PHYS 390 Lecture 3
... Aside: the minus sign confirms that m increases as F decreases. The reference point of m is fixed by convention; the brightest star is Sirius (now known to be a binary - see below) with a negative apparent magnitude of m = -1.43. Many familiar stars have m in the +3 to +8 range. As seen from Earth, ...
... Aside: the minus sign confirms that m increases as F decreases. The reference point of m is fixed by convention; the brightest star is Sirius (now known to be a binary - see below) with a negative apparent magnitude of m = -1.43. Many familiar stars have m in the +3 to +8 range. As seen from Earth, ...
Page 1 of 4 Name PSCI 1055 Test #4 (Form B) Spring 2008 Buckley
... b. What type of star has the lowest temperature but the highest level of brightness on the H-R diagram? ...
... b. What type of star has the lowest temperature but the highest level of brightness on the H-R diagram? ...
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1
... Which, if any, are observable (zenith distance <60o )? Which, if any, are above the horizon? 4. Which of these 5 stars can be observed at some time on this night from Cerro Tololo? At what times? 5. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? 6. The sidereal time at ...
... Which, if any, are observable (zenith distance <60o )? Which, if any, are above the horizon? 4. Which of these 5 stars can be observed at some time on this night from Cerro Tololo? At what times? 5. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? 6. The sidereal time at ...
Planisphere Exercise
... Use the planisphere you obtained in this course to answer the following questions: Note the location of the North Star at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. It is located just beneath the brass fastener that holds the star wheel to the frame of the planisphere. As the night progresses, whic ...
... Use the planisphere you obtained in this course to answer the following questions: Note the location of the North Star at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. It is located just beneath the brass fastener that holds the star wheel to the frame of the planisphere. As the night progresses, whic ...
Monday, October 27
... The Earth orbits the Sun at a distance of one meter Proxima Centauri lies 270 kilometers (170 miles) away Barnard’s Star lies 370 kilometers (230 miles) away Less than 100 stars lie within 1000 kilometers (600 miles) ...
... The Earth orbits the Sun at a distance of one meter Proxima Centauri lies 270 kilometers (170 miles) away Barnard’s Star lies 370 kilometers (230 miles) away Less than 100 stars lie within 1000 kilometers (600 miles) ...
February - Bristol Astronomical Society
... Batista Hodierna around 1654, it was probably quite well known to ancient astronomers. Charles Messier, was one of many people who later rediscovered the cluster. He added it to his famous catalogue on January 16, 1765 ...
... Batista Hodierna around 1654, it was probably quite well known to ancient astronomers. Charles Messier, was one of many people who later rediscovered the cluster. He added it to his famous catalogue on January 16, 1765 ...
Planisphere Exercise
... located just beneath the brass fastener that holds the star wheel to the frame of the planisphere. As the night progresses, which way do the stars appear to move around the North Star (which is hidden under the brass fastener) – clockwise or counterclockwise? As the night progresses, how do stars ap ...
... located just beneath the brass fastener that holds the star wheel to the frame of the planisphere. As the night progresses, which way do the stars appear to move around the North Star (which is hidden under the brass fastener) – clockwise or counterclockwise? As the night progresses, how do stars ap ...
The winter sky over Bosham
... outshining both Betelgeuse and Rigel, it actually far smaller and less luminous, with its relative brightness reflecting the fact that it is one of the Sun's closest neighbours. In ancient Egypt the appearance of Sirius in the morning sky coincided with the flooding of the Nile and the start of the ...
... outshining both Betelgeuse and Rigel, it actually far smaller and less luminous, with its relative brightness reflecting the fact that it is one of the Sun's closest neighbours. In ancient Egypt the appearance of Sirius in the morning sky coincided with the flooding of the Nile and the start of the ...
AST 207 Homework 5 Due 14 October 2011
... 2. Life on Deneb. Here you will find out what it means to live near a giant like Deneb. Recall that the luminosity of a star, where T is its temperature and R is its radius. Star ...
... 2. Life on Deneb. Here you will find out what it means to live near a giant like Deneb. Recall that the luminosity of a star, where T is its temperature and R is its radius. Star ...
May 2017 - Museums Wellington
... constellation of Virgo, and below, just above the horizon is orange coloured Arcturus, the brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere and the 4th brightest in the night sky. Arcturus has a similar mass to the Sun, but has already expanded to become a red giant, with 25 times the diameter an ...
... constellation of Virgo, and below, just above the horizon is orange coloured Arcturus, the brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere and the 4th brightest in the night sky. Arcturus has a similar mass to the Sun, but has already expanded to become a red giant, with 25 times the diameter an ...
