* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Causes of Economic Growth
Survey
Document related concepts
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Italy under fascism wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Consumerism wikipedia , lookup
Okishio's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Marx's theory of alienation wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Rostow's stages of growth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
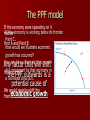
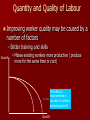
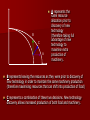
Causes of Economic Growth The PPF model If the economy were operating on it If the economy is working below its frontier frontier Point C. Pont A and Point B How would we illustrate economic growth has occurred? How would we illustrate that growth Any factor that will shift Anyoccurred? movement by that economy in has the PPF outwards is a a northeast direction. potential cause of We would need to shift the economic growth frontier to the right. Factors that shift the PPF New natural resources are discovered, e.g. oil is discovered on the West Coast. Increase in the quantity or quality of labour, e.g. quality- an apple picker begins to pick 5kg more apples in an hour than previously; quantity- more people are employed to pick apples. Investment (capital goods or man-made resources), e.g. more tractors are purchased by the local contractor. Food Discovery and Use of New Resources Show this effect on the PPF. PPF2 This effect shows an increase in the productive capacity of the economy. PPF1 Manufactured Goods This assumes that the new resources that have been discovered are used in the production of both products. Draw on this PPF what it would look like if the new resources discovered were only useful in the production of manufactured goods Food PPF2 PPF1 Manufactured Goods Questions: Good A 1. Show the effect of: – A. a discovery of new corn crops Good B (good a- Cornflakes, good b- Cornbread) – B. a depletion of a recently discovered tree plantation. (good a- furniture, good b- ipod’s) Quality and Quantity of Labour (human) More workers (quantity) – Increase in natural birth rate (over time) – Increased Immigration will have an immediate effect – An increase in labour force participation (decreased unemployment) from the working age population. This could be due to decrease in welfare payments, making working more attractive. Quantity and Quality of Labour Improving worker quality may be caused by a number of factors – Better training and skills Good A Makes existing workers more productive ( produce more for the same time or cost) The effect of improvements in the skills of workers producing good B. Good B Quality and Quantity of Labour (human) Improving worker quality may be caused by a number of factors – Better training and skills Makes existing workers more productive – Reorganisation of production and the workplace Work practices become more efficient – worker productivity increases. – Improved attitudes at work More people are willing to work Increases the labour force participation rate ( proportion of the population that is either employed or looking for work) Also mean workers are happier at their work so productivity increases as a result. Good A Questions Show the effect of: Good B – Previously happy workers who now resent their manager because he/she took away the privilege of having tea and coffee at break time (this manager is in charge of producing lego) (good a- lego, good b- barbies) – Immigrants coming into NZ who have skills in making clothes (good a- dresses, good b- track pants) Investment (physical) Investment = more capital goods (man-made resources used to produce goods and services) More investment means productive capacity of the economy has increased e.g. investment is additional machinery or plant (these aren’t necessarily being used yet but the ability to produce more has increased). Investment Influenced by two key factors – Interest rates – Business confidence and expectations Interest rates are the cost of borrowing Higher interest rates will reduce the amount of investment that will occur in the economy. But if interest rates fall producers are likley to undertake more investment Key terms to memorise Investment – Firms using bank loans to purchase capital goods Physical investment – Purchase of capital goods (Capital formation) Human investment – Training, skill improvement qualifications of workers Productivity – Output relative to input. Rate of production Resources – Endowments/inputs used in production Technology An improvement in method or resource use (a.k.a innovation) – E.g. a machine to print out receipts for paying customers instead of hand writing. Technology enables productivity levels to increase as well as more efficient use of resources. – Tasks can be completed faster, using resources more efficiently (less wastage: time, cost, resources etc) Key terms Technology- New innovative methods that improve ways of doing things. Productive capacity – Maximum possible potential output Opportunity cost of consumption Present consumption means firms sell more (increasing confidence/profits increase in output = GDP) Present saving means decreased consumption, leads to firms selling less. Firms then reduce output which leads to GDP decreasing. Capital vs. Consumer goods NOTES to stick in. More consumer goods produced NOW means less capital goods. This is great for the present but this restricts FUTURE growth. More capital goods produced NOW means we can produce more consumer goods in the future. This will shift the PPC out further than if we increase consumption in consumer goods. Imagine that the economy has resources that it’s technology are unable to use. Example: Iron sands (used to produce steel) are unable to be used because of impurities given fixed technology. Say they come across new technology that enables them to use the iron sands as it is already to produce steel. Since the economy can now produce more machinery, they are also able to produce more food…how can this be? B C A A represents the same resource allocation prior to discovery of new technology (therefore taking full advantage of new technology to maximise extra production of machinery. B represents leaving the resources as they were prior to discovery of new technology in order to maintain the same machinery production (therefore maximising resources that can shift into production of food) C represents a combination of these two decisions. New technology discovery allows increased production of both food and machinery.