Population Genetics
... • Migration: The movement of alleles from one population to another, typically by the movement of individuals or via long-range dispersal of gametes. • Genetic Drift: Change in the frequencies of alleles in a population resulting from chance variation in the survival and/or reproductive success of i ...
... • Migration: The movement of alleles from one population to another, typically by the movement of individuals or via long-range dispersal of gametes. • Genetic Drift: Change in the frequencies of alleles in a population resulting from chance variation in the survival and/or reproductive success of i ...
Population Genetics
... • Migration: The movement of alleles from one population to another, typically by the movement of individuals or via long-range dispersal of gametes. • Genetic Drift: Change in the frequencies of alleles in a population resulting from chance variation in the survival and/or reproductive success of i ...
... • Migration: The movement of alleles from one population to another, typically by the movement of individuals or via long-range dispersal of gametes. • Genetic Drift: Change in the frequencies of alleles in a population resulting from chance variation in the survival and/or reproductive success of i ...
UTKEEB464_Lecture22_Darwin_2015
... ■ Individuals less suited to the environment are less likely to survive and less likely to reproduce; individuals more suited to the environment are more likely to survive and more likely to reproduce and leave their inheritable traits to future generations, which produces the process of natural sel ...
... ■ Individuals less suited to the environment are less likely to survive and less likely to reproduce; individuals more suited to the environment are more likely to survive and more likely to reproduce and leave their inheritable traits to future generations, which produces the process of natural sel ...
Darwin - Brian O`Meara Lab
... ■ Individuals less suited to the environment are less likely to survive and less likely to reproduce; individuals more suited to the environment are more likely to survive and more likely to reproduce and leave their inheritable traits to future generations, which produces the process of natural se ...
... ■ Individuals less suited to the environment are less likely to survive and less likely to reproduce; individuals more suited to the environment are more likely to survive and more likely to reproduce and leave their inheritable traits to future generations, which produces the process of natural se ...
Darwin - Brian O`Meara Lab
... ■ Individuals less suited to the environment are less likely to survive and less likely to reproduce; individuals more suited to the environment are more likely to survive and more likely to reproduce and leave their inheritable traits to future generations, which produces the process of natural se ...
... ■ Individuals less suited to the environment are less likely to survive and less likely to reproduce; individuals more suited to the environment are more likely to survive and more likely to reproduce and leave their inheritable traits to future generations, which produces the process of natural se ...
Evolution
... – Among the first scientists to recognize that living things change over time, and that all species were descended from other species – Animals adapted to their environments, – 1809 – Year Darwin was born – Lamarck proposed that by selective use or disuse of organs, organisms acquired certain traits ...
... – Among the first scientists to recognize that living things change over time, and that all species were descended from other species – Animals adapted to their environments, – 1809 – Year Darwin was born – Lamarck proposed that by selective use or disuse of organs, organisms acquired certain traits ...
Evolutionary view of life
... • In reassessing his observations, Darwin perceived adaptation to the environment and the origin of new species as closely related processes • In 1844, Darwin wrote an essay on natural selection as the mechanism of descent with modification, but did not introduce his theory publicly • Natural select ...
... • In reassessing his observations, Darwin perceived adaptation to the environment and the origin of new species as closely related processes • In 1844, Darwin wrote an essay on natural selection as the mechanism of descent with modification, but did not introduce his theory publicly • Natural select ...
BioFundamentals - Selection and drift
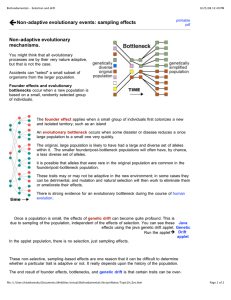
... The founder effect applies when a small group of individuals first colonizes a new and isolated territory, such as an island An evolutionary bottleneck occurs when some disaster or disease reduces a once large population to a small one very quickly. The original, large population is likely to have h ...
... The founder effect applies when a small group of individuals first colonizes a new and isolated territory, such as an island An evolutionary bottleneck occurs when some disaster or disease reduces a once large population to a small one very quickly. The original, large population is likely to have h ...
Theory of Natural Selection
... • Overproduction Organisms have more offspring than can survive. This results in competition among offspring for resources. • Adaptation Some individuals have certain variations that allow them to survive better than other individuals in their environment. These individuals are “naturally select ...
