Algebra II Module 3
... judgments about the domain over which a model is a good fit. The description of modeling as, “the process of choosing and using mathematics and statistics to analyze empirical situations, to understand them better, and to make decisions,” is at the heart of this module. In particular, through repeat ...
... judgments about the domain over which a model is a good fit. The description of modeling as, “the process of choosing and using mathematics and statistics to analyze empirical situations, to understand them better, and to make decisions,” is at the heart of this module. In particular, through repeat ...
Polar and exponential forms
... Although the exponential (and polar) forms differ by multiples of 2π — the Cartesian forms are all identical. The complex logarithm is sometimes called “a multivalued function”. As we saw in Semester 1, functions are supposed to have one input and one output so this name is a misnomer! We will retur ...
... Although the exponential (and polar) forms differ by multiples of 2π — the Cartesian forms are all identical. The complex logarithm is sometimes called “a multivalued function”. As we saw in Semester 1, functions are supposed to have one input and one output so this name is a misnomer! We will retur ...
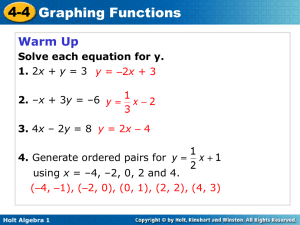
Graph the function
... Check It Out! Example 2b Continued Graph the function y = |x – 1|. Check If the graph is correct, any point on the graph should satisfy the function. Choose an ordered pair on the graph that is not in your table. (3, 2) is on the graph. Check whether it satisfies y = |x − 1|. y = |x – 1| ...
... Check It Out! Example 2b Continued Graph the function y = |x – 1|. Check If the graph is correct, any point on the graph should satisfy the function. Choose an ordered pair on the graph that is not in your table. (3, 2) is on the graph. Check whether it satisfies y = |x − 1|. y = |x – 1| ...
Word - The University of Toledo
... Sometimes, the parabola can be sketched using the x-intercept(s) of the quadratic function and/or the axis of symmetry to find the x-coordinate of the vertex of the parabola. If the quadratic function has one x-intercept, then this x-intercept is the vertex of the parabola. To sketch the graph of th ...
... Sometimes, the parabola can be sketched using the x-intercept(s) of the quadratic function and/or the axis of symmetry to find the x-coordinate of the vertex of the parabola. If the quadratic function has one x-intercept, then this x-intercept is the vertex of the parabola. To sketch the graph of th ...
Characteristic functions and the central limit theorem
... Our goal at the end of the day is to determine the distribution of Snn as n approaches infinity. So we need a better way to deal with sequences of random variables. It is natural to ask, “if we have a sequence of random variables X1 , X2 , . . . such that their characteristic function converge, then ...
... Our goal at the end of the day is to determine the distribution of Snn as n approaches infinity. So we need a better way to deal with sequences of random variables. It is natural to ask, “if we have a sequence of random variables X1 , X2 , . . . such that their characteristic function converge, then ...
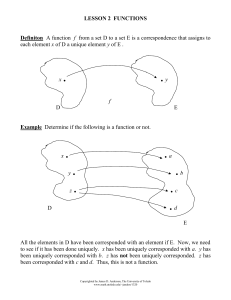
Functional decomposition

Functional decomposition refers broadly to the process of resolving a functional relationship into its constituent parts in such a way that the original function can be reconstructed (i.e., recomposed) from those parts by function composition. In general, this process of decomposition is undertaken either for the purpose of gaining insight into the identity of the constituent components (which may reflect individual physical processes of interest, for example), or for the purpose of obtaining a compressed representation of the global function, a task which is feasible only when the constituent processes possess a certain level of modularity (i.e., independence or non-interaction). Interactions between the components are critical to the function of the collection. All interactions may not be observable, but possibly deduced through repetitive perception, synthesis, validation and verification of composite behavior.