document
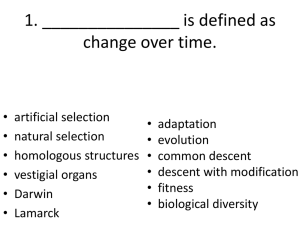
... Which one of the following was not a main idea that Darwin advanced in his works? A) species change over time B) living species have arisen from earlier life forms C) modern species arose through a process known as "descent with modification" D) new species can form by inheritance of characteristic ...
... Which one of the following was not a main idea that Darwin advanced in his works? A) species change over time B) living species have arisen from earlier life forms C) modern species arose through a process known as "descent with modification" D) new species can form by inheritance of characteristic ...
Read pgs. 556-564
... What is the source of variation? How are subtle differences passed from generation to generation? These questions that puzzled Darwin have been answered by the scientific understanding of genetics and mutations. Mutations provide a continuous supply of new genetic variations, which may be inherited ...
... What is the source of variation? How are subtle differences passed from generation to generation? These questions that puzzled Darwin have been answered by the scientific understanding of genetics and mutations. Mutations provide a continuous supply of new genetic variations, which may be inherited ...
High School Biology-Honors
... Biochemistry, Cell Biology, Molecular and Mendelian Genetics, Classification, Evolution and the Origin of Species Diversity, and Ecology comprise the main topics of Biology Honors. Four student-generated projects will be carried out during the year. All students are required to produce a project and ...
... Biochemistry, Cell Biology, Molecular and Mendelian Genetics, Classification, Evolution and the Origin of Species Diversity, and Ecology comprise the main topics of Biology Honors. Four student-generated projects will be carried out during the year. All students are required to produce a project and ...
Linnaean Taxonomy Taxonomic Levels
... • Approximately what percent of all species are extinct? • Define fecundity and its relationship to natural selection and biological evolution. • What is a gene? An allele? • What is the ultimate source of all genetic variation? Is this source of variation usually beneficial (selected for)? • Define ...
... • Approximately what percent of all species are extinct? • Define fecundity and its relationship to natural selection and biological evolution. • What is a gene? An allele? • What is the ultimate source of all genetic variation? Is this source of variation usually beneficial (selected for)? • Define ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... Mutation: a change in a organism’s DNA - if mutation is in gametes, immediate change can be seen in the gene pool - if the new allele produced by a mutation increases in frequency, it is because the mutant alleles are producing a disproportionate number of offspring by NS or genetic drift ...
... Mutation: a change in a organism’s DNA - if mutation is in gametes, immediate change can be seen in the gene pool - if the new allele produced by a mutation increases in frequency, it is because the mutant alleles are producing a disproportionate number of offspring by NS or genetic drift ...
Chapter 1 Notes - Social Circle City Schools
... Mutation: a change in a organism’s DNA - if mutation is in gametes, immediate change can be seen in the gene pool - if the new allele produced by a mutation increases in frequency, it is because the mutant alleles are producing a disproportionate number of offspring by NS or genetic drift ...
... Mutation: a change in a organism’s DNA - if mutation is in gametes, immediate change can be seen in the gene pool - if the new allele produced by a mutation increases in frequency, it is because the mutant alleles are producing a disproportionate number of offspring by NS or genetic drift ...
Unit 3: Introduction and Lesson 6
... Unit Introduction: This unit studies the questions: “What is natural selection and why is natural selection the driving force of biological evolution”. Through the study of genetics and biotechnology, this unit will look at what factors influence species’ survivability as well as the evolution of po ...
... Unit Introduction: This unit studies the questions: “What is natural selection and why is natural selection the driving force of biological evolution”. Through the study of genetics and biotechnology, this unit will look at what factors influence species’ survivability as well as the evolution of po ...
the origin of species
... young, they were home to many plants and animals known nowhere else in the world. – Darwin thought it unlikely that all of these species could have been among the original colonists of the islands. ...
... young, they were home to many plants and animals known nowhere else in the world. – Darwin thought it unlikely that all of these species could have been among the original colonists of the islands. ...