... • Overproduction Organisms have more offspring than can survive. This results in competition among offspring for resources. • Adaptation Some individuals have certain variations that allow them to survive better than other individuals in their environment. These individuals are “naturally select ...
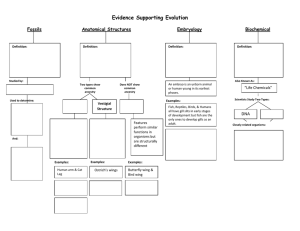
Evidence Supporting Evolution
... all have gill slits in early stages of development but fish are the only ones to develop gills as an adult. ...
... all have gill slits in early stages of development but fish are the only ones to develop gills as an adult. ...
Assessing how ecology influences evolutionary transitions to
... Introduction: Animal behaviour does not evolve in a vacuum. Rather, ecological factors play an important role in shaping the evolution of animal behaviour by establishing the context under which individuals and species interact. For example, complex social interactions are unlikely to evolve in spec ...
... Introduction: Animal behaviour does not evolve in a vacuum. Rather, ecological factors play an important role in shaping the evolution of animal behaviour by establishing the context under which individuals and species interact. For example, complex social interactions are unlikely to evolve in spec ...
Adaptive Landscape - University of Arizona | Ecology and
... *some argue that recombination is a force, others believe it only ‘reshuffles’genetic variation ...
... *some argue that recombination is a force, others believe it only ‘reshuffles’genetic variation ...
NOTES: Natural Selection
... for those traits that helped them survive. Organisms without those traits helpful for survival are less likely to reproduce, so their genes are not likely to be passed on to the next generation. Organisms that can survive long enough to reproduce are able to determine the characteristics of the ...
... for those traits that helped them survive. Organisms without those traits helpful for survival are less likely to reproduce, so their genes are not likely to be passed on to the next generation. Organisms that can survive long enough to reproduce are able to determine the characteristics of the ...
THEORIES OF EVOLUTION :
... Useful variations arc quite significant and make the organism fit in the struggle for existence. Such variations are inherited by the progeny, so that the progeny has better chances of survival. Natural selection : According to Darwin during the struggle for existence, the organisms with beneficial ...
... Useful variations arc quite significant and make the organism fit in the struggle for existence. Such variations are inherited by the progeny, so that the progeny has better chances of survival. Natural selection : According to Darwin during the struggle for existence, the organisms with beneficial ...
MT XM - ltcconline.net
... 9. Explain why seedless vascular plants are most commonly found in damp habitats. ...
... 9. Explain why seedless vascular plants are most commonly found in damp habitats. ...
Chapter 16 common ancestor
... – We have fossils for 1% of species believed to have lived on earth – Some organisms left no fossils, others decomposed, others have yet to be found. ...
... – We have fossils for 1% of species believed to have lived on earth – Some organisms left no fossils, others decomposed, others have yet to be found. ...
Slide 1
... • Biosystematics is the application of genetics (and cytogenetics) , statistics and chemistry to the solution of systematics questions in order to provide explanations abaout the diversity of organisms within the frame of the theory of evolution ...
... • Biosystematics is the application of genetics (and cytogenetics) , statistics and chemistry to the solution of systematics questions in order to provide explanations abaout the diversity of organisms within the frame of the theory of evolution ...
Notes - Pierce College
... uniform rate. Darwin read Lyell during voyage of Beagle. This was very important to Ch. Darwin as it gave him the time necessary for evolution to occur. 3) Lyell was rejected by much of established science at the time. 6. Early theories of evolution a. Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) wrote Zoologi ...
... uniform rate. Darwin read Lyell during voyage of Beagle. This was very important to Ch. Darwin as it gave him the time necessary for evolution to occur. 3) Lyell was rejected by much of established science at the time. 6. Early theories of evolution a. Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) wrote Zoologi ...
Speciation Book Worksheet
... 2. When the scientists Peter and Rosemary Grant measured beak size, feather colors, and wing length, they graphed these numbers. What was the shape of their graphs? (p 407) ...
... 2. When the scientists Peter and Rosemary Grant measured beak size, feather colors, and wing length, they graphed these numbers. What was the shape of their graphs? (p 407) ...
