What are examples of common agonists and antogonists?
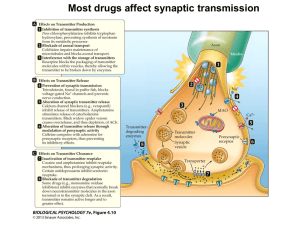
... • Agonists facilitate the effects of neurotransmitters. Antagonists inhibit the effects of neurotransmitters. • Agonists and antagonists may influence synaptic transmission in a number of ways: ...
... • Agonists facilitate the effects of neurotransmitters. Antagonists inhibit the effects of neurotransmitters. • Agonists and antagonists may influence synaptic transmission in a number of ways: ...
Neuropharmacology I Parkinson`s Disease and Movement
... multiple cerebral infarcts. In general, these do not respond as well to medication as idiopathic PD ...
... multiple cerebral infarcts. In general, these do not respond as well to medication as idiopathic PD ...
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters are the nervous system`s “off switches
... presynaptic dopaminergetic neuron or adjacent noradrenergic neurons. Some of the enzymes that degrade dopamine are only found in specific regions of the body. As such some dopamine metabolites are only produced in specific tissues. Understanding how and where these enzymes function can proved valuab ...
... presynaptic dopaminergetic neuron or adjacent noradrenergic neurons. Some of the enzymes that degrade dopamine are only found in specific regions of the body. As such some dopamine metabolites are only produced in specific tissues. Understanding how and where these enzymes function can proved valuab ...
Dopamine Agonists - Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Trust
... dopamine agonists, the Ergots (Bromocryptine, Pergolide and Cabergoline) and the Non Ergots (Ropinerole, Pramipexole and Rotigotine). The Ergot dopamine agonists are very rarely used now as they can cause scarring problems in the heart, lungs or abdomen in some patients. We now use the Non Ergot ago ...
... dopamine agonists, the Ergots (Bromocryptine, Pergolide and Cabergoline) and the Non Ergots (Ropinerole, Pramipexole and Rotigotine). The Ergot dopamine agonists are very rarely used now as they can cause scarring problems in the heart, lungs or abdomen in some patients. We now use the Non Ergot ago ...
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lec 7: Schizophrenia and Parkinson`s
... • Literally means thins neural transmission • In practice both terms refer to drugs used to treat schizophrenia only • Wide variety of off-label applications • Incorrectly known as "major tranquilizers" ...
... • Literally means thins neural transmission • In practice both terms refer to drugs used to treat schizophrenia only • Wide variety of off-label applications • Incorrectly known as "major tranquilizers" ...
How antipsychotics become anti-”psychotic” –from dopamine to
... • A delusion can be seen as the creation of some kind of “new reality, or new insight”, where all the strange feelings and perceptions suddenly “make perfect sense” to the patient • When the world around the patient doesnt fit his or her perception of it the creation of a ”new world” becomes the o ...
... • A delusion can be seen as the creation of some kind of “new reality, or new insight”, where all the strange feelings and perceptions suddenly “make perfect sense” to the patient • When the world around the patient doesnt fit his or her perception of it the creation of a ”new world” becomes the o ...
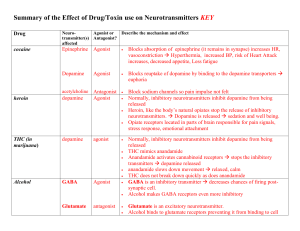
Mouse party Summary-the Effect of Drug use on Neurotransmitters
... transmitter(s) Antagonist? affected ...
... transmitter(s) Antagonist? affected ...
Parkinsonian Treatments and L-Dopa vs. D
... D- and L-Dopa produced a change in dopamine levels with similar efficacy. This turning behavior was attributed to the stimulation of sensitive dopamine receptors in the lesioned striata by the extraneuronally formed dopamine. D-Dopa was converted to dopamine via transamination and/or Damino acid oxi ...
... D- and L-Dopa produced a change in dopamine levels with similar efficacy. This turning behavior was attributed to the stimulation of sensitive dopamine receptors in the lesioned striata by the extraneuronally formed dopamine. D-Dopa was converted to dopamine via transamination and/or Damino acid oxi ...
Fig 4.9a Synaptic Transmission
... – nicotine stimulates GABAergic neurons • Which inhibits the reward system • however after chronic exposure to nicotine this cell desensitizes so there is less inhibition leading to even more dopamine being released ...
... – nicotine stimulates GABAergic neurons • Which inhibits the reward system • however after chronic exposure to nicotine this cell desensitizes so there is less inhibition leading to even more dopamine being released ...