Document
... j. How is it possible that Canopus is more luminous than Achernar, given their respective spectral types? Canopus is cooler than Achernar; therefore, the only way Canopus can be more luminous is because it is LARGER. 2. List the evolutionary stages of the Sun’s life cycle & describe how its size (Ra ...
... j. How is it possible that Canopus is more luminous than Achernar, given their respective spectral types? Canopus is cooler than Achernar; therefore, the only way Canopus can be more luminous is because it is LARGER. 2. List the evolutionary stages of the Sun’s life cycle & describe how its size (Ra ...
GeoDome Notes
... appears stationary in the night sky. This can be demonstrated by having the students stand in place, notice what is over their heads, make one slow rotation (this will also tell you if they understand rotation), and look up to see their overhead view hasn’t changed. Sailors used the North Star to gu ...
... appears stationary in the night sky. This can be demonstrated by having the students stand in place, notice what is over their heads, make one slow rotation (this will also tell you if they understand rotation), and look up to see their overhead view hasn’t changed. Sailors used the North Star to gu ...
Stars
... Barnard discovered that it had the largest proper motion of any star in our neighborhood. In about 10,000 years it will actually pass us closer than Alpha Centauri is now. It appears to move about 0.5 degrees (the diameter of the Moon as seen from Earth) every 175 years. ...
... Barnard discovered that it had the largest proper motion of any star in our neighborhood. In about 10,000 years it will actually pass us closer than Alpha Centauri is now. It appears to move about 0.5 degrees (the diameter of the Moon as seen from Earth) every 175 years. ...
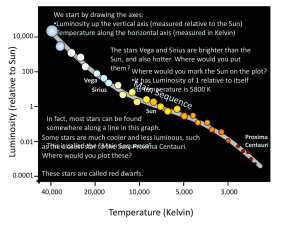
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature?
... 3. Stars with surface temperatures up to 3,500 K are red. Shade a vertical band from 2000 K to 3500 K a light red. 4. Shade other color bands as follows: Stars up to 5000 K are orange-red, up to 6000 K yellow-white, up to 7500 K blue-white, and up to 40,000 K blue. 5. Look for patterns in your graph ...
... 3. Stars with surface temperatures up to 3,500 K are red. Shade a vertical band from 2000 K to 3500 K a light red. 4. Shade other color bands as follows: Stars up to 5000 K are orange-red, up to 6000 K yellow-white, up to 7500 K blue-white, and up to 40,000 K blue. 5. Look for patterns in your graph ...
The star and the trees prostrate
... During most of a star's lifetime, nuclear fusion in the core generates electromagnetic radiation, including photons, the particles of light. This radiation exerts an outward pressure that exactly balances the inward pull of gravity caused by the star's mass. As the nuclear fuel is exhausted, the out ...
... During most of a star's lifetime, nuclear fusion in the core generates electromagnetic radiation, including photons, the particles of light. This radiation exerts an outward pressure that exactly balances the inward pull of gravity caused by the star's mass. As the nuclear fuel is exhausted, the out ...
Compact Objects
... Can produce strong, high-energy radiation and outbursts when in binary systems ...
... Can produce strong, high-energy radiation and outbursts when in binary systems ...
Winter Stargazing - Trimble County Schools
... find his shoulders: Bellatrix, his western shoulder, and Betelgeuse, his eastern shoulder. • Make an imaginary line between the two stars from Bellatrix to Betelgeuse, and extend it outward toward the East. • About three shoulder-widths away you will nearly run into Procyon. ...
... find his shoulders: Bellatrix, his western shoulder, and Betelgeuse, his eastern shoulder. • Make an imaginary line between the two stars from Bellatrix to Betelgeuse, and extend it outward toward the East. • About three shoulder-widths away you will nearly run into Procyon. ...
The First Star at Night
... Canopus is the second brightest star in the night sky, so given that it is always above our horizon from here in Tasmania, one might expect that without Sirius in the sky, Canopus would always be the first star visible. However, it is rather more complicated than that. Even though we can always see ...
... Canopus is the second brightest star in the night sky, so given that it is always above our horizon from here in Tasmania, one might expect that without Sirius in the sky, Canopus would always be the first star visible. However, it is rather more complicated than that. Even though we can always see ...
Astronomy 120
... Sirius (bluish). List these stars in order of increasing surface temperature. Estimate the surface temperature of Betelgeuse and of Sirius. 2. Zeilik Study Exercise 13.9 Jupiter is about 5 times as far from the sun as the earth is ( 5 A.U.’s compared to 1 A.U. ). By how much less is the sun’s flux ...
