract and conjugate complex numbers. Content Differential calculus The concept of a derivative at a point on a curve and as a rate of change. Derivative of xn and axn . Exponential and logarithmic functions and their derivatives. Revision of trigonometric functions and derivatives of sin x, cos x and tan x. Sum, product, quotient and chain rules. Second derivative. Simple applications: maxima, minima and optimisation; curve sketching; velocity and acceleration; models of growth and decay. Integral calculus The definite integral, areas of plane regions. Indefinite integration as the reverse of differentiation and the fundamental theorem of calculus. Simple examples of integration by substitution. Engineering applications of integrals as the limits of sums, e.g. volume, mass, moment of inertia. Matrix methods Notation, addition, subtraction, inversion, determinants. Complex numbers Argand diagrams, conjugation, algebra, polar form, de Moivre’s theorem, Engineering applications. Teaching and learning strategies Lectures and workshops 5 hours per week. The course will be based around the text "Mathematics for Engineers" by A Croft and R Davidson, Addison Wesley. Students will work through the relevant sections of the book under guidance of the tutors. The treatment will be informal and additional learning support will be provided where required through the tutorial system. Taught material will emphasise the use of mathematics to model and solve problems. Suitable use of calculators will be made. Learning support Timetabled tutorial sessions Assessment Two tests under examination conditions, 50% (LO1, 2, 3,4 & 5) End of semester examination 50% (LO1, 2, 3,4 & 5) Brief description of module and/or aims Area examination boards Foundation Year Area Examination Board. Module team/authors (Dr D H Lawrence) / Mr Ian Watts Semester offered 2 Date of first approval July 2000. Date of last revision April 2012. Date of approval of this version May 2012. Version number 3 Replacement for previous module FY009. Field for which module Electrical & Mechanical Engineering Routes. is acceptable and status in that field Course(s) for which module is acceptable and status in course Engineering Foundation Year. School Home School of Computing, Engineering and Mathematics. External examiner Dr. Chak W. Cheung. Compulsory - Electrical and Mechanical routes, Home and EU + English Language.