* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2 - Science @ St John`s
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
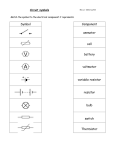
P2.6a Varying the potential difference How do the resistances of filament lamps and diodes change when the potential difference is changed? Apparatus power supply filament lamp diode connecting wires ammeter voltmeter resistors Method A Set up a circuit as shown in the diagram. Put the resistor in position X. B Ask your teacher to check your circuit before you switch on. Set your power supply to 2 V. Switch on and write down the readings on the voltmeter and ammeter. C Repeat step B with the power supply set to 4 V, 6 V, 8 V, 10 V and 12 V. D Swap over the connections at the power supply and repeat steps B and C. You will find that the ammeter and voltmeter give negative readings. E Replace the resistor with a filament lamp and repeat steps B to D. F Set up this circuit. The resistor is used to prevent too much current flowing through the diode being tested and damaging it. G Ask your teacher to check your circuit before you switch on. Repeat steps B to D. Recording your results 1 Draw up a table like this for each component you test. Power supply setting (V) 2 Voltmeter reading (V) Ammeter reading (A) Resistance () 2 Calculate the resistance for each set of readings you have for each component. Use the formula: resistance = voltage/current. 3 Plot a graph to show how the resistance of each component changes as the potential difference changes. Use axes like these: Considering your results/conclusions 4 How does the resistance of each component change when the potential difference changes? © Pearson Education 2011. Edexcel Additional GCSE Science Activity Pack This document may have been altered from the original. P2.6b Investigating LDRs and thermistors Apparatus power supply LDR thermistor resistor connecting wires ammeter voltmeter table lamp 2 beakers hot and cold water thermometer light meter Health and safety Beware of hot lamp housing. Method A Set up circuit X. Use a light meter to record the light level in the room. The resistor is used to prevent too much current flowing through the LDR. Ask your teacher to check your circuit before you switch on. B Switch on and write down the readings on the voltmeter and ammeter. C Place the table lamp so it is shining directly onto the LDR and switch it on. Adjust its position so the light meter is showing a higher reading than for your first measurement. Write down the readings on the ammeter and voltmeter again. D Move the lamp closer to the LDR and repeat step C. Keep doing this until the lamp is right next to the LDR. You should be able to obtain four or five different readings. E Set up circuit Y. Switch on and write down the readings on the voltmeter and ammeter. Use the thermometer to measure the temperature of the air in the room. F Mix some hot and cold water so that the temperature of the mixture is about 10 °C hotter than the air in the room. G Switch off the circuit and carefully put the thermistor into the beaker of hot water. Take care not to spill the water onto other electrical equipment. Wait for a minute to make sure the thermistor has warmed up, then take it out of the water and quickly switch the circuit on. Write down the voltmeter and ammeter readings without delay. H Repeat steps F and G so you get a set of readings at steadily increasing temperatures. Recording your results 1 Calculate the resistance for each set of readings you have for each component. Use the formula: resistance = voltage/current 2 Plot a graph to show how the resistance of each component changes with changing conditions. Use axes like these: Considering your results/conclusions 3 How does the resistance of each component change when the conditions change? © Pearson Education 2011. Edexcel Additional GCSE Science Activity Pack This document may have been altered from the original. P2.6c Components and graphs Cut out the cards and match them up in groups of three to show each component’s name, symbol and the graph of its characteristics. Label the axes on the graphs using words from the box. You will need to use some words more than once. current light intensity potential difference resistance © Pearson Education 2011. Edexcel Additional GCSE Science Activity Pack This document may have been altered from the original. temperature P2.6d Components and resistances 1 Which component is each phrase describing? Choose your answers from the box. You do not need all the words in the box. fixed resistor a b c d e 2 variable resistor filament lamp diode light dependent resistor thermistor The resistance can be changed by moving a slider or a knob. The resistance increases when there is a high potential difference. The resistance gets less when it gets warmer. It will only conduct electricity in one direction. The resistance is highest in the dark. You have a circuit with a variable resistor in it. How will the current in the circuit change if you increase the resistance? Use these equations to help you to answer the following questions. potential difference = current × resistance current = potential difference resistance resistance = potential difference current 3 The potential difference across a resistor is 10 V. There is a 2 A current flowing through it. What is the resistance of the resistor? 4 A light dependent resistor (LDR) has a resistance of 100 Ω. a What current will flow through it if the potential difference is 5 V? b You shine a light on the LDR. What will happen to its resistance? c What will happen to the current in b if the potential difference stays the same? 5 A thermistor is in a circuit with a potential difference of 12 V. The current is 3 A. a What is the resistance of the thermistor? b The circuit is put in a freezer. What will happen to the resistance of the thermistor? c What will happen to the current in b if the potential difference stays the same? © Pearson Education 2011. Edexcel Additional GCSE Science Activity Pack This document may have been altered from the original. P2.6e Changing resistances The table shows the results of an experiment to measure the current and potential difference for a filament lamp. The lamp looked brighter and brighter as the voltage was increased. Potential difference (V) 0.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0 12.0 14.0 Current (A) Resistance (Ω) 0.00 0.38 0.64 0.83 0.98 1.10 1.18 1.24 1 Copy the table and complete it to show the resistance of the filament lamp for each potential difference. 2 What happens to the resistance of the filament lamp as the potential difference increases? 3 a Plot a graph of the potential difference and current. Put potential difference on the horizontal axis. b How can you tell from the graph that the resistance increases as the potential difference increases? Use the word 'gradient' in your answer. Use your graph or the table to help you to work out the answers to these questions. 4 By how much does the current increase if you increase the potential difference: a from 2 V to 4 V b from 12 V to 14 V? 5 What do your answers to question 4 tell you about how the resistance of the filament lamp changes? Explain your answer. 6 Sketch graphs to show how the resistance of the following components change: a an LDR when the light levels change b a thermistor when the temperature changes. Extra challenge 7 Sketch a graph of potential difference (horizontal axis) against resistance for a diode. © Pearson Education 2011. Edexcel Additional GCSE Science Activity Pack This document may have been altered from the original.