* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Y9 prob practice testA
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
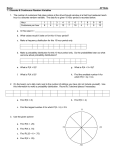
Probability REVISION Name ____________________ Level 2 Probability: Understand probability terms (unlikely, even chance, certain, impossible, likely) Understand the probability scale ( Never ----------- Certain) Calculate one stage probabilities eg. P(6 on a dice) Calculate probabilities from simple summary tables 1) All of the letters of the word atawhai are written on separate pieces of paper and put in a bag. Without looking you take out at letter. What is the probability that you choose: a) a _____________________ b) w _____________________ c) i or t _____________________ 2) What is the probability that the spinner will land on a. b. c. d. 3) The weather forecast for Nelson says that the probability of rain tomorrow is 0.8 Should you bring an umbrella to school with you tomorrow? Explain. (hint; words such as likely, very likely etc may be helpful.) 4) Describe the probability of each situation happening as either Impossible Unlikely Possible Likely Certain and give a decimal value. Eg. Probability that… You will see a teacher with dark hair today 1. It will rain tomorrow in Nelson 2. It will rain tomorrow somewhere in the world 3. You will write on paper today 4. You will sit on paper today 5. You will write a book one day 6. You will work at a supermarket one day 7. You will be a builder one day 8. You toss a coin and get heads 9. You have a birthday party within the next year 10. You get a new family pet within the next year 5) Word Likely Decimal 0.9 For each situation, write down the sample space and find the theoretical probability. Level 3 Probability: Use probability terms (unlikely, even chance, certain, impossible, likely) Use the probability scale ( Never ----------- Certain) Calculate one stage probabilities eg. P(6 on a dice) Calculate probabilities from simple summary tables Simple models of situations (which could be good, poor or not possible) 6) Angie, Afi and Alex did an experiment where they counted the number of jellybeans of each colour in 12 different packets. They put all the results together as follows : Colour blue black yellow red green orange purple pink No of jellybeans 28 18 25 25 20 19 17 8 a) What was the probability, in their experiment, of getting a black jellybean ? b) How many black jelly beans would you expect to get if you had 1600 jellybeans ? c) How many black jelly beans would you expect to get if you had 5000 jellybeans ? (2 marks) 7) The school nurse tested the blood type of 200 year 9 students at Rainbow High School. The results are shown in the table: Blood type 0+ 0- A+ A- B+ B- AB+ AB- Frequency 76 14 68 12 18 4 6 2 A year 9 student is chosen at random. What is the probability that the student will have blood type: a. 0+ ____________________ b. B- ____________________ c. A+ or A- ____________________ d. that is positive (+) e What is the sample space for this situation? ___________________ Level 4 Probability: Estimate probabilities from experiments Calculate probabilities from two stage events eg P(Total of 12 when rolling two dice) Recognise events that are not equally likely Calculate probabilities from summary tables of experiments Understand independence concept (eg result of one coin does not influence the next) Compare experiment to theoretical probabilities Use systematic methods (such as tree diagrams) to list outcomes Understand that increasing the number of trials will lead to more accurate estimates of probabilities 6 Second dice 8) Paul and Pippa are playing a game of monopoly, in which two fair dice are tossed together. The total of the two numbers showing on the dice are used to make a move. 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 First dice 5 6 a) What total does each dot in the shaded strip stand for : __________ b) What is the probability of throwing a total of 4? c) Use the diagram above to help you complete the table. Total on dice 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Probability __________ a) What is the chance of getting a total of 3? 0 b) What is the chance of a total of 5? c) Which total(s) have the least chance of happening? d) Which total(s) have the most chance of happening? 9) Laurie, Lester and Lauren each toss a coin. H= head, T= tail a) Finish the tree diagram to show the outcomes Laurie’s coin Lester’s coin H ● T b) List the outcomes c) What is the probability of getting 3 heads ? Lauren’s coin Outcomes d) What is the probability that exactly two of the coins show heads ? 10) Label or colour the spinner shown to make the following statements true a. b. c. d. Probability of red is 0.1 Probability of yellow is 0.4 Probability of blue is 0.3 Probability of green is 0.2 11) impossible certain Indicate where these events A , B , C and D should lie on the scale above A tossing a coin and getting a head __________________________ B getting a number less than 2 on the roll of a standard dice ______________________ C it will snow in Nelson on Christmas day ________________________ D that it will rain again in Nelson before the end of the year ______________________ Level 5 Probability: Compare probabilities between an experiment and theory Calculate probabilities from three stage events eg P(Total of three spins on a spinner) Recognise haw changing an event can increase or decrease the probability of outcomes Calculate probabilities from summary tables and comparing experiments Understand independence concept (eg result of one coin does not influence the next) Compare experiment to theoretical probabilities Use systematic methods (such as tree diagrams) to list outcomes 12) Yvonne and Yori are playing a game using four sided dice. The two regular tetrahedron dice (shown below) are rolled and their scores added together. a) Fill in the table of possible outcomes 9 7 0 2nd dice 0 4 The hidden numbers on the first dice are _____ and _____ And on the second dice are _____ and _____ Yvonne wins if she gets a total under four What is her probability of winning _________ 1 5 3 First dice (2 marks) 13) Emma and John are talking about starting a family. They want to have 3 children. Complete the tree diagram below to show the different possibilities for the sex of the 3 children. a. First child second child third child outcome B G b. How many combinations (outcomes) are possible? _______________________ What is the probability that: c. Emma and John have 1 boy ______________________ d. Emma and John have at least 2 girls____________________ 14) A standard pack of cards has 4 suits, (Hearts, Clubs, Diamonds, Spades) Each suit has : Ace, 2, 3k, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, Jack, Queen, King Picture cards are Jack, Queen, King, Ace. 1 How many cards are in a standard pack ? 2 How many picture cards are in a standard pack ? If you are given 1 card at random from a standard pack what is the probability that it is 3 the 5 of clubs 4 an Ace 5 a diamond 6 a picture card 7 a club or a spade 8 a heart or a picture card 15) Rachael, the president of the Nelson Women’s Soccer Association kept a record of the number of goals scored in each game in the women’s league. The results are recorded below: # of goals Frequency 0 2 1 16 2 32 3 19 4 5 5 2 6 3 7 1 Relative frequency Total a. How many games were played in total? b. Complete the relative frequency column in the table c. In how many games were less than 3 goals scored? 16) If in 2001 the number of teams in the league increases from 8 to 10 and assuming that the 2000 season is similar to other seasons, calculate the expected number of times that d. 2 goals will be scored e. 6 or more goals will be scored. (4 marks) 16 (Spinners circles for working) Draw the spinner above from the following information. 1 The four numbers on the spinner are equally likely and they are also all different. 2 It is impossible to get an odd number if you spin this spinner twice and add the results. 3 The most likely sum of two spins of this spinner is eight. 4 The smallest sum you can get in two spins of this spinner is –4; the largest is 20. 5 It is impossible to get an add number on this spinner if you spin three times and add 6 If you spin this spinner twice and add two numbers you are just as likely to get 12 as 4. 7 One of the numbers is less than zero.