* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10 – Reconstruction Debate Over Reconstruction SECTION
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
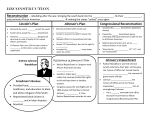
Chapter 10 – Reconstruction Debate Over Reconstruction SECTION 1 Lincoln’s Plan - Moderate policy that would reconcile Southerns with Union instead of punishing them for treason - Offered a general amnesty to all Southerns who took a oath of loyalty to the United States and accepted the unions proclamation concerning slavery - Only people not voted pardon -1 -2 -3 - Resistance to Lincoln’s plan - Radical Republicans – did not want to reconcile with the South - 1) wanted to prevent leaders of Confederacy form returning to power (after the war) - 2) wanted Republican party to become a powerful institution in the South - 3) wanted federal gov’t to help African Americans achieve political equality by guaranteeing their right to vote in the South - Number of Republicans thought Lincolns plan was too lenient but that radicals were too supporting of African Americans - The Wade-Davis Bill - Required majority of adult white males in former Confederate states to take an oath of allegiance to the union - Each states convention would have to abolish slavery - Reject all debts the state had acquired as part of the Confederacy - Deprive all former Confederate gov’t officials and military officers of voting or hold office - Lincoln would pocket-veto, he wanted “no persecution, no bloody work” - Freedmen’s Bureau - Started when thousands of freed African Americans began following Union troops seeing food and shelter - To feed themselves, Sherman reserved abandoned land for the use of freed African Americans - Congress established Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abolished Lands – Freedmen’s Bureau - Helped get them clothes and find work - Johnson Takes Over - Took over after Lincoln was assassinated and remained loyal to North - His plan resembled Lincoln’s - May 1865 he issued an amnesty proclamation - 1. - 2. - 3. - Same day of pardon, Johnson issued another proclamation for North Carolina - It became a model of how he wanted to restore the South to the Union 1. 2. 3. •Next Congress session in Dec. 1865, Many Congressmen were angered that Southerner voters had elected former Confederate soldiers to Congress - Southern state legislature also passed black codes which severely limited African Americans rights - Black codes varied by state, seemed to have same conditions as slavery - 1. 2. 3. Radical Republicans Take Control - Late 1865, House and Senate Republicans created a Joint Committee on Reconstruction - Goal to develop their own program for rebuilding the Union - Effort to override black codes, Congress passed the Civil Rights Acts of 1866 - Granted all persons born in U.S. Citizenship besides native Americans - Blacks own property and Treated equally in court - Fourteenth Amendment -Granted citizenship to all persons born or naturalized in the U.S. and declared that no stat could deprive any person of life, liberty, or property law” - Also declared that no state could deny any person “equal protection of the - March 1867, Congressional Republicans passed the Military Reconstruction Act - Divided former Confederacy into 5 military districts each having a Union general in charge - Each state had to create new state constitution giving all adult male citizens the right to vote regardless of race - After state ratified their constitution it had to ratify 14th Amendment before it would be allowed to elect members to Congress - By end of 1868, 6 former Confederate states me all requirements and were readmitted to the Union - Republicans were taking control and wanted to keep it that way - They distrusted President Johnson and wanted to keep Johnson from interfering with their plans - Republicans kept trust with Grant and Stanton-Secretary of War - Congress passed Command of the Army Act - Required all orders from the President to go through the headquarters of the general - And tenure of Office Act - Required the Senate to approve the removal of any government official whose appointment had required the Senate’s consent - Johnson wanted to challenge the Tenure Act and fired Stanton - House voted to impeach Johnson for breaking the law by refusing to uphold the Tenure Act - He would go to trial and be found not guilty by the Senate - Some Republicans joined Democrats in refusing to convict him because the president did not agree with Congressional policies - Johnson would stay in office but not run to be re-elected – Grant would be voted into office in 1868 - Republicans now had majority in Congress and a president they trusted - The Fifteenth Amendment - Declared the right to vote “shall not be denied…on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude.” - Radical Reconstruction impacted the South in the short term brought African Americans into political process and changed Southern society SECTION 2 Radical Rule - Lots of resistance from white Southerners who did not like the overtaking of Republicans in South because the party included Northerners and African Americans - Also believed the Union Army forced new Republican government on them - Many Northerners moved down South 1. 2. 3. - Southerners called Northern newcomers carpetbaggers because they viewed them as intruders seeking to exploit the South - Southerners also disliked other Southerners who supported reconstruction – called scalawags - Scalawags were: 1. 2. 3. - African Americans gained political power as well after the pass of the 15th Amendment - Won local election up to serving in both houses of Congress - Republican Reforms --Positive --Negative 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. - African Americans worked to improve their lives in many ways - Churches, education, and other organizations to support each other - Southerners were unhappy with “Black Republican” government - Southerners were unable to openly strike at the Republicans running their state – organized secret societies - Ku Klux Klan (KKK) – largest group – formed by former Confederate states - Goal – drive out carpetbaggers and intimidate black voters so as to regain control of the South for the Democratic Party - Some Republicans and African Americans organized groups to fight back - As violence increased the federal government would step in - Congress passed 3 Enforcement Acts 1. first act made it a federal crime to interfere with a citizens right to vote 2. put federal elections under supervision of federal marshals 3. Ku Klux Klan Act – outlawed the activities of the Klan SECTION 3 Reconstruction Collapses The Grant Administration - Grant believed the President should only carry out laws and leave development of policy to Congress. Radical Republicans were pleased but this left the President weak and have ineffective power. - Republican control in Congress expanded programs put in place by Reconstruction 1. 2. 3. - Democrats would attack Republican economic policies and have Liberal Republicans agree with them - Grant would win re-election despite the Democrats push for a new President - Series of scandals would hurt Grants second term – all over money - the Panic of 1873 - economic crisis - from scandals and economic depression the Democrats would win back control of the House of Representatives Reconstruction Ends - rising power of the Democrats made enforcing Reconstruction difficult - 1870s Southern Democrats had regained control of local and state governments from Republicans - they won back control by intimidation 1. 2. The Compromise of 1877 - new election – Grants reputation damaged, Republicans nominated Rutherford B Hayes – Democrats nominated Samuel Tilden - On Election Day 184 votes - Tilden; 165 – Hayes - 3 states had so much election fraud the winner was unclear - to solve issue – Congress appointed 15 persons commission made up equally of members of the House, Senate and Supreme Court - vote was 8 to 7 – Southern Democrats joined Republicans and voted to accept the commission’s finding - deal was made giving Hayes the win, election would be known as the Compromise of 1877 - from it Republicans promised to pull federal troops out of the South - from pulling troops out caused the last Republican government in South to collapse and Democrats “redeemed” South – ending Reconstruction - “New South” created - develop a strong industrial economy - powerful white Southerners and Northern financiers brought great economic changes 1. railroads 2. Iron and steel industry 3. Tobacco processing 4. Cotton mills - collapse of Reconstruction ended blacks hopes of getting their own land - many went back to plantations and worked for wages or became tenant farmers - some became sharecroppers - this would trap some African American into debt and limited rights