* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic 5 Problem Set
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Battery charger wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
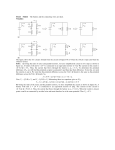
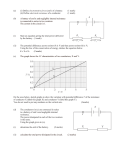
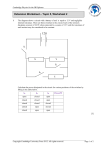
Topic 5 - Problem Set Do your homework on a separate piece of paper, or in a notebook of some kind. Written work and answers on this sheet will not be counted. Show all your work including formulas and substitutions. Minimum credit will be awarded for answers without work. Topic 5.1.2 1. A +85 C charge is moved from an electric potential energy of 1.0 J to an electric potential energy of 6.0 J. Through what potential difference was it moved? 2. How many electrons are in -85 C? Topic 5.1.4 3. A voltmeter records the displayed potential difference when the leads are placed across a battery. What is the raw uncertainty in the measurement? 2.45 4. A voltmeter records the displayed potential difference when the leads are placed across a battery. What is the fractional error in this measurement? 5. An electron passes through the potential difference shown. What will its energy change be, in electron volts? 6. An electron is accelerated in a vacuum through the potential difference shown. What will its speed be at the end of that acceleration? Topic 5.1.6 7. A voltmeter records the displayed potential difference when the leads are placed across a 330 resistor. What is the current passing through the resistor? 6.45 8. How much charge passes through the resistor in exactly 1.0 minute? 9. How much electrical energy is required to pass the charge you found in (8) through the resistor? Topic 5.1.7 10. A carbon-core resistor consists of a carbon rod having a length of 3.25 mm, a diameter of 0.0350 mm and a resistivity of 350010-8 m. What is the value of the cross-sectional area of the carbon rod. Be sure your answer is in m2. 11. What is the resistance of the carbon rod? 12. If a current of 2.25 A passes through the resistor, what is the voltage across the resistor? Topic 5 - Problem Set Topic 5.1.9 13. An unknown material has the V-I characteristics shown in the graph. What is the resistance of the material when the current is 0.6 mA? 14. What is the resistance of the material when the current is 0.8 mA? 15. What is the resistance of the material when the voltage is 1.8 V? 16. Is this material ohmic? Explain. Topic 5.1.10 17. Using the same graph answer the following questions. What is the power dissipation of the material when the current is 0.6 mA? 18. What is the power dissipation of the material when the current is 0.8 mA? 19. Using P = VI and Ohm’s law (V = IR) prove that P = I2R. 20. Using P = VI and Ohm’s law (V = IR) prove that P = V2/R. 21. Using the fact that power is energy divided by time, prove that P = VI. Topic 5.1.11 22. A filament lamp has a rating of 5.0 W. While the bulb is lit, the meter displays the value shown. What is the power dissipation of the lamp? 2.75 23. What is the current in the lamp? 24. What is the resistance of the lamp? 25. Is the meter in series, or is it in parallel? Topic 5.2.2 26. A cell has an unloaded potential difference of 1.45 V. A 330 resistor is connected as a load as shown in the picture. The meter shows the new p.d. What is the emf of the cell? 27. What is the current through the resistor? 28. What is the internal resistance of the battery? 1.31 Topic 5 - Problem Set 29. Explain what emf stands for, and in words, what in general is the emf of a cell? 30. What is the rate at which heat is being produced in the in the 330 resistor? 31. What is the rate at which heat is being produced in the battery? 32. What is the rate at which chemical energy is bring converted to electrical energy in the cell? Topic 5.2.4 33. A series circuit powered by an ideal battery (no internal resistance) is shown. What is the total or equivalent resistance of this circuit? R1 220 R2 2100 R3 4500 6.0 V 34. What is the current through this circuit? 35. What is V1, the p.d. across R1? 36. What is V2, the p.d. across R2? 37. What is V3, the p.d. across R3? 38. What do you notice about the sum of the three voltages? R2 R3 4500 2100 R1 220 39. A parallel circuit powered by an ideal battery (no internal resistance) is shown. What is the total or equivalent resistance of this circuit? 40. What is the current through the cell? 41. What is I1, the current through R1? 42. What is I2, the current through R2? 43. What is I3, the current through R3? 44. What do you notice about the sum of the three currents? 45. A combination circuit powered by an ideal battery (no internal resistance) is shown. What is the total or equivalent resistance of this circuit? 46. What is the total current through this circuit? 220 R1 2100 R2 4500 R3 6.0 V 6.0 V Topic 5 - Problem Set 47. With different colors sketch in all the currents. There are only two of them! 48. What is the current in R1? 49. What is the voltage across R1? 50. In light of the fact that the voltages along a current loop must add up to the battery voltage, what are V2 and V3? 51. What, then, are I2 and I3? Topic 5.2.6 52. A series circuit powered by an ideal battery whose emf is 6.0 V is shown in the schematic diagram. Label VOUT and VIN in this circuit. R1 53. Suppose the value of R1 is 1600 . If we would like to “tap” 2.5 V at VOUT what should the value of R2 be? R2 54. Suppose the value of R2 is 1600 . If we would like to “tap” 2.5 V at VOUT what should the value of R1 be? 12 4.0 2.0 Topic 5.2.8 55. The emf of the ideal battery is 6.0 V. What does the voltmeter read? 56. What does the ammeter read? 57. The emf of the ideal battery is 6.0 V. What does the voltmeter read? 2.0 58. What does the ammeter read? 59. Three circuits using identical cells and resistors are shown here. Which one has the highest resistance? 60. Which one has the highest current? A 12 4.0 B C