Evolution vs. Creation Genesis 1:1 1. 3 How did life begin? A vitally
... C. Fossil Record: The fossil record in the Earth’s outer crust serves as a natural museum of past life. If TOE is true, random mutation and natural selection would over millions of years have produced a vast array of fossils demonstrating the gradual change of one organism into another (e.g., one-ce ...
... C. Fossil Record: The fossil record in the Earth’s outer crust serves as a natural museum of past life. If TOE is true, random mutation and natural selection would over millions of years have produced a vast array of fossils demonstrating the gradual change of one organism into another (e.g., one-ce ...
Running head: UNDERSTANDING EVOLUTION 1 Understanding
... Fact 3: Natural resources are limited. In a stable environment they remain relatively constant. Inference 1: Since more individuals are produced than can be supported by the available resources but population size remains stable, it means that there must be a fierce struggle for existence among indi ...
... Fact 3: Natural resources are limited. In a stable environment they remain relatively constant. Inference 1: Since more individuals are produced than can be supported by the available resources but population size remains stable, it means that there must be a fierce struggle for existence among indi ...
Evolutionary Limits and Constraints
... humans are often around 0.5 to 0.8), while they tend to be lower for behavioral and physiological traits; however, heritability estimates for natural populations of animals and plants can be quite variable, particularly for traits that are important in determining the ecological niche of species. Fo ...
... humans are often around 0.5 to 0.8), while they tend to be lower for behavioral and physiological traits; however, heritability estimates for natural populations of animals and plants can be quite variable, particularly for traits that are important in determining the ecological niche of species. Fo ...
The Origin of Species
... large volcanic eruption occurs and separates the valley with a huge volcanic dike that the squirrels cannot cross, thus producing and isolating two populations of squirrels. What change needs to occur for the two populations of squirrels to become separate species? A. The two squirrel populations mu ...
... large volcanic eruption occurs and separates the valley with a huge volcanic dike that the squirrels cannot cross, thus producing and isolating two populations of squirrels. What change needs to occur for the two populations of squirrels to become separate species? A. The two squirrel populations mu ...
Dr. Katja Nowick
... The role of transcription factors in human evolution Humans differ from other primates by a number of traits, for example their upright gait, their larger brain, and their cognitive abilities. What is the molecular basis for these phenotypic differences? Since differences in gene regulation are like ...
... The role of transcription factors in human evolution Humans differ from other primates by a number of traits, for example their upright gait, their larger brain, and their cognitive abilities. What is the molecular basis for these phenotypic differences? Since differences in gene regulation are like ...
Lecture 2
... and IF that variation is inherited; THEN there is a somewhat better than average chance that organisms with that variation will survive to bear the next generation. Over the long expanse of geologic time, the accumulation of these variations will change the population from one form to another: the o ...
... and IF that variation is inherited; THEN there is a somewhat better than average chance that organisms with that variation will survive to bear the next generation. Over the long expanse of geologic time, the accumulation of these variations will change the population from one form to another: the o ...
Evolution
... SC.912.L.15.10 Identify basic trends in hominid evolution from early ancestors six million years ago to modern humans, including brain size, jaw size, language, and manufacture of tools. SC.912.L.15.13 Describe the conditions required for natural selection, including: overproduction of offspring, in ...
... SC.912.L.15.10 Identify basic trends in hominid evolution from early ancestors six million years ago to modern humans, including brain size, jaw size, language, and manufacture of tools. SC.912.L.15.13 Describe the conditions required for natural selection, including: overproduction of offspring, in ...
History of the Theory Comprehension Worksheets
... • He experienced an earthquake that lifted the ocean floor 2.7 meters (9 feet) above sea level. He also found rocks containing fossil sea shells in mountains high above sea level. These observations suggested that continents and oceans had changed dramatically over time and continue to change in dra ...
... • He experienced an earthquake that lifted the ocean floor 2.7 meters (9 feet) above sea level. He also found rocks containing fossil sea shells in mountains high above sea level. These observations suggested that continents and oceans had changed dramatically over time and continue to change in dra ...
How Evolution Works - The Teacher-Friendly Guide™ to Evolution
... survive to reproduce and pass on those traits to their offspring. 6. Genetic composition: In subsequent generations, there will be a higher percentage of individuals that possess advantageous traits. Therefore, the advantageous traits (that help certain individuals survive and reproduce) are said to ...