Neural Impulse Cell membrane is a semipermeable boundary – ion
... a. Cell membrane is a semipermeable boundary – ion concentration inside and outside the cell creates all-or-none action potential b. Synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into synapse. Find receptor sites in a lock-and-key fashion Neurotransmitters a. Acetylcholine i. Responsible for muscle ac ...
... a. Cell membrane is a semipermeable boundary – ion concentration inside and outside the cell creates all-or-none action potential b. Synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into synapse. Find receptor sites in a lock-and-key fashion Neurotransmitters a. Acetylcholine i. Responsible for muscle ac ...
File
... • (Abbreviations: GPe: globus pallidus external; GPi: globus pallidus internal; STN: subthalamic nucleus; SNc: substantia nigra compacta; SNr: substantia nigra reticulata) ...
... • (Abbreviations: GPe: globus pallidus external; GPi: globus pallidus internal; STN: subthalamic nucleus; SNc: substantia nigra compacta; SNr: substantia nigra reticulata) ...
A1985AUG6600001
... turnover of the catecholamines. It did not seem farfetched, then, to propose that rather than reducing the availability of monoamines, as does reserpine, the major antipsychotic drugs block the receptors mediating dopamine and noradrenaline neurotransmission. This would explain their reserpine-like ...
... turnover of the catecholamines. It did not seem farfetched, then, to propose that rather than reducing the availability of monoamines, as does reserpine, the major antipsychotic drugs block the receptors mediating dopamine and noradrenaline neurotransmission. This would explain their reserpine-like ...
Addiction
... Blum et al (1990, 1996); Spear (2000): Reward deficiency syndrome Nader et al. (2002) ...
... Blum et al (1990, 1996); Spear (2000): Reward deficiency syndrome Nader et al. (2002) ...
Dopamine 2013
... brain and not just a precursor of norepinephrine. ● Discovered that a lack of dopamine in some areas of the brain could disrupt pathways among nerves that control movement and motor functions. ● This causes Parkinson’s disease. ...
... brain and not just a precursor of norepinephrine. ● Discovered that a lack of dopamine in some areas of the brain could disrupt pathways among nerves that control movement and motor functions. ● This causes Parkinson’s disease. ...
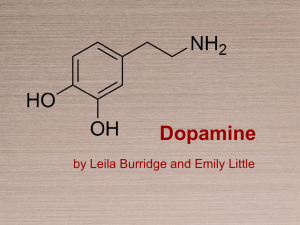
Dopamine
Dopamine is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families that plays a number of important roles in the human brain and body, as well as elsewhere in biology. Its name derives from its chemical structure: it is an amine formed by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of L-DOPA. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by nerve cells to send signals to other nerve cells. The brain includes several distinct dopamine systems, one of which plays a major role in reward-motivated behavior. Most types of reward increase the level of dopamine in the brain, and a variety of addictive drugs increase dopamine neuronal activity. Other brain dopamine systems are involved in motor control and in controlling the release of various hormones.Several important diseases of the nervous system are associated with dysfunctions of the dopamine system. Parkinson's disease, a degenerative condition causing tremor and motor impairment, is caused by loss of dopamine-secreting neurons in a midbrain area called the substantia nigra. There is evidence that schizophrenia involves altered levels of dopamine activity, and the antipsychotic drugs that are frequently used to treat it have a primary effect of attenuating dopamine activity. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and restless legs syndrome are associated with decreased dopamine activity.Outside the nervous system, dopamine functions in several parts of the body as a local chemical messenger. In the blood vessels, it inhibits norepinephrine release and acts as a vasodilator (at normal concentrations); in the kidneys, it increases sodium excretion and urine output; in the pancreas, it reduces insulin production; in the digestive system, it reduces gastrointestinal motility and protects intestinal mucosa; and in the immune system, it reduces the activity of lymphocytes. With the exception of the blood vessels, dopamine in each of these peripheral systems has a ""paracrine"" function: it is synthesized locally and exerts its effects on cells that are located near the cells that release it.A variety of important drugs work by altering the way the body makes or uses dopamine. Dopamine itself is available for intravenous injection: although it cannot reach the brain from the bloodstream, its peripheral effects make it useful in the treatment of heart failure or shock, especially in newborn babies. L-DOPA, the metabolic precursor of dopamine, does reach the brain and is the most widely used treatment for Parkinson's disease. Dopaminergic stimulants can be addictive in high doses, but some are used at lower doses to treat ADHD. Conversely, many antipsychotic drugs act by suppressing the effects of dopamine. Drugs that act against dopamine by a different mechanism are also some of the most effective anti-nausea agents.