On the Evolution of Premating Isolation after a Founder Event
... will decline in frequency if the probability of matings between common homozygotes is higher than the average of the probabilities of matings involving a common homozygote and a heterozygote. With n → ∞, the probability of matings between common homozygotes should be higher than the probability of m ...
... will decline in frequency if the probability of matings between common homozygotes is higher than the average of the probabilities of matings involving a common homozygote and a heterozygote. With n → ∞, the probability of matings between common homozygotes should be higher than the probability of m ...
7D Booklet 2011
... example, identical twins inherit exactly the same features from their parents. But if you take a pair of twins, and twin 'A' is given more to eat than twin 'B', twin 'A' is likely to end up heavier. Natural and Artificial selections Natural selection: Within a population of animals, plants or any li ...
... example, identical twins inherit exactly the same features from their parents. But if you take a pair of twins, and twin 'A' is given more to eat than twin 'B', twin 'A' is likely to end up heavier. Natural and Artificial selections Natural selection: Within a population of animals, plants or any li ...
Weeks 3-4 Essential Questions March 8-18
... What are 3 environmental things that could cause An evolutionary change over a long time? ...
... What are 3 environmental things that could cause An evolutionary change over a long time? ...
Reprint - Queen`s University Department of Mathematics and Statistics.
... evolutionarily stable resource exploitation strategy (i.e., an ESS). This analysis is used for two purposes. First, it is used to determine how such ESS’s are affected by the genetic structuring of the population which is inherent in the model (to be described shortly). The answer to this question p ...
... evolutionarily stable resource exploitation strategy (i.e., an ESS). This analysis is used for two purposes. First, it is used to determine how such ESS’s are affected by the genetic structuring of the population which is inherent in the model (to be described shortly). The answer to this question p ...
Meaning of Life Packet
... can list certain characteristics that living things have. Here is such a list. It is not complete. Some of the characteristics could be described in some other way. But it is a fairly good test for deciding whether something is alive. ...
... can list certain characteristics that living things have. Here is such a list. It is not complete. Some of the characteristics could be described in some other way. But it is a fairly good test for deciding whether something is alive. ...
Lesson Overview - Mr. Pelton Science
... • Today, we know that Lamarck’s hypotheses were incorrect in several ways. • Organisms don’t have an inborn drive to become more perfect. Evolution does not mean that over time a species becomes “better” somehow, and evolution does not progress in a predetermined direction. • In addition, traits acq ...
... • Today, we know that Lamarck’s hypotheses were incorrect in several ways. • Organisms don’t have an inborn drive to become more perfect. Evolution does not mean that over time a species becomes “better” somehow, and evolution does not progress in a predetermined direction. • In addition, traits acq ...
If a strand of DNA has the following nucleotide sequence
... E. FNA = RNA; FNS > RNS 32. Which combination of the following statements represent general principles of island colonization? 1) more species are likely to be established on larger islands, and fewer on smaller islands 2) there is a greater probability of colonization if the island is closer to ano ...
... E. FNA = RNA; FNS > RNS 32. Which combination of the following statements represent general principles of island colonization? 1) more species are likely to be established on larger islands, and fewer on smaller islands 2) there is a greater probability of colonization if the island is closer to ano ...
Weighing the evidence for adaptation at the molecular level
... The extent to which molecular evolution is driven by positive selection has long been debated. The neutral theory (see Glossary) holds that the vast majority of DNA sequence differences between species are neutral [1] or nearly neutral [2] with respect to fitness. However, models assuming that natur ...
... The extent to which molecular evolution is driven by positive selection has long been debated. The neutral theory (see Glossary) holds that the vast majority of DNA sequence differences between species are neutral [1] or nearly neutral [2] with respect to fitness. However, models assuming that natur ...
CHAPTER 3 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... combinations that allow them to survive, reproduce and pass their genes on to the next generation Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... combinations that allow them to survive, reproduce and pass their genes on to the next generation Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Charles Darwin`s Origin of Species, directional selection, and the
... Darwin (1859, 1872a) was basically right (Herrada et al. 2008). However, one-step endosymbiotic events have “punctuated” the history of life on Earth, so that novel unicellular body plans emerged in aquatic organisms. The origin of eukaryotic cells with organelles (mitochondria, chloroplasts) was on ...
