* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution of IBM Mainframes - People at VT Computer Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
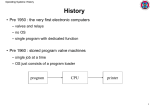
IBM Mainframe Introduction and Job Opportunities Marc Smith IBM System z Channel Enablement zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 © 2005 IBM Corporation IBM Agenda Whose this guy? Why is he here? What is a mainframe & who uses them? Why should I care? What next? 2 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM What is a Mainframe/Who uses them? 40 years of IBM innovation Built from the ground up for business Widely used by businesses of all sizes – Online transaction processing – Batch – WebServing – More… – Data mining 3 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM What is a Mainframe/Who uses them? Quiz? Can you name a company that uses a mainframe? 4 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM What is a Mainframe/Who uses them? Quiz? Can you name a company that uses a mainframe? Do you know what attributes set the Mainframe apart from other platforms? 5 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM What is a Mainframe/Who uses them? Quiz? Can you name a company that uses a mainframe? Do you know what attributes set the Mainframe apart from other platforms? How important do you think they may be to business and governments? 6 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM A Visual Walk Through IBM Mainframe History 7 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM IBM 701 – 1952 1st generation The first IBM large-scale electronic computer manufactured in quantity IBM's first commercially available scientific computer The first IBM machine in which programs were stored in an internal, addressable, electronic memory The first of the pioneering line of IBM 700 series computers, including the 702, 704, 705 and 709 701 8 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM IBM 1401 – 1959 2nd generation The all-transistorized IBM 1401 Data Processing System placed the features found in electronic data processing systems at the disposal of 1402 1401 1403 smaller businesses, previously limited to the use of conventional punched card equipment These features included: high speed card punching and reading, magnetic tape input and output, high speed printing, stored program, and arithmetic and logical ability 9 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 729 IBM IBM 7094 – 1962 7094 2nd generation 10 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM System/360 – Announced April 7, 1964 IBM decided to implement a wholly new architecture specifically designed both for data processing and to be compatible across a wide range of performance levels IBM invested $5B to develop a family of five increasingly powerful computers that run the same S/360-75 operating systems and can use the same 44 peripheral devices with the same architecture 2401 11 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 2311 IBM System/360 – a child is born Hardware – One main storage, maximum size is 16MB – One or two Central Processing Units (CPUs) – One to seven Channels – Control Units (which connect to Channels) – Devices (which connect to Control Units) Family of operating systems – Operating System/360 (OS/360) – Disk Operating System/360 (DOS/360) – TOS, BPS, … – ACP 12 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 S/360 Model 65 Console IBM System/360 Model 67 First IBM system with virtual storage capabilities – S/360 Model 65 with addition of the Dynamic Address Translation facility S/360-67 Operating systems – Time Sharing System – The “official” operating system from IBM Data Systems Division – Control Program/67 with the Cambridge Monitor System – The “unofficial” operating system from the IBM Cambridge Scientific Center “DAT box” University of Newcastle Upon Tyne 13 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM System/370 with Virtual Storage – Announced August 2, 1972 Compatible upgrade from S/370 with virtual storage First multiprocessor models (158MP, 168MP) Family of operating systems 3850 3705 S/370-148 – OS/360 OS/VS – DOS/360 DOS/VS – CP/67 VM/370 3505 14 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 3203 3525 3350 3270 IBM S/370 – the architecture matures Virtual storage – 2KB or 4KB pages of memory – 64KB or 1MB segment sizes – Translation of virtual addresses to real addresses using Dynamic Address Translation (DAT) logic – Segment tables point to page locations 3033 3031 Channel architecture – 256 channels CPU changes – Extended MP support via CPU address 15 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM 9672-G5 System/390 with Enterprise Systems Architecture – Announced September 1990 Evolution of ESA/370 1994 – S/390 Parallel Transaction Server – Family of CMOS processors 1998 – System/390 Generation 5 server – more than 1,000 MIPS 1999 – System/390 Generation 6 server – copper chip technology Common set of peripheral devices – RAMAC, Enterprise Storage Subsystem disk – 3590 Magstar tape Family of operating systems 16 – MVS/ESA OS/390 – VSE/ESA – VM/ESA – Linux for S/390 (December 1999) zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 ES/9000 IBM zSeries with z/Architecture – Announced October 2000 Evolution of ESA-390 zSeries 900 – 24-bit, 31-bit, and 64-bit addressing supported concurrently – z900 – up to 16 processors – z800 – up to 4 processors • Linux-only model in January 2002 • General purpose model in February 2002 – Integrated Facility for Linux on z900/z890 Family of operating systems – OS/390 z/OS – VSE/ESA z/VSE – VM/ESA z/VM – TPF z/TPF – Linux for S/390 Linux for zSeries 17 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM System z9 – Announced July 26, 2005 IBM System z9 109 (z9-109) delivers excellence in large scale enterprise computing and is designed and optimized as the hub of the on demand enterprise Built on more than 40 years as an industry-acknowledged leader and taking that leadership to new levels – Scalability – Availability and security – Balanced system design – Virtualization technology Breaking new ground – Designed to minimize outages to help your business stay always on – Greater scalability and performance to grow with your business – Flexibility to enable efficient response to your business needs 18 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM Touch the technology……. 19 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM z9-109 12-way MCM Advanced 95mm x 95mm MCM – 102 Glass Ceramic layers – 16 chip sites, 217 capacitors – 0.545 km of internal wire CMOS 10K chip Technology – PU, SC, SD and MSC chips – Copper interconnections, 10 copper layers – 8 PU chips/MCM • 15.78 mm x 11.84 mm • 121 million transistors/chip • L1 cache/PU – 256 KB I-cache – 256 KB D-cache • 0.58 ns Cycle Time MSC PU PU MSC PU SD SD PU – 4 System Data (SD) cache chips/MCM • 15.66 mm x 15.40mm • L2 cache per Book – 660 million transistors/chip – 40 MB – One Storage Control (SC) chip PU SD SD PU CLK PU SC PU • • • • 16.41mm x 16.41mm 162 million transistors L2 cache crosspoint switch L2 access rings to/from other MCMs – Two Memory Storage Control (MSC) chips • • • • 14.31 mm x 14.31 mm 24 million transistors/chip Memory cards (L3) interface to L2 L2 access to/from MBAs (off MCM) – One Clock (CLK) chip - CMOS 8S • Clock and ETR Receiver 20 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM Why do you care? Your in the computer science class Your thinking about going to college You want to get a job when you graduate? There are job opportunities being created – One might be right for you! 21 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM Job types 22 Application Programmer Systems Programmer Systems Operator Network Administrator Database Manager Database Administrator Technical Writer Test Specialists Project managers IT Managers CIO More… zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM Twelve zSeries courses 23 Introduction to the New Mainframe Linux on zSeries Introduction to z/VM UNIX System Services (modules) e-business with WebSphere Application Server for z/OS Basic Interfaces: ISPF (self-study modules) JCL Assembler VSAM (modules) z/OS Transaction Management with CICS z/OS Data Management with DB2 An Introduction to IMS zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19 IBM More Information http://www.developer.ibm.com/us/en/university/scholars /products/zseries/index.html – List of participating colleges and universities – Access to this multi-media presentation http://www.ibm.com/zseries – General information about the platform 24 zSeries Expo 2005 Session V51 2005-09-19