Evolution Notes : Theories on the Origin of Life is the theory that life
... Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection #1 ________________________________________________ (got from Malthus) Organisms tend to have many more than two offspring so at least some will survive (yet populations usually do not grow rapidly in the wild) #2 _______________________________________________ - ...
... Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection #1 ________________________________________________ (got from Malthus) Organisms tend to have many more than two offspring so at least some will survive (yet populations usually do not grow rapidly in the wild) #2 _______________________________________________ - ...
Evolution - WordPress.com
... of many animals and plants varied noticeably among the different islands of the Galapagos. See how the turtles are different on the three different islands. ...
... of many animals and plants varied noticeably among the different islands of the Galapagos. See how the turtles are different on the three different islands. ...
here - My Haiku
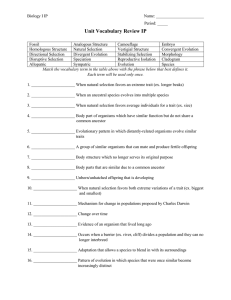
... Match the vocabulary term in the table above with the phrase below that best defines it. Each term will be used only once. 1. _____________________ When natural selection favors an extreme trait (ex. longer beaks) 2. _____________________ When an ancestral species evolves into multiple species 3. __ ...
... Match the vocabulary term in the table above with the phrase below that best defines it. Each term will be used only once. 1. _____________________ When natural selection favors an extreme trait (ex. longer beaks) 2. _____________________ When an ancestral species evolves into multiple species 3. __ ...
Name - Naber Biology
... Testing Natural Selection H. Allen Orr Scientific American, January, 2009, Vol. 300 Number 1 1. Why was Darwinism revolutionary? 2. What are the three goals of the recent experimental work in natural selection? 3. What is the best way to appreciate (witness) evolution by natural selection? 4. Based ...
... Testing Natural Selection H. Allen Orr Scientific American, January, 2009, Vol. 300 Number 1 1. Why was Darwinism revolutionary? 2. What are the three goals of the recent experimental work in natural selection? 3. What is the best way to appreciate (witness) evolution by natural selection? 4. Based ...
Ch 15 Jeopardy Review
... the flying phalanger of Australia. They are similar in size and have long, bushy tails and skin folds that allow them to glide through the air. The squirrel is a placental mammal (carries its young internally), while the phalanger is a marsupial (has a pouch). These close resemblances, even though g ...
... the flying phalanger of Australia. They are similar in size and have long, bushy tails and skin folds that allow them to glide through the air. The squirrel is a placental mammal (carries its young internally), while the phalanger is a marsupial (has a pouch). These close resemblances, even though g ...
11.6 Patterns in Evolution
... • Mass extinctions are rare but much more intense. – destroy many species at global level – thought to be caused by catastrophic events – at least five mass extinctions in last 600 million years ...
... • Mass extinctions are rare but much more intense. – destroy many species at global level – thought to be caused by catastrophic events – at least five mass extinctions in last 600 million years ...
Chapter 19: Descent with Modification
... James Hutton and Charles Lyell were geologists whose ideas strongly influenced Darwin’s thinking. What were the ideas each of them contributed? James Hutton ...
... James Hutton and Charles Lyell were geologists whose ideas strongly influenced Darwin’s thinking. What were the ideas each of them contributed? James Hutton ...
Chapter 5, Section 1 Darwin’s Voyage
... species over time. Darwin thought that species gradually changed over many generations and became better adapted to the new condition. Darwin’s ideas are often referred to as the theory of evolution. A scientific theory is a well-tested concept that explains a wide range of observations. ...
... species over time. Darwin thought that species gradually changed over many generations and became better adapted to the new condition. Darwin’s ideas are often referred to as the theory of evolution. A scientific theory is a well-tested concept that explains a wide range of observations. ...
Chapter 16 - Biology
... Similar to artificial, but nature is controlling When does it occur? ...
... Similar to artificial, but nature is controlling When does it occur? ...
Topic 10: How do living things evolve?
... . . . when we come to inspect the watch, we perceive. . . that its several parts are framed and put together for a purpose, e.g. that they are so formed and adjusted as to produce motion, and that motion so regulated as to point out the hour of the day; that if the different parts had been differen ...
