* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Half Term Work On Telescopes and Lenses
History of Mars observation wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy in the medieval Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Year of Astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
Reflecting instrument wikipedia , lookup
European Southern Observatory wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical seeing wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Jodrell Bank Observatory wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
History of the telescope wikipedia , lookup
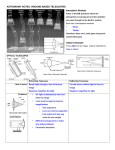
Half Term Work On Telescopes and Lenses 1. “In the simple astronomical refracting telescope the real image produced by a thin converging lens is used as the object for a lens of much shorter focal length” a) In the sentence above explain why it is important to have an eyepiece lens with much shorter focal length. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… b) (I )Draw a ray diagram for the simple telescope in normal operation where the eyepiece lens is 3 times the power of the objective lens (Remember the power of a lens =1/f where f is the focal length of the lens.). 2. a) The Sun subtends an angle of 0.5 degrees at a distance of 149 600 km. Calculate the diameter of the Sun. b) (i) The Closest approach of the planet Mars in recent history was 55 000 000 km. Calculate the angle subtended at the eye on Earth by this planet. (ii) Calculate the the angle subtended by Mars through a simple astronomical telescope 1.5m long with an objective lens of focal length 1.37m 3. “Newton’s great leap forward in telescope design was in part the elimination of chromatic aberration from the image.” Explain how Newton’s telescope eliminated chromatic aberration. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 5 How does a Cassegrain telescope produce a magnification approximately double the magnification of a Newtonian telescope of the same length? ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6. “The purpose of the hyperbolic mirror in the Cassegrain reflector is to correct for spherical aberration due to the primary.” a) What do you understand by “spherical aberration” and how does this differ from “chromatic aberration. b) Why is there no chromatic aberration due to the primary mirror of the telescope? 7. “Infra red telescopes provide a window on the birth of stars” a) Give 3 examples of IR telescopes and where they are sighted giving the reasons. b) Why is it necessary to cool an IR telescope. c) What is “a cold dark nebula” and what is its role in star formation? d) Explain the meaning of the sentence in italics giving reasons for the superiority of infra red astronomy over visible astronomy in this area of study.