... survive to reproduce and pass on those traits to their offspring. 6. Genetic composition: In subsequent generations, there will be a higher percentage of individuals that possess advantageous traits. Therefore, the advantageous traits (that help certain individuals survive and reproduce) are said to ...
Name - 7th Grade Life Science and STEM
... 5. Briefly explain Darwin’s contribution to science. Darwin was a naturalist. Darwin’s theory of evolution is still accepted today. Realize that the most favorable/dominant trait will be passed on to the next generation. Formulate the theory of natural selection and survival of the fittest through ...
... 5. Briefly explain Darwin’s contribution to science. Darwin was a naturalist. Darwin’s theory of evolution is still accepted today. Realize that the most favorable/dominant trait will be passed on to the next generation. Formulate the theory of natural selection and survival of the fittest through ...
I CAN - Montgomery County Public Schools
... increase its numbers, (2) the genetic variability of offspring due to mutation and recombination of genes, (3) a finite supply of the resources required for life and (4) natural selection. The consequences of change over time provide a scientific explanation for the fossil record of ancient life for ...
... increase its numbers, (2) the genetic variability of offspring due to mutation and recombination of genes, (3) a finite supply of the resources required for life and (4) natural selection. The consequences of change over time provide a scientific explanation for the fossil record of ancient life for ...
Natural Selection
... genetic makeup of the next generation • Genetic bottlenecks – result in a loss in genetic diversity following an extreme reduction in the size of the population (following a natural disaster, over-hunting, etc) • Founder effect – occurs when individuals establish a new population (the finches moving ...
... genetic makeup of the next generation • Genetic bottlenecks – result in a loss in genetic diversity following an extreme reduction in the size of the population (following a natural disaster, over-hunting, etc) • Founder effect – occurs when individuals establish a new population (the finches moving ...
Introduction to evolution

Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, and evolutionary biology is the study of how evolution occurs. Biological populations evolve through genetic changes that correspond to changes in the organisms' observable traits. Genetic changes include mutations, which are caused by damage or replication errors in an organism's DNA. As the genetic variation of a population drifts randomly over generations, natural selection gradually leads traits to become more or less common based on the relative reproductive success of organisms with those traits.The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.Evolution does not attempt to explain the origin of life (covered instead by abiogenesis), but it does explain how the extremely simple early lifeforms evolved into the complex ecosystem that we see today. Based on the similarities between all present-day organisms, all life on Earth originated through common descent from a last universal ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. All individuals have hereditary material in the form of genes that are received from their parents, then passed on to any offspring. Among offspring there are variations of genes due to the introduction of new genes via random changes called mutations or via reshuffling of existing genes during sexual reproduction. The offspring differs from the parent in minor random ways. If those differences are helpful, the offspring is more likely to survive and reproduce. This means that more offspring in the next generation will have that helpful difference and individuals will not have equal chances of reproductive success. In this way, traits that result in organisms being better adapted to their living conditions become more common in descendant populations. These differences accumulate resulting in changes within the population. This process is responsible for the many diverse life forms in the world.The forces of evolution are most evident when populations become isolated, either through geographic distance or by other mechanisms that prevent genetic exchange. Over time, isolated populations can branch off into new species.The majority of genetic mutations neither assist, change the appearance of, nor bring harm to individuals. Through the process of genetic drift, these mutated genes are neutrally sorted among populations and survive across generations by chance alone. In contrast to genetic drift, natural selection is not a random process because it acts on traits that are necessary for survival and reproduction. Natural selection and random genetic drift are constant and dynamic parts of life and over time this has shaped the branching structure in the tree of life.The modern understanding of evolution began with the 1859 publication of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species. In addition, Gregor Mendel's work with plants helped to explain the hereditary patterns of genetics. Fossil discoveries in paleontology, advances in population genetics and a global network of scientific research have provided further details into the mechanisms of evolution. Scientists now have a good understanding of the origin of new species (speciation) and have observed the speciation process in the laboratory and in the wild. Evolution is the principal scientific theory that biologists use to understand life and is used in many disciplines, including medicine, psychology, conservation biology, anthropology, forensics, agriculture and other social-cultural applications.