... Darwin (1859, 1872a) was basically right (Herrada et al. 2008). However, one-step endosymbiotic events have “punctuated” the history of life on Earth, so that novel unicellular body plans emerged in aquatic organisms. The origin of eukaryotic cells with organelles (mitochondria, chloroplasts) was on ...
in the Nesospiza bunting species complex and its sister
... the original variation. As the population adapts to its new environment, the MHC allelic diversity will be made up of a combination of ancestral polymorphism and novel genetic variation. Trans-species evolution [27] or ancestral polymorphism [28] refers to the long-term maintenance of ancestral alle ...
... the original variation. As the population adapts to its new environment, the MHC allelic diversity will be made up of a combination of ancestral polymorphism and novel genetic variation. Trans-species evolution [27] or ancestral polymorphism [28] refers to the long-term maintenance of ancestral alle ...
Learning to Change - We can offer most test bank and solution
... It is hard for some students to believe that mutations can play a role in evolution. You might want to emphasize that the vast majority of mutations are harmful or of no consequence. It is also helpful to remind students that evolution is a play in which a single act may last millions of years. Robe ...
... It is hard for some students to believe that mutations can play a role in evolution. You might want to emphasize that the vast majority of mutations are harmful or of no consequence. It is also helpful to remind students that evolution is a play in which a single act may last millions of years. Robe ...
Evolutionary and comparative aspects of longevity and aging
... Evolutionary aspects of aging • Organisms must survive long enough to reproduce--ls matches the ecological niche. • Events after reproduction aren’t subject to selection. • Lifespan is an evolutionarily labile trait-increases and decreases in ls have frequently occurred. ...
... Evolutionary aspects of aging • Organisms must survive long enough to reproduce--ls matches the ecological niche. • Events after reproduction aren’t subject to selection. • Lifespan is an evolutionarily labile trait-increases and decreases in ls have frequently occurred. ...
SUMMARY Module 1: Characteristics, Classification and Diversity of
... Viruses are so different from other organisms that they cannot be classified as living organisms. They are non cellular as they are not made up of cells. They do not have organelles that are in all living cells. Viruses are made up of a single strand of either DNA or RNA that is surrounded by a prot ...
... Viruses are so different from other organisms that they cannot be classified as living organisms. They are non cellular as they are not made up of cells. They do not have organelles that are in all living cells. Viruses are made up of a single strand of either DNA or RNA that is surrounded by a prot ...
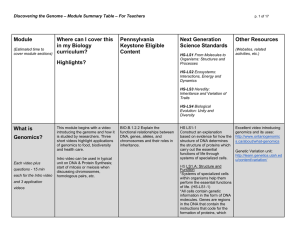
Module Summary Table - Tips For Teachers
... inheritable genetic variations may result from: (1) new genetic combinations through meiosis, (2) viable errors occurring during replication, and/or (3) mutations caused by environmental factors ...
... inheritable genetic variations may result from: (1) new genetic combinations through meiosis, (2) viable errors occurring during replication, and/or (3) mutations caused by environmental factors ...
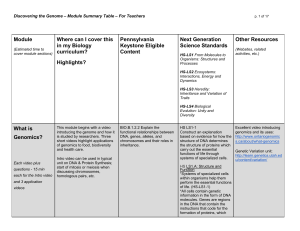
Module Summary Table -Tips For Teachers
... inheritable genetic variations may result from: (1) new genetic combinations through meiosis, (2) viable errors occurring during replication, and/or (3) mutations caused by environmental factors ...
... inheritable genetic variations may result from: (1) new genetic combinations through meiosis, (2) viable errors occurring during replication, and/or (3) mutations caused by environmental factors ...
Ernst Mayr, 1904-2005
... definition of evolution as “a change in gene frequencies” in Animal Species and Evolution (1963), and would only distance himself from it years later. Mayr also never bought into the “gene’s-eye-view” of evolution promoted by first-wave sociobiologists like Hamilton, Dawkins, and Williams. To Mayr, th ...
... definition of evolution as “a change in gene frequencies” in Animal Species and Evolution (1963), and would only distance himself from it years later. Mayr also never bought into the “gene’s-eye-view” of evolution promoted by first-wave sociobiologists like Hamilton, Dawkins, and Williams. To Mayr, th ...
