* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.4 Notes
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
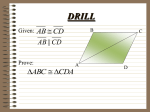
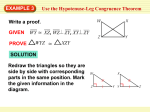
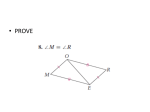
Geometry notes 5.4 Hypotenuse-Leg Congruence Theorem (HL) Hypotenuse-Leg Congruence Theorem (HL): If the hypotenuse and a leg of a right triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and a leg of a second right triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. If D A ABC and DEF are right triangles, and AC and DF , and BC EF , then ABC ≅ DEF . B Using the HL Theorem: J K G H C E F Example: Is it possible to show that JGH HKJ using the HL Theorem? Explain your reasoning. In the diagram, we are given that JGH and HKJ are right triangles. By the Reflexive Property, we know JH JH (hypotenuse) and we are given that JG HK (leg). We can use the HL Congruence Theorem to show that JGH HKJ . Example: Use the diagram to prove that PRQ PRS . S P R Given: PR SQ and PQ PS Q Prove: PRQ PRS Statement Reason ____________________________ 1. PR SQ 1. Given 2. PRQ and PRS are right angles 2. lines form rights angles 3. PRQ and PRS are right 's 3. Def. of right triangle 4. PQ PS 4. Given 5. PR PR 6. PRQ PRS 5. Reflexive Property 6. HL Congruence Theorem