* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Assessment - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
Survey
Document related concepts
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Celestial spheres wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
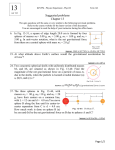
Date: Name: Assessment Class: Chapter 12 Test Chapter 12 BLM 12-5 Goal Assess your understanding of the concepts introduced in Chapter 12. Procedure Answer the following questions. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes each statement. 1. During its orbital period, as a planet moves closer to the Sun, the orbital velocity of the planet ___. (a) increases (b) decreases (c) remains the same 2. According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, the force of attraction between any two masses is directly related to the ___. (a) distance between the masses (c) velocity of the two masses (b) product of the two masses (d) sum of the two masses 3. As the distance between two bodies increases, the force of attraction between the bodies ___. (a) increases (b) decreases (c) remains the same 4. Astronauts in an orbiting space shuttle experience a sensation of weightlessness because ___. (a) the space shuttle is falling freely toward Earth (b) the space shuttle is not affected by Earth’s gravity (c) the mass of the space shuttle decreases as the distance from Earth increases (d) the space shuttle is moving away from Earth 5. The force of gravity exerts a ___ on an orbiting satellite. (a) balanced force (c) tangential force (b) centripetal force (d) all these choices 6. In the diagram below, the pair of spheres that experiences the greatest force of attraction is ___. (a) A and B (b) B and C Copyright © 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited. (c) A and C Date: Name: Class: Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 7. Explain why Kepler was able to use Tycho Brahe’s data about the positions of stars and planets to develop his laws of planetary motion, while Brahe was unable to use the same data successfully. 8. Earth is closer to the Sun in December than it is in July. What happens to the orbital speed of the planet between July and December? Explain your answer. 9. What would happen to the magnitude of the gravitational force between two bodies under the following circumstances? (a) the mass of one of the bodies was doubled (b) the distance between the two bodies was doubled 10. What information do you need to find the period of a planet using Kepler’s third law? 11. The mass of Jupiter is approximately 318 times that of Earth, yet the surface gravity of Jupiter is less than three times the surface gravity of Earth. How do you account for this apparent discrepancy? 12. How does an artificial satellite remain in orbit at a constant distance from Earth’s surface? Answer the following questions, showing your calculations. 13. Which of the pairs of masses below will have the greatest force of attraction between the spheres? 14. Two spheres, each having a mass of 20.0 kg, are positioned so that their centres are 8.00 m apart. What is the gravitational force between the spheres? 15. What will be the force if the spheres described in question 14 are positioned with their centres 4.00 m apart? 16. If the mass of one of the spheres described in question 14 was doubled, how far apart would the spheres have to be to maintain the same gravitational force between them? 17. The distance between Earth and the Sun is often expressed as one astronomical unit (AU). Using this unit, find the distance between the Sun and Mars, which has a period of approximately 686 Earth days. Copyright © 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited. Date: Name: Class: 18. The mean distance between the centre of Earth and the centre of the Moon is 3.84 108 m, and the Moon has an orbital period of 27.3 days. Find the distance from Earth of an artificial satellite that has an orbital period of 9.1 days. 19. The gravitational force between two spheres is 2.50 10–8 N. Their centres are 105 cm apart. The smaller sphere has a mass of 8.2 kg. Find the mass of the larger sphere. 20. An object orbits the Sun at a distance 10 times the mean distance of Earth’s orbit from the Sun. The Sun’s mass is 1.99 1030 kg, and its distance from Earth is 1.49 1011 m. (a) Find the period of the object in years. (b) Determine the speed of the object. Copyright © 2003 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited.