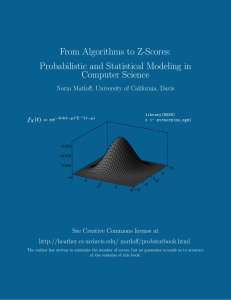
STAT310/MATH230 September 3, 2016 Amir Dembo
... Chapter 8 sets the framework for studying right-continuous stochastic processes indexed by a continuous time parameter, introduces the family of Gaussian processes and rigorously constructs the Brownian motion as a Gaussian process of continuous sample path and zero-mean, stationary independent incr ...
... Chapter 8 sets the framework for studying right-continuous stochastic processes indexed by a continuous time parameter, introduces the family of Gaussian processes and rigorously constructs the Brownian motion as a Gaussian process of continuous sample path and zero-mean, stationary independent incr ...
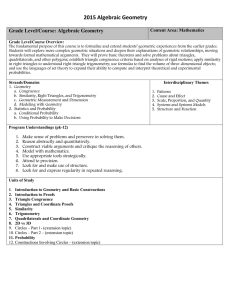
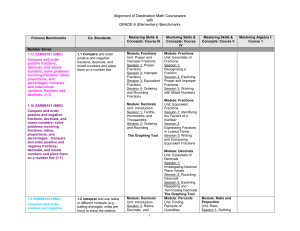
Grade 6 Elementary Complete B1-B3
... fractions, decimals, and mixed numbers; solve problems involving fractions, ratios, proportions, and percentages: Use proportions to solve problems (e.g., determine the value of n if 4/7 = n/21; find the length of a side of a polygon similar to a known polygon); use cross-multiplication as a method ...
... fractions, decimals, and mixed numbers; solve problems involving fractions, ratios, proportions, and percentages: Use proportions to solve problems (e.g., determine the value of n if 4/7 = n/21; find the length of a side of a polygon similar to a known polygon); use cross-multiplication as a method ...
Some previous powerpoint slides by Dr. Welch
... Conditional probability of A given that B occurs, denoted Pr[A|B], is defined to be Pr[AB]/Pr[B] CSCE 411, Spring 2012: Set 10 ...
... Conditional probability of A given that B occurs, denoted Pr[A|B], is defined to be Pr[AB]/Pr[B] CSCE 411, Spring 2012: Set 10 ...
5 International Probabilistic Workshop acco
... walls provide data during four fire scenarios. The temperature measurements of these testseries build the basis for comparable numerical models and analyses. The measurements also served for the adaptation of fire fighting systems such as a fire section creator. For example, a fire fighting system a ...
... walls provide data during four fire scenarios. The temperature measurements of these testseries build the basis for comparable numerical models and analyses. The measurements also served for the adaptation of fire fighting systems such as a fire section creator. For example, a fire fighting system a ...
A New Proof of the Likelihood Principle
... their long-run performance (e.g. [1933], pp. 290–1).7 The use of the Likelihood Principle as an objection to frequentist methods simply begs the question against this view. Many frequentists regard the Neyman-Pearson approach as too ‘behavioristic’ for use in science (e.g. Fisher [1955]), but there ...
... their long-run performance (e.g. [1933], pp. 290–1).7 The use of the Likelihood Principle as an objection to frequentist methods simply begs the question against this view. Many frequentists regard the Neyman-Pearson approach as too ‘behavioristic’ for use in science (e.g. Fisher [1955]), but there ...
Appendix C
... is the point at which the decision maker is in control. It is also called decision fork, decision node, and decision point. actions– In decision theory, the mutually exclusive choices of decision alternatives available to a decision maker. active controlled trial– A clinical trial in which experimen ...
... is the point at which the decision maker is in control. It is also called decision fork, decision node, and decision point. actions– In decision theory, the mutually exclusive choices of decision alternatives available to a decision maker. active controlled trial– A clinical trial in which experimen ...
Part I - ECSE - Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
... Variable: Exponential Used to represent time, e.g. until the next arrival ...
... Variable: Exponential Used to represent time, e.g. until the next arrival ...
Notes on Artificial Intelligence
... Differentiation rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... Differentiation rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Markov Chains and Monte Carlo Methods
... a stochastic process in continuous time. We can distinguish between processes not only based on their index set T , but also based on their state space S, which gives the “range” of possible values the process can take. An important special case arises if the state space S is a countable set. We sha ...
... a stochastic process in continuous time. We can distinguish between processes not only based on their index set T , but also based on their state space S, which gives the “range” of possible values the process can take. An important special case arises if the state space S is a countable set. We sha ...
C 3 A hapter
... and classified simply as conforming (they meet certain specifications) or nonconforming (they do not meet the specifications). The classification is typically carried out with respect to one or more of the specifications on some desired characteristics. We label such characteristics “attributes” and ...
... and classified simply as conforming (they meet certain specifications) or nonconforming (they do not meet the specifications). The classification is typically carried out with respect to one or more of the specifications on some desired characteristics. We label such characteristics “attributes” and ...
paper 4: fundamentals of business mathematics and statistics
... Section B: Fundamentals of Business Statistics 3. Statistical representation of Data 4. Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion 5. Correlation and Regression ...
... Section B: Fundamentals of Business Statistics 3. Statistical representation of Data 4. Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion 5. Correlation and Regression ...