... . . . when we come to inspect the watch, we perceive. . . that its several parts are framed and put together for a purpose, e.g. that they are so formed and adjusted as to produce motion, and that motion so regulated as to point out the hour of the day; that if the different parts had been differen ...
Process of Evolution
... From the observations and insights made on the voyage and new ideas from geologists, like Charles Lyell, about how the Earth has been shaped by slow acting forces that are still active today. ...
... From the observations and insights made on the voyage and new ideas from geologists, like Charles Lyell, about how the Earth has been shaped by slow acting forces that are still active today. ...
EVOLUTION AND CHANGE POWERPOINT
... became isolated from the other groups. • Eventually, each group became a different species. ...
... became isolated from the other groups. • Eventually, each group became a different species. ...
Glenbard District 87
... • LS4-2: Construct an explanation based on evidence that the process of evolution primarily results from four factors: (1) the potential for a species to increase in number, (2) the heritable genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for l ...
... • LS4-2: Construct an explanation based on evidence that the process of evolution primarily results from four factors: (1) the potential for a species to increase in number, (2) the heritable genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for l ...
Evolution By Means of Natural Selection (Chapter
... How did he positively influence modern evolutionary thought? ___________________________________________________________ Charles Darwin more-complex forms developed from less-complex forms Species on the Galapagos Islands were similar to the mainland, but differ in each environment _______ ...
... How did he positively influence modern evolutionary thought? ___________________________________________________________ Charles Darwin more-complex forms developed from less-complex forms Species on the Galapagos Islands were similar to the mainland, but differ in each environment _______ ...
EVOLUTION REVIEW
... 21. Name the type of macroevolution in which two organisms evolve in response to changes in each other. _________________________________ ...
... 21. Name the type of macroevolution in which two organisms evolve in response to changes in each other. _________________________________ ...
EVOLUTION REVIEW
... 21. Name the type of macroevolution in which two organisms evolve in response to changes in each other. _________________________________ ...
... 21. Name the type of macroevolution in which two organisms evolve in response to changes in each other. _________________________________ ...
Natural Selection Notes
... • In the same way, man is not believed to evolve from apes, man and apes are believed to share a common ancestor. ...
... • In the same way, man is not believed to evolve from apes, man and apes are believed to share a common ancestor. ...
File
... of the organism. What differences among us are caused by variation? A good variation for some humans? FIV in Cats and HIV in Humans ...
... of the organism. What differences among us are caused by variation? A good variation for some humans? FIV in Cats and HIV in Humans ...
WHAT EVOLUTION IS NOT
... for all we know, evolution could be part of God's creation, or it might not, but science cannot determine that). 13. does NOT conflict with any religion...(It can't, since it is only another way of trying to make sense of the natural world, based on scientific observation and critical analysis. Most ...
... for all we know, evolution could be part of God's creation, or it might not, but science cannot determine that). 13. does NOT conflict with any religion...(It can't, since it is only another way of trying to make sense of the natural world, based on scientific observation and critical analysis. Most ...
Homologous Structures Convergent Evolution
... animals (Allendorf, F.W. and J. J. Hard. 2009. PNAS. Vol. 106) • The nature of fisheries- and farming-induced evolution (Hutchings, J.A. and D.J. Fraser. 2007.Molecular Ecology. Vol.17) ...
... animals (Allendorf, F.W. and J. J. Hard. 2009. PNAS. Vol. 106) • The nature of fisheries- and farming-induced evolution (Hutchings, J.A. and D.J. Fraser. 2007.Molecular Ecology. Vol.17) ...
Early Ideas About Evolution
... Local catastrophes (like floods) would wipe out the organisms of that time and they would be replaced with newly created forms. • It explained the fossils but not the increasing complexity. ...
... Local catastrophes (like floods) would wipe out the organisms of that time and they would be replaced with newly created forms. • It explained the fossils but not the increasing complexity. ...
Evolution Lecture
... • Large changes, such as the evolution of major features, like wings in birds, or legs in fish, are examples of macroevolution. Macroevolution leads to significant evolutionary change. Results from rapid microevolutionary ...
... • Large changes, such as the evolution of major features, like wings in birds, or legs in fish, are examples of macroevolution. Macroevolution leads to significant evolutionary change. Results from rapid microevolutionary ...