* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.1 - Cornell Math
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
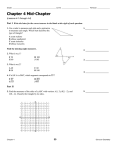
2.1 Shape Explorations Experiencing Geometry on a Unitless Plan 10/16-17/08 Topic: The students are given an opportunity to put their own flavor into their math journal. Thus far the students have copied many of the notes that I have given them and not been able to create their own pages in their notebooks. The two days budgeted for this lesson is to allow the students to perform some research using the collection of math text books in the classroom. The students are given a list of geometry words that would come in handy to be conversational with and then allowed to research them and take notes for each. Student Goals Learn to use math textbooks as a resource. Learn to divide work among each other in groups. Teacher Goals Keep students focused and on task during this group activity. Guiding Questions -How can we group this information into more manageable chunks? Skills: Expected - To Be Learned Materials List: - Math Text Books -Math Note Books -List of vocabulary words Overview: -(10-15 min) Students enter and begin working on their warm up. -(5 min) The teacher introduces the activity and tells the students some things to look for. He emphasizes that this is a time to make the notebook their own and there are many ways of doing this assignment. He also stresses the concentration on the organization of the information they are finding. -(rest of class and into the next day) The students use math textbooks from around the room to look up key vocabulary and concepts and then place them in their notes. Notes: Things that went well/did not go so well and memorable moments. Shape Exploration: In Your notebook, using the resources available in the room find the definitions/become familiar with the following terms and ideas. Be familiar with the ideas first because there will be questions to be interspersed in your notes that are expected to be answered. This is your time to do some research about geometry and organize it in your notes in a way that works for you. If you want to keep all the definitions in the glossary, that is fine. If you want to make a section for each shape and list the properties of that shape that is also fine. Also keep in mind that it is the intention to use the properties of these shapes and ideas to explain how/why certain constructions can be built. Terms and Ideas:(in no particular order) Angle Quadrilateral Circle Rhombus Obtuse Rectangle Hexagon Radius Right Triangle Trapezoid Equilateral Polygon Triangle Scalene Parallelogram Acute Square Center Right Angle Parallel Isosceles Chord Questions to be answered through this exploration: If you had a little brother, how would you describe to him what an angle is? What does it do? Do you think a circle is a polygon? Why or Why not? When looking at a triangle what is the most important feature describing its shape? Why? Why is a line segment not considered a polygon? Do you think it is possible to have an “any number sided-gon” (n gon)? Example: Hexagon has six sides, Does one exist for every number? Definitions for Section 2: Angle- A pair of rays that have the same endpoint Quadrilateral- A four sided polygon Circle- The set of all points in a plane that are a given distance from a point in the plane Rhombus- A quadrilateral all of whose sides are equal Obtuse Angle- An angle whose measure is more than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees Obtuse Triangle- A triangle that has an obtuse angle Rectangle- A quadrilateral each of whose sides is a right angle Hexagon- a polygon that has six sides Radius- The distance between the center of a circle and any point on it Right Triangle- A triangle that contains a right angle Trapezoid- A quadrilateral that has exactly one pair of parallel sides Equilateral Triangle- A triangle whose sides are all equal Polygon- A connected set of at least three line segments in the same plane such that each segment intersects exactly two others, one at each endpoint. Triangle- A polygon with three sides Scalene Triangle- A triangle whose sides are each a different length Parallelogram- A quadrilateral whose opposite sides are parallel Acute Angle- An angle whose measure is less than 90 degrees Acute triangle- A triangle all of whose angles are acute Square- A quadrilateral all of whose sides and angles are equal Center- A point or place that is equally distant from the sides or outer boundaries of something; the middle Right Angle- An angle whose measure is 90 degrees Parallel- Lines that lie in the same plane and never intersect Isosceles Triangle- A triangle that has at least two equal sides Chord- A line segment that connects two points on a circle