Evolutionary Change Without Selection File
... natural selection. • Some changes such as genetic drift, bottlenecks and the founder effect are not influenced by the traits of individuals. • Each of these changes tends to reduce genetic diversity within a population ...
... natural selection. • Some changes such as genetic drift, bottlenecks and the founder effect are not influenced by the traits of individuals. • Each of these changes tends to reduce genetic diversity within a population ...
Biology 1B Evolution practice questions Fall 2002 Thomson
... C. the potential for population growth exceeds what the environment can support. D. species become better adapted to their local environments through natural selection. E. favorable variations accumulate in a population after many generations of being by natural selection. ...
... C. the potential for population growth exceeds what the environment can support. D. species become better adapted to their local environments through natural selection. E. favorable variations accumulate in a population after many generations of being by natural selection. ...
1 Populations are the units of evolution The gene pool of a
... •a collision between the earth and a gigantic asteroid rich in iridium •the force of thousands of atomic bombs •A dust cloud high into the sky. •This cloud would block out nearly all of the sunlight, creating a long, cold, unnatural winter, drastically changing the climate for years to come. •The fe ...
... •a collision between the earth and a gigantic asteroid rich in iridium •the force of thousands of atomic bombs •A dust cloud high into the sky. •This cloud would block out nearly all of the sunlight, creating a long, cold, unnatural winter, drastically changing the climate for years to come. •The fe ...
Study Guide for Evolution Test • Be sure to know all
... covered it. Read over your class notes for 1.2 and 1.3 Know what‘s included in the process of Natural Selection. Be able to explain what Darwin observed on the Galapagos Islands that made him develop the theory of evolution. Know what the evidences of evolution are- and how they show evoluti ...
... covered it. Read over your class notes for 1.2 and 1.3 Know what‘s included in the process of Natural Selection. Be able to explain what Darwin observed on the Galapagos Islands that made him develop the theory of evolution. Know what the evidences of evolution are- and how they show evoluti ...
Introduction to evolution

Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, and evolutionary biology is the study of how evolution occurs. Biological populations evolve through genetic changes that correspond to changes in the organisms' observable traits. Genetic changes include mutations, which are caused by damage or replication errors in an organism's DNA. As the genetic variation of a population drifts randomly over generations, natural selection gradually leads traits to become more or less common based on the relative reproductive success of organisms with those traits.The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.Evolution does not attempt to explain the origin of life (covered instead by abiogenesis), but it does explain how the extremely simple early lifeforms evolved into the complex ecosystem that we see today. Based on the similarities between all present-day organisms, all life on Earth originated through common descent from a last universal ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. All individuals have hereditary material in the form of genes that are received from their parents, then passed on to any offspring. Among offspring there are variations of genes due to the introduction of new genes via random changes called mutations or via reshuffling of existing genes during sexual reproduction. The offspring differs from the parent in minor random ways. If those differences are helpful, the offspring is more likely to survive and reproduce. This means that more offspring in the next generation will have that helpful difference and individuals will not have equal chances of reproductive success. In this way, traits that result in organisms being better adapted to their living conditions become more common in descendant populations. These differences accumulate resulting in changes within the population. This process is responsible for the many diverse life forms in the world.The forces of evolution are most evident when populations become isolated, either through geographic distance or by other mechanisms that prevent genetic exchange. Over time, isolated populations can branch off into new species.The majority of genetic mutations neither assist, change the appearance of, nor bring harm to individuals. Through the process of genetic drift, these mutated genes are neutrally sorted among populations and survive across generations by chance alone. In contrast to genetic drift, natural selection is not a random process because it acts on traits that are necessary for survival and reproduction. Natural selection and random genetic drift are constant and dynamic parts of life and over time this has shaped the branching structure in the tree of life.The modern understanding of evolution began with the 1859 publication of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species. In addition, Gregor Mendel's work with plants helped to explain the hereditary patterns of genetics. Fossil discoveries in paleontology, advances in population genetics and a global network of scientific research have provided further details into the mechanisms of evolution. Scientists now have a good understanding of the origin of new species (speciation) and have observed the speciation process in the laboratory and in the wild. Evolution is the principal scientific theory that biologists use to understand life and is used in many disciplines, including medicine, psychology, conservation biology, anthropology, forensics, agriculture and other social-cultural applications.