* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab2: Oscilloscopes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
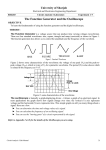
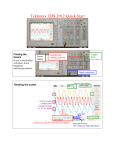
Name: Due Date: Grade: ECE 2006 LABORATORY 2 OSCILLOSCOPE X AND Y AXIS Pre-Lab Calculations: None Objectives The learning objectives for this laboratory are to give the student the ability to: Use the oscilloscope vertical and horizontal position, sensitivity, and coupling controls. Use the oscilloscope to measure voltages. References Digital Oscilloscope TDS 3012 B Series Reference Manual Background This lab presents the basic controls of the oscilloscope. The oscilloscope can operate in either X-Y mode or in time base mode. In this lab the oscilloscope is operated in X-Y mode, which makes it similar to a piece of graph paper. There is an X channel and a Y channel on the oscilloscope. If only one is turned on then a one-dimensional graph will be displayed, whereas if both channels are on then the graph will be two-dimensional. The Vertical Menu has options to control the beam position, sensitivity, and coupling. The beam position control internally adds a DC offset voltage to the input voltage. This is used to move the display without changing the characteristics of the input. The sensitivity controls set the display scaling, specifying the number of volts per division in the graticule. The coupling control has three positions DC, AC and ground. In the DC position the scope will display the voltage for all frequencies from DC up to the scopes upper limit, typically 50 to 100 MHz. The AC position will filter out the DC component of the input signal. This has application when you want to observe a small AC signal superimposed on a large DC signal. The ground position replaces the input with 0 volts. This is useful when adjusting the beam to a 0 volt reference position. Note: The scope can also automatically set the 0 volt reference to the middle of the screen. Tip: The Quick menu sumarizes the important information about the scope channels. To change which channel is displayed, just press the channel selector button (yellow or blue). Equipment Digital Oscilloscope TDS 3012 B Series Function Generator Power Supply Resistor Capacitors Procedure 1. Y axis beam deflection. 1.1: Using the Oscilloscope in XY mode. - turn channel 1 OFF and turn channel 2 ON - Press the Display menu button - At the bottom there is a button that says “XY display”. Right now it should say “OFF”, select it. On the right side of the screen select “Triggered XY” to put the oscilloscope into XY mode. 1.2: Referencing the scope. In order to understand what is being displayed on the screen, there needs to be a reference point, a place where we define the voltage to be a specific value. Ground is the easiest. - Press the Vertical Menu button - Press the “Coupling button” - Select Ground from the options on the right side of the display - Use the Vertical position knob to move the ground to –4.00 divisions 1.3: Now that there is a reference point, there still needs to be a way to determine what voltage is being displayed, this is done by selecting the number of volts per division. - Press the Vertical Menu button - Press the “Fine Scale x/div” - Use the Vertical Scale knob to select 2 volts per division 1.4: Next connect the power supply to Channel 2 of the oscilloscope using a BNC to alligator clip connector. - Set the power supply to 10 volts. Notice that your dot has not moved. This is because the oscilloscope is still grounded. To allow the oscilloscope to take measurements return to the Vertical Menu, choose the “Coupling button” and choose “DC” from the options on the right. - Use the oscilloscope grid to measure the amplitude, to the nearest tenth of a volt, of the power supplies output. Have your Lab Instructor verify this measurement: _________________________ 2: Square Wave. 2.1: Connect the function generator to channel 2 of the oscilloscope using a BNC to BNC connector. Press the “FREQ” button on the function generator Set to 1.00 Hz. Use the knob to change the value of the selected precision. Use the > < buttons to change the precision. - Press the square wave button - Press “AMPL” button to adjust the amplitude of the square wave. - Use the knob and > < keys to set 3.0 Vp-p - Press “OFFSET” and adjust to 0.00 V DC Ground the oscilloscope to 0.00 divisions Return the oscilloscope to DC mode Adjust the function generator to 10.00 Hz (press the “Frequency” button) Adjust the function generator to 100.00 Hz - 2.2: 2.3: 2.4: 2.4: Have your Lab Instructor verify this measurement: _________________________ 3: Sinusoidal Wave. 3.1: Select a “SINE” wave on the function generator. - Adjust the function generator to 2.5 Vp-p. - Adjust the function generator to 1.00 Hz. - Adjust the function generator to 10.00 Hz. - Adjust the function generator to 100.00 Hz. Notice the output is alternating between two voltage levels, however between the time delay on the screen and the time delay in your eye, you observe a straight line between +2.5 volts and –2.5 volts. - Save this screen image to foppy disk for use in a report. Have your Lab Instructor verify this measurement: _________________________ 4: X axis beam deflection. 4.1: Switch the BNC connector from channel 2 to channel 1. Turn channel 1 ON and channel 2 OFF. 4.2: Ground channel 1 to 0.00 V. 4.3: Set the Volts per Division to 1 V / div. 4.4: Return to DC mode. 4.5: Adjust the function generator to a 1.00 Hz, 3 Vp-p SINE wave with no DC offset. - Adjust to 10.00 Hz - Adjust to 100.00 Hz Have your Lab Instructor verify this measurement: _________________________ 5: X-Y axes. 5.1: Ground both channels to 0.00 div, so that the dot is in the center of the screen. Connect the output of the function generator to both channel 1 and channel 2. - Adjust the function generator to a 1.00 Hz, 3 Vp-p SINE wave with no DC offset. - Adjust the function generator to a 10.00 Hz. - Adjust the function generator to a 100.00 Hz. Have your Lab Instructor verify this measurement: _________________________ 6: Circle. 6.1: Connect the circuit in figure 1. Figure 1. π/2 radian phase shifting circuit 6.2: Adjust the function generator to 100.00 Hz. 6.3: Adjust the oscilloscopes sensitivity (V/div) to obtain a circle with a radius of three divisions. 6.4: To reduce noise, select bandwidth limit of 20 MHz - Press the Vertical Menu button. - Select “Bandwidth” from the menu on the bottom. - Select “20 MHz” from the options on the right. 6.5: Save this screen image to foppy disk for use in a report. Have your Lab Instructor verify this measurement: _________________________ 7: Ellipse. 7.1: Connect the figure shown in Figure 2 below: Figure 2. Phase shifting circuit 7.2: Adjust the function generator to 100.00 Hz. 7.3: Adjust the oscilloscopes sensitivity (V/div) to 1 V/div on both channel 1 and 2. 7.4: Save this screen image to foppy disk for use in a report. Have your Lab Instructor verify this measurement: _________________________ Conclusions: Include screen captures in report and explain what function of the oscilliscope you found easy or difficult. Also, explain what results you saw for each section of the lab.