* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Economics - Avon Community School Corporation
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Circular economy wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Gross domestic product wikipedia , lookup
Protectionism wikipedia , lookup
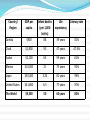
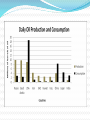
$ Economy A social system that produces, distributes, and consumes goods and services in a society What role do citizens play in the economy? Citizens make money and spend money!!! Their jobs might produce things that are sold and increase the country’s wealth. Their jobs might provide some type of service needed in the country. People buy goods and pay for services which increases the country’s wealth. Income Earned money Poverty Poor People living on less than $2 a day are said to be living in poverty How can people make themselves more valuable so that employers will pay them more??? More education More training More experience Human Capital The knowledge, skills, and experience that make a person more valuable to employers Citizens also save money, too! Believe it or not when an individual saves money that can help the economy as well. How is a country’s economy measured? How do we determine if it’s successful? How much money do they make? (GDP and GNP) Is the country modern? Do they have a lot factories and jobs? (Developed or developing) Is there money worth a lot? Do they sell a lot of stuff? Do the people there have a nice lifestyle? (standard of living) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) The value of all goods and services produced within a country in a year Gross National Product (GNP) The value of all goods and services produced by a country within and outside of the country in a year Includes factories and businesses in other countries GDP per capita How much money there is per person GDP divided by total population GDP per capita If a country has a GDP of $1,000,000 and 1,000 people, what is its GDP per capita? Does $1,000 sound like a lot of money for one person for an entire year? USA Per capita GDP in 2008 was $46,900 We have a high standard of living In regard to possessions, what is life like in the USA? Standard of living Quality of life based on the possession of necessities and luxuries that make life easier We can also use other statistics to evaluate standard of living Health care (death rate, life expectancy, infant deaths, etc.) Literacy rate (how many adults can read or write) Country GDP per capita Life Literacy Rate Expectancy Afghanistan $1,000 45 years 28% China $7,400 74 years 92% Japan $34,200 82 years 99% How does a country and its citizens make money? Agriculture: Farming Industry: Manufacturing (factories that produce goods) Services (service industries or service jobs): Jobs that provide services rather than produce goods Economic Development Developed Countries: Countries that have a great deal of manufacturing and service industries and have high incomes (Examples: US, France, Japan) Newly Industrialized Countries: Countries that are becoming more industrialized by creating new businesses and are moving away from agriculture (Examples: South Korea, Thailand, Singapore) Developing Countries: Countries where most people work in agriculture, there are low incomes, and poverty is an issue (Examples: Sierra Leone, Cambodia, Guatemala) Developed, Newly Industrialized, or Developing??? The United Kingdom GDP per capita $34,800 Breakdown of workers: Agriculture .7% Industry 21.8% Service Industries 77.5% Developed, Newly Industrialized, or Developing??? Togo (West Africa) GDP per capita $900 Breakdown of workers: Agriculture 46.6% Industry 23.4% Service Industries 30% Developed, Newly Industrialized, or Developing??? China GDP per capita $7,600 Breakdown of workers: Agriculture 10% Industry 46.9% Service Industries 43.1% Who helps developing countries? The World Bank An international organization that works to reduce poverty and increase development. The World Bank makes loans to countries to help them become developed Loans for schools Loans for health care Loans for infrastructure Is industrialization a good thing or a bad thing? Harmful Spillovers The negative effects of a country’s economic development Pollution Helpful spillover The positive effects of a country’s economic growth Countries that are more industrialized, have more money to provide people with things like health care and education. What helps a country become industrialized? Infrastructure: Services and facilities necessary for an economy to function (transportation systems, water and sewage, communication systems, etc.) Tolenesia is a very small island country in the Pacific Ocean with a population of only 53 people. Tolenesia produced $10,000 worth of pineapples, $25,000 worth of crab meat, and $18,000 worth of grass skirts in its country in a single year. Tolenesia’s people realized that their dream was to sell grass skirts throughout the world. Tolenesia expanded its grass skirt business by building factories in neighboring island countries. Now, Tolenesia produces $7,000 worth of grass skirts in the neighboring country of Velthousenville, $9,000 worth in Parseystan, and $5,000 worth in Lottland. Country/ Region Life expectancy Literacy rate $900 Infant deaths (per 1,000 births) 88 39 years 81% Chad $1,900 93 47 years 47.5% Sudan $2,100 63 59 years 61% Mexico $10,000 21 75 years 92% Japan $30,400 3.26 81 years 99% United States $41,800 6.5 77 years 97% The World $9,300 50 64 years 82% Zambia GDP per capita Country % of GDP % of GDP from from Agriculture Industry % of GDP from Services GDP per capita Liberia 76.9% 5.4% 17.7% $500 Australia 3.9% 25.6% 70.5% $41,000 In recent decades, Indonesia has been trying to improve its economy. Indonesia has increased trade with its neighbors, developed a huge palm oil industry, and exports or sells over 400,000 barrels of oil a day. While palm oil has helped Indonesia’s economic growth, it has led to vast deforestation. Many of Indonesia’s rainforests have been cut down to make room for palm oil plantations. Indonesia has been trying to ensure that its economy continues to grow by investing in education. In the early 1980’s, Indonesia’s leader decided to set aside a portion of money made from oil each year to build schools and improve education. Today, only 2% of Indonesia’s people ages 15-24 cannot read and the overall adult literacy rate is 90%. Economic System System that sets rules for deciding what goods and services to produce, how to produce them, and who will receive them What to produce? How to produce? For whom to produce? Economic System Market Economy (capitalism or free market) Command Economy (communism) Traditional Economy Decisions are Examples of based on… countries Business owners and USA consumers (supply and demand) North Korea Government and Cuba Native groups Traditions that live in and customs rural areas (Inuit and Mbuti) A MIXED Economy has elements of different economic systems mixed together. (Example: China) China used to be a strictly command economy, but in recent decades China has added free market to its economy. Now, in China businesses and people have more choices. Communism vs. Capitalism Capitalism: You have two cows. You sell one and buy a bull. Communism: You have two cows. The government takes them both and provides you with milk, but it may not be very much milk. An important part of a region’s economy and trade Natural Resources Renewable Resources Nonrenewable Resources Resources that can be Resources that cannot be replaced over time Sun, wind, water, forests, etc. replaced or take a very long time to be replaced Oil (petroleum) Coal Minerals (gold, silver, iron, diamonds) Which resources probably play the biggest role in the world’s economy today? World’s Top Producers Legend Diamonds Gold Petroleum Coal Terms to know Interdependence: Condition that exists when countries rely on each other for ideas, goods, services, and markets Globalization: The development of a worldwide culture with an interdependent economy What is Free Trade? Free Trade: removal of trade restrictions so that goods flow freely between countries Examples of free trade agreements: NAFTA (North America Free Trade Agreement) and AFTA (ASEAN Free Trade Area) Necessary for world trade and travel Exchange Rates 2006 Are most currencies worth more or less than the US dollar????? MCVeggie Burger Combo MEAL 206 Indian Rupees Xbox 360 1,454 Chinese Yuan iPhone 5 in Japan 45,049Japanese Yen McVeggie burger meal in India $5.22 Xbox 360 in China $199 iPhone 5 in Japan $399 Today $1 equals 80 Japanese Yen--- The value of the US dollar has gone down, while the value of the Yen has gone up.