* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Demand Curve Shifts
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
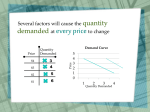
LAW OF DEMAND When price goes up quantity demand decreases, and when price goes down quantity demanded increases Several factors will cause the quantity demanded at every price to change $4 1 3 $3 2 4 $2 3 5 $1 4 6 Price Price Demand Curve Quantity Demanded 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 Quantity Demanded 4 Can you come up with the 5 factors economists have identified that would cause this increase in quantity demanded at every price? What Causes the Demand Curve to Shift? Five factors cause the demand curve to shift: • TINER! • Changes in tastes or preferences • Change in income • Change in the number of buyers in the market • Change in expectations • Change in the price of of future price related goods Demand Curve Shifts If demand for a good increases the demand curve to the right. If demand for a good decreases the demand curve to the left 1. Tastes or Preferences Jennifer Aniston advertises for Smartwater. 2. Income Description: • As income changes, people may buy more or less of a particular good—BUT it depends on the type of good it is As it turns out, those were the droids you were looking for. Change in Income Cont. Suppose you got fired—what will happen to your consumption of these? Change in Income Cont. Normal goods are goods for which the demand rises as income rises and falls as income falls Change in Income Cont. Suppose you got fired—what will happen to your consumption of these? Change in Income Cont. Inferior goods are goods for which the demand falls as income rises and rises as income falls Change in Income Cont. Suppose you got fired—what will happen to your consumption of these? Change in Income Cont. Neutral goods are goods for which the demand remains unchanged as income rises or falls 3. Number of Buyers in the market • The demand for a good in a particular market area is related to the number of buyers in the area 3. Number of Buyers in the market • The demand for a good in a particular market area is related to the number of buyers in the area Description: The more buyers, the higher the demand • The fewer buyers, the lower the demand 4. Expectations of Future Price 4. Expectations of Future Price If you were looking to buy a house in Seattle and read this, what would you do? 4. Expectations of Future Price Description: • Buyers who expect the price of a good to be higher in the future may buy the good NOW, thus increasing the current demand • Buyers who expect the price of a good to be lower in the future may WAIT until the future to buy the good, thus decreasing the current demand for the good 5. Prices of Related Goods Demand for goods is affected by the prices of related goods • Price of Peanut Butter Increases • What happens to the demand for jelly? 5. Prices of Related Goods Demand for goods is affected by the prices of related goods • Price of Hot Dogs Decreases • What happens to the demand for hot dog buns? 5. Prices of Related Goods Description: • Complements are goods that are consumed jointly with another good. • With complements, the price of one and the demand for the other move in opposite directions • P of peanut butter • P of hot dogs demand for jelly demand for hot dog buns 5. Prices of Related Goods Demand for goods is affected by the prices of related goods • Price of Donuts Increases • What happens to the demand for Danishes? 5. Prices of Related Goods Demand for goods is affected by the prices of related goods • Price of Apples Decreases • What happens to the demand for oranges? 5. Prices of Related Goods Description: • Substitutes are similar goods. • With substitutes, the price of one and the demand for the other move in the same direction • P of Donuts demand for Danishes • P of apples demand for oranges