American Scientist
... The Beginning of Radiation Darwin’s finches arose in South America. The ancestors arrived on the Galápagos islands by flying over water for at least 1,000 kilometers. There has been little debate about these two points. The only credible alternative is that the finches arose on Cocos Island, which l ...
... The Beginning of Radiation Darwin’s finches arose in South America. The ancestors arrived on the Galápagos islands by flying over water for at least 1,000 kilometers. There has been little debate about these two points. The only credible alternative is that the finches arose on Cocos Island, which l ...
Transhumanism
... consciousness. Because this would mean that the number of people living on earth would naturally increase even more rapidly than it is already, it will be necessary to continue life on other planets. That would not present a problem, however, because our non-organic bodies would be better suited to ...
... consciousness. Because this would mean that the number of people living on earth would naturally increase even more rapidly than it is already, it will be necessary to continue life on other planets. That would not present a problem, however, because our non-organic bodies would be better suited to ...
CHAPTER 2 Evolution: Constructing a Fundamental Scientific Theory
... 2. Before 1700, most Western scientists thought the Earth was about 4.6 billion years old. ANS: F ...
... 2. Before 1700, most Western scientists thought the Earth was about 4.6 billion years old. ANS: F ...
Monday – May 19, 2014 - B Topic: Human Systems Standards: MST
... pigment. However, in the winter, the arctic fox appears white because the dark pigment is not produced. The color change is most likely due to the effect of (1) different genes produced in the different seasons (2) increased pollution on genetic mutations (3) environmental conditions on gene express ...
... pigment. However, in the winter, the arctic fox appears white because the dark pigment is not produced. The color change is most likely due to the effect of (1) different genes produced in the different seasons (2) increased pollution on genetic mutations (3) environmental conditions on gene express ...
FREE Sample Here
... 2. Before 1700, most Western scientists thought the Earth was about 4.6 billion years old. ANS: F ...
... 2. Before 1700, most Western scientists thought the Earth was about 4.6 billion years old. ANS: F ...
Introduction to evolution

Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, and evolutionary biology is the study of how evolution occurs. Biological populations evolve through genetic changes that correspond to changes in the organisms' observable traits. Genetic changes include mutations, which are caused by damage or replication errors in an organism's DNA. As the genetic variation of a population drifts randomly over generations, natural selection gradually leads traits to become more or less common based on the relative reproductive success of organisms with those traits.The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.Evolution does not attempt to explain the origin of life (covered instead by abiogenesis), but it does explain how the extremely simple early lifeforms evolved into the complex ecosystem that we see today. Based on the similarities between all present-day organisms, all life on Earth originated through common descent from a last universal ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. All individuals have hereditary material in the form of genes that are received from their parents, then passed on to any offspring. Among offspring there are variations of genes due to the introduction of new genes via random changes called mutations or via reshuffling of existing genes during sexual reproduction. The offspring differs from the parent in minor random ways. If those differences are helpful, the offspring is more likely to survive and reproduce. This means that more offspring in the next generation will have that helpful difference and individuals will not have equal chances of reproductive success. In this way, traits that result in organisms being better adapted to their living conditions become more common in descendant populations. These differences accumulate resulting in changes within the population. This process is responsible for the many diverse life forms in the world.The forces of evolution are most evident when populations become isolated, either through geographic distance or by other mechanisms that prevent genetic exchange. Over time, isolated populations can branch off into new species.The majority of genetic mutations neither assist, change the appearance of, nor bring harm to individuals. Through the process of genetic drift, these mutated genes are neutrally sorted among populations and survive across generations by chance alone. In contrast to genetic drift, natural selection is not a random process because it acts on traits that are necessary for survival and reproduction. Natural selection and random genetic drift are constant and dynamic parts of life and over time this has shaped the branching structure in the tree of life.The modern understanding of evolution began with the 1859 publication of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species. In addition, Gregor Mendel's work with plants helped to explain the hereditary patterns of genetics. Fossil discoveries in paleontology, advances in population genetics and a global network of scientific research have provided further details into the mechanisms of evolution. Scientists now have a good understanding of the origin of new species (speciation) and have observed the speciation process in the laboratory and in the wild. Evolution is the principal scientific theory that biologists use to understand life and is used in many disciplines, including medicine, psychology, conservation biology, anthropology, forensics, agriculture and other social-cultural applications.