* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Questions - HCC Learning Web
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
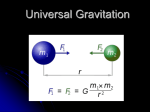
University Physics-1 Ch-13 NAME: _____________________________________________ HOMEWORK CHAPTER 13: UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION NOTE: 1 Hand in your solutions in class in the lecture period after which the chapter is completed. 2 Show the equations and calculations, and box your answer. Be sure to include the units. 3 You are required to solve all problems. Instructor will select and grade any four questions, and the marks for this HW will be based on these only. 1. Determine the gravitational force that you exert on another person 3.0 m away. State the assumptions that you have made. 2. Calculate the gravitational force of attraction between the Earth and the Sun, hence calculate the acceleration of the Earth towards the sun. Verify if this is equal to earth’s centripetal acceleration. 3. When a falling meteoroid is at a distance above the Earth’s surface of 4.00 times the Earth’s radius, what is its acceleration due to the Earth’s gravitation? University Physics-1 Ch-13 4. A synchronous satellite, which always remains above the same point on a planet’s equator, is put in orbit around the Moon. Find the radius of its orbit. 5. A 50-kg satellite is orbiting the Earth in an orbit with a radius of 12 x 106 m. What should be its speed so that it remains in orbit? 6. Three 5.0-kg masses are located at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side 30 cm in the xy plane. What is the magnitude of the resultant force (caused by the other two masses) on the mass at the origin? University Physics-1 7. Ch-13 What is the escape speed from Earth, and the Moon? 8. The figure below shows a planet traveling in a counterclockwise direction on an elliptical path around a star located at one focus of the ellipse. When the planet is at point A its speed is increasing, Give the reason for this. 9. The planet Mars requires 5.94 x 107 s to orbit the sun, which has a mass M = 1.99 x 1030 kg, Assume that the orbit is circular, calculate the radius of the orbit and the orbital speed of Mars as it circles the sun. 10. The Space shuttle is placed in a circular orbit about 170 mi above Earth. Determine (A) the orbital speed of the satellite and (B) the time required for one complete revolution.