... Sirius (bluish). List these stars in order of increasing surface temperature. Estimate the surface temperature of Betelgeuse and of Sirius. 2. Zeilik Study Exercise 13.9 Jupiter is about 5 times as far from the sun as the earth is ( 5 A.U.’s compared to 1 A.U. ). By how much less is the sun’s flux ...
Sample exam 2
... Essay questions — choose three of the following questions; circle the numbers of the ones chosen, so I know which ones to grade. Please answer each question in sentence/paragraph format or a drawing, depending on what is asked. 11. The Sun started off its trajectory on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagra ...
... Essay questions — choose three of the following questions; circle the numbers of the ones chosen, so I know which ones to grade. Please answer each question in sentence/paragraph format or a drawing, depending on what is asked. 11. The Sun started off its trajectory on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagra ...
The Evening Sky in February 2016
... In the late evening, at the beginning of the month, Jupiter rises due east. It is brighter than any of the stars and shines with a steady golden light. Later on Jupiter is already up at dusk, appearing in the eastern sky soon after sunset. Any telescope will easily show Jupiter's four bright moons. ...
... In the late evening, at the beginning of the month, Jupiter rises due east. It is brighter than any of the stars and shines with a steady golden light. Later on Jupiter is already up at dusk, appearing in the eastern sky soon after sunset. Any telescope will easily show Jupiter's four bright moons. ...
ASTR100 Homework #5 Solutions Chapter 11 #29, 31 Due
... If you could look inside the Sun today, you’d find that its core contains a much higher proportion of helium and a lower proportion of hydrogen than it did when the Sun was born. This statement makes sense because over the last 4.5 billion years the Sun has been busy converting its Hydrogen into Hel ...
... If you could look inside the Sun today, you’d find that its core contains a much higher proportion of helium and a lower proportion of hydrogen than it did when the Sun was born. This statement makes sense because over the last 4.5 billion years the Sun has been busy converting its Hydrogen into Hel ...
1Although they seem to remain unchanged, many mountains undergo steady... erosion and weathering are ignored, some mountains, like the San...
... edge of the Pacific Ocean. If you were to leave Moscow and travel on the railroad with an average speed of 90.0 km/h, how long would it take for you to reach Vladivostok? 3.The largest sheep and cattle ranches in the world are in Australia. The areas of some of these ranches are about equal to the a ...
... edge of the Pacific Ocean. If you were to leave Moscow and travel on the railroad with an average speed of 90.0 km/h, how long would it take for you to reach Vladivostok? 3.The largest sheep and cattle ranches in the world are in Australia. The areas of some of these ranches are about equal to the a ...
Sirius
Sirius (/ˈsɪriəs/) is the brightest star (in fact, a star system) in the Earth's night sky. With a visual apparent magnitude of −1.46, it is almost twice as bright as Canopus, the next brightest star. The name ""Sirius"" is derived from the Ancient Greek Σείριος (Seirios), meaning ""glowing"" or ""scorcher"". The system has the Bayer designation Alpha Canis Majoris (α CMa). What the naked eye perceives as a single star is actually a binary star system, consisting of a white main-sequence star of spectral type A1V, termed Sirius A, and a faint white dwarf companion of spectral type DA2, called Sirius B. The distance separating Sirius A from its companion varies between 8.2 and 31.5 AU.Sirius appears bright because of both its intrinsic luminosity and its proximity to Earth. At a distance of 2.6 parsecs (8.6 ly), as determined by the Hipparcos astrometry satellite, the Sirius system is one of Earth's near neighbors. Sirius is gradually moving closer to the Solar System, so it will slightly increase in brightness over the next 60,000 years. After that time its distance will begin to increase, but it will continue to be the brightest star in the Earth's sky for the next 210,000 years.Sirius A is about twice as massive as the Sun (M☉) and has an absolute visual magnitude of 1.42. It is 25 times more luminous than the Sun but has a significantly lower luminosity than other bright stars such as Canopus or Rigel. The system is between 200 and 300 million years old. It was originally composed of two bright bluish stars. The more massive of these, Sirius B, consumed its resources and became a red giant before shedding its outer layers and collapsing into its current state as a white dwarf around 120 million years ago.Sirius is also known colloquially as the ""Dog Star"", reflecting its prominence in its constellation, Canis Major (Greater Dog). The heliacal rising of Sirius marked the flooding of the Nile in Ancient Egypt and the ""dog days"" of summer for the ancient Greeks, while to the Polynesians in the Southern Hemisphere the star marked winter and was an important reference for their navigation around the Pacific Ocean.