* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - Wall ISD
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
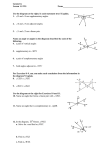
1.3 Objectives Name and classify angles. Measure and construct angles and angle bisectors. An angle is a figure formed by ______ ______, or sides, with a common __________ called the _______________(plural: vertices). You can name an angle several ways: 1. 2. 3. The set of all points between the sides of the angle is the _______________ _________________. The exterior of an angle is _____________________________ _________________________________________________________________________. What are all of the names to this angle? Example 1A A surveyor recorded the angles formed by a transit (point A) and three distant points, B, C, and D. Name three of the angles. Example 1B Write the different ways you can name the angles in the diagram. Remember: when naming an angle using three letters, the center letter should ALWAYS be the vertex!!! The measure of an angle is usually given in ________________. If OC corresponds with c and OD corresponds with d, mDOC = |d – c| or |c – d|. Types of Angles: Acute Between o˚ and 90˚ Right 90˚ Obtuse Between 9o˚ and 180˚ Straight 180˚ Example 2 Find the measure of each angle. Then classify each as acute, right, or obtuse. a) WXV b) ZXW Congruent angles are angles that have the ____________ _____________________. In the diagram ABC = mDEF, so you can write ABC DEF. This is read as “________________________________________________________________________.” ___________ ____________ are used to show that the two angles are congruent. ANGLE ADDITION POSTULATE If S is in the interior of PQR, then mPQS + mSQR = mPQR Example 3A mDEG = 115°, and mDEF = 48°. Find mFEG Example 3B mXWZ = 121° and mXWY = 59°. Find mYWZ. An angle bisector is a ray that ______________an angle into two ______________ ___________________. JK bisects LJM; thus _________________________ Example 4A KM bisects JKL, mJKM = (4x + 6)°, and mMKL = (7x – 12)°. Find mJKM. Example 4B QS bisects PQR, mPQS = (5y – 1)°, and mPQR = (8y + 12)°. Find mPQS. Protractor practice Use a protractor to draw an angle with each of the following measures. a) 33˚ b) 142˚ c) 90˚